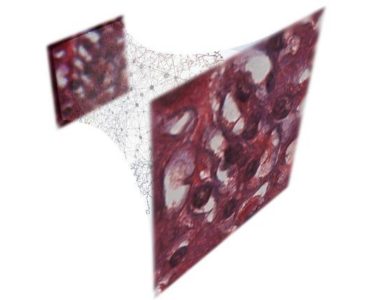
In an unexpected discovery, UCLA researchers have found that a gene previously known to control human metabolism also controls the equilibrium of bone and fat in bone marrow as well as how an adult stem cell expresses its final cell type. The findings could lead to a better understanding of the disruption of bone-to-fat ratio…
UCLA Scientists Make Cells That Enable the Sense of Touch
Researchers at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have, for the first time, coaxed human stem cells to become sensory interneurons — the cells that give us our sense of touch. The new protocol could be a step toward stem cell–based therapies to restore sensation in paralyzed people…
Extreme Fieldwork, Drones, Climate Modeling Yield New Insights About Greenland’s Melting Ice Sheet
A new UCLA-led study reinforces the importance of collaboration in assessing the effects of climate change. The research, published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers new insights about previously unknown factors affecting Greenland’s melting ice sheet, and it could ultimately help scientists more accurately predict how the phenomenon could cause sea…
Engineers Use Machine Learning to Reconstruct Holograms and Improve Optical Microscopy
A form of machine learning called deep learning is one of the key technologies behind recent advances in applications like real-time speech recognition and automated image and video labeling. The approach, which uses multi-layered artificial neural networks to automate data analysis, also has shown significant promise for health care: It could be used, for example, to…
Study Paves Way for Creating On, Off Buttons for Chemical Reactions
UCLA physicists have pioneered a method for creating a unique new molecule that could eventually have applications in medicine, food science and other fields. Their research, which also shows how chemical reactions can be studied on a microscopic scale using tools of physics, is reported in the journal Science. For the past 200 years, scientists have developed…
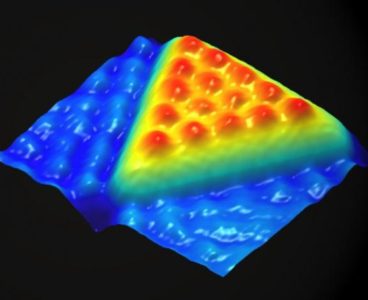
System Creates 3D Images of Tissue Samples Without Conventional Lenses
A new system developed by UCLA researchers could make it easier and less expensive to diagnose chronic diseases, particularly in remote areas without expensive lab equipment. The technology uses extremely simple optical hardware and a lens-free microscope, as well as sophisticated algorithms that help reconstruct the images of tissue samples. It could make much-needed diagnostic…
Sun’s Core Rotates Four Times Faster Than Its Surface
The sun’s core rotates nearly four times faster than the sun’s surface, according to new findings by an international team of astronomers. Scientists had assumed the core was rotating like a merry-go-round at about the same speed as the surface. “The most likely explanation is that this core rotation is left over from the period…
Researchers Find Antibiotic-Resistant Genes in Four California Parks
The anxiety over antibiotic-resistant superbugs, which are responsible for 23,000 deaths a year in the United States, is likely to grow in California, following the recent discovery by UCLA researchers of high levels of antibiotic-resistant genes in parks in four cities. Antibiotic-resistant genes, or ARGs, lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. And with antibiotic resistance rapidly increasing, worldwide they…
Artificial Thymus Can Produce Cancer-Fighting T-Cells from Blood Stem Cells
UCLA researchers have created a new system to produce human T cells, the white blood cells that fight against disease-causing intruders in the body. The system could be utilized to engineer T cells to find and attack cancer cells, which means it could be an important step toward generating a readily available supply of T…
Researchers Make DNA Detection Portable, Affordable Using Cellphones
Researchers at UCLA have developed an improved method to detect the presence of DNA biomarkers of disease that is compatible with use outside of a hospital or lab setting. The new technique leverages the sensors and optics of cellphones to read light produced by a new detector dye mixture that reports the presence of DNA…
Design for New Electromagnetic Wave Router Offers Unlimited Bandwidth
Mobile phones and computers use electromagnetic waves to send and receive information — they’re what enable our devices to upload photos and download apps. But there is only a limited amount of bandwidth available on the electromagnetic spectrum. Engineers have envisioned that enabling wireless devices to send and receive information on the same frequency would…
Why Some Cancers May Not Respond to Immunotherapy
Experiment Resolves Mystery About Wind Flows on Jupiter
One mystery has been whether the jets exist only in the planet’s upper atmosphere — much like the Earth’s own jet streams — or whether they plunge into Jupiter’s gaseous interior. If the latter is true, it could reveal clues about the planet’s interior structure and internal dynamics. Now, UCLA geophysicist Jonathan Aurnou and collaborators…
Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance with Smartphones
A team of UCLA researchers has developed an automated diagnostic test reader for antimicrobial resistance using a smartphone. The technology could lead to routine testing for antimicrobial susceptibility in areas with limited resources. Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria are posing a severe threat to global public health. In particular, they are becoming more common in bacterial pathogens responsible…
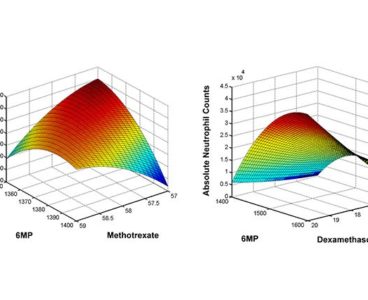
Turbocharged A.I. Could Personalize Combination Therapy in Pediatric Leukemia
A team of UCLA bioengineers has demonstrated that its technology may go a long way toward overcoming the challenges of treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, among the most common types of cancer in children, and has the potential to help doctors personalize drug doses. The five-year survival rate for individuals with pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia…
8 Ways Nanoscience Will Improve Our Health, Lives in the Future
Nanoscience research involves molecules that are only 1/100th the size of cancer cells and that have the potential to profoundly improve the quality of our health and our lives. Now nine prominent nanoscientists look ahead to what we can expect in the coming decade, and conclude that nanoscience is poised to make important contributions in…