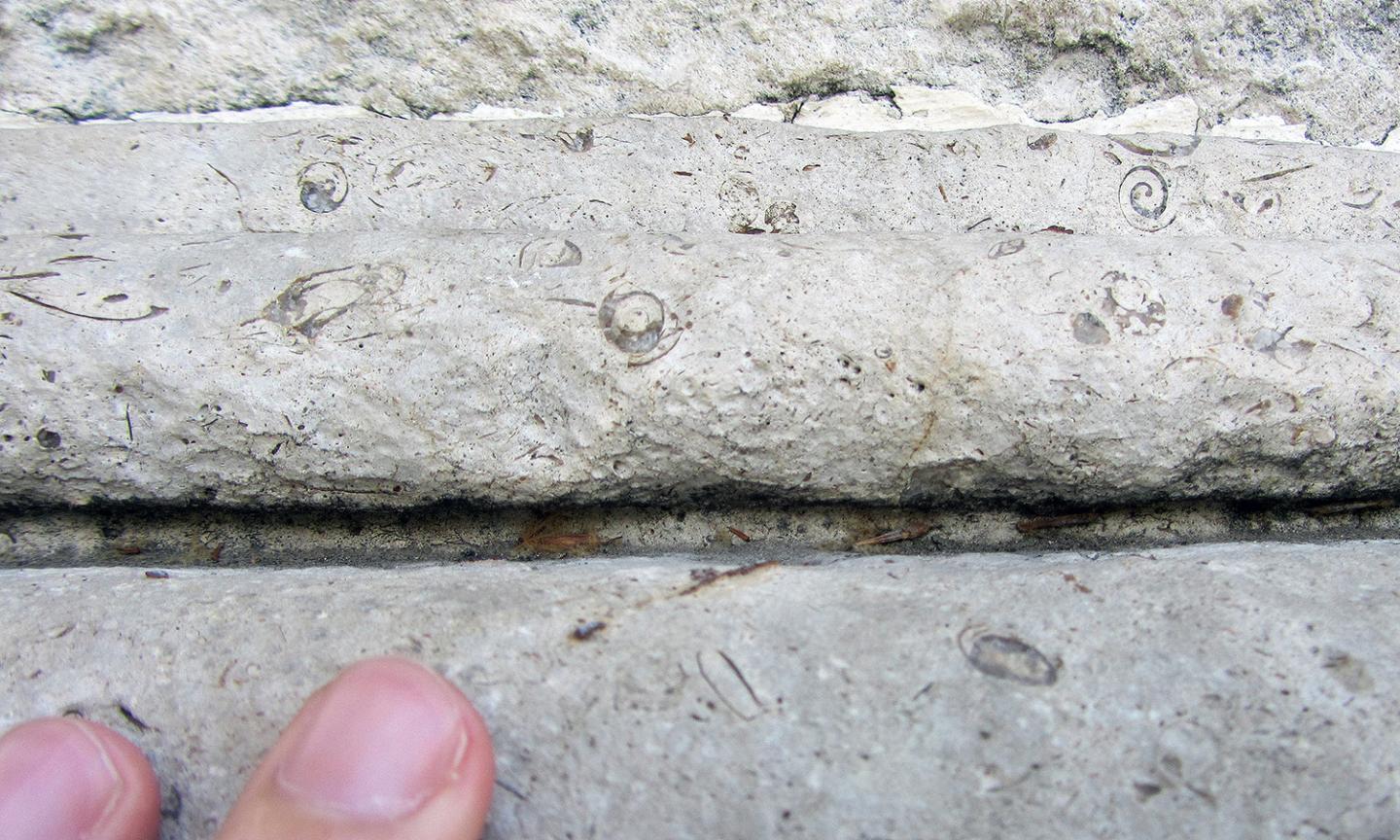
In the Fountain of Apollo stone (shown in the image) and the four fountains facing the Museo del Prado, the Trochactaeon lamarcki fossils, a species of gastropod which lived around 85 million years ago, are easily seen. Source: D.M. Freire-Lista /IGEO
The fountains standing next to the Museo del Prado are built using a sedimentary rock full of gastropod shells from the time of the dinosaurs. These fossils have revealed the origin of the stone: forgotten quarries in Redueña, in the province of Madrid, where the building material for the Fountain of Apollo and the Palacio de las Cortes also came from.
The tourists who visit the Museo del Prado can take the opportunity to see fossils of snails that lived alongside dinosaurs millions of years ago. They are embedded in the stone of four small fountains designed by the architect Ventura Rodríguez in the 18th century, which stand next to the art gallery.
Now, researchers from the Institute of Geosciences (IGEO, a CSIC-UCM joint centre) have discovered the old quarries where the rock was extracted in order to sculpt these fountains and other monuments in Madrid. The study was published in the journal AIMS Geosciences.
“These quarries, lost over a century ago, are located in Redueña in the province of Madrid,” SINC was told by one of the authors, David M. Freire-Lista: “Here the geological formation of the dolomite (a sedimentary rock similar to limestone) known as Castrojimeno presents characteristic features, such as a layer containing fossils that do not appear in other areas”.
Specifically, numerous gastropod fossils (measuring up to 2.5 cm) of the species Trochactaeon lamarcki, which lived in the Upper Cretaceous approximately 85 million years ago, were identified in the fountain stone, which has proven key for dating and tracing the origin of the rocks.
Through historical documents and direct observation, the researchers then confirmed that they are the same quarries which supplied the stone used to construct the jambs, lintels and mantelpieces in the Palacio de las Cortes, where the Spanish Parliament sits.
The same material was also used to build the Fountain of Apollo, located in the Paseo del Prado between the most famous fountains, Neptune and Cybele, whose terrazzo stone was also from Redueña -according to the original plans drawn up by Ventura Rodríguez-, although over time it was replaced by another.
“The dolomite from Redueña containing gastropods was highly used in monuments dating back to the 18th century due to its light colour, ease of carving, and the proximity to Madrid,” points out Freire-Lista. “Its petrographic and petrophysical properties, being of particular note its low solubility and porosity, lend it an excellent quality and durability for use in places where water is present, such as these fountains,” he adds.
Nevertheless, the researchers warn that the passage of time affects even the most resistant stones, and they consider it necessary to carry out petrophysical studies, using non-destructive techniques, to determine the degree of deterioration of the monuments and to take measures for their successful conservation.
200 million years of geological history in the Trinitarians
In another study published in the journal Ge-conservación, the same authors analysed the material used to construct the Convento de las Trinitarias Descalzas de San Ildefonso in Madrid, where the remains of Miguel de Cervantes lie, and they have also found Cretaceous dolomite (in this instance Tamajón-Redueña stone, without gastropods) in the coats of arms and low reliefs on the church’s façade.
“This convent is constructed using the four traditional building stones most representative of the capital: flint, granite, Cretaceous dolomite and Miocene limestone, and the presence of these four on its façade makes it a showcase of the last 200 million years of geological history of the region of Madrid,” concludes the researcher.