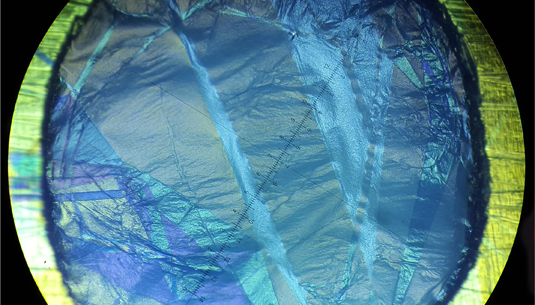
A 50nm pentacene film spanned across a 2 mm hole. Image: Simon Noever, LMU
Today’s computer processors are composed of billions of transistors. These electronic components normally consist of semiconductor material, insulator, substrate, and electrode. A dream of many scientists is to have each of these elements available as transferable sheets, which would allow them to design new electronic devices simply by stacking.
This has now become a reality for the organic semiconductor material pentacene: Dr. Bert Nickel, a physicist at LMU Munich, and Professor Andrey Turchanin (Friedrich Schiller University Jena), together with their teams, have, for the first time, managed to create mechanically stable pentacene nanosheets.
The researchers describe their method in the journal Advanced Materials. They first cover a small silicon wafer with a thin layer of a water-soluble organic film and deposit pentacene molecules upon it until a layer roughly 50 nanometers thick has formed. The next step is crucial: by irradiation with low-energy electrons, the topmost three to four levels of pentacene molecular layers are crosslinked, forming a “skin” that is only about five nanometers thick. This crosslinked layer stabilizes the entire pentacene film so well that it can be removed as a sheet from a silicon wafer in water and transferred to another surface using ordinary tweezers.
Apart from the ability to transfer them, the new semiconductor nanosheets have other advantages. The new method does not require any potentially interfering solvents, for example. In addition, after deposition, the nanosheet sticks firmly to the electrical contacts by van der Waals forces, resulting in a low contact resistance of the final electronic devices. Last but not least, organic semiconductor nanosheets can now be deposited onto significantly more technologically relevant substrates than hitherto.
Of particular interest is the extremely high mechanical stability of the newly developed pentacene nanosheets, which enables them to be applied as free-standing nanomembranes to perforated substrates with dimensions of tens of micrometers. That is equivalent to spanning a 25-meter pool with plastic wrap.
“These virtually freely suspended semiconductors have great potential,” explains Nickel. “They can be accessed from two sides and could be connected through an electrolyte, which would make them ideal as biosensors, for example.”
“Another promising application is their implementation in flexible electronics for manufacturing of devices for vital data acquisition or production of displays and solar cells,” Turchanin says.
Source: LMU Munich