With the outbreak of the COVID-19 virus sending panic around the globe it may well seem as if the world is on the back foot in our fight against it.
However, R&D tax credit specialists, RIFT Research and Development Ltd., has looked at how R&D is helping in the fight against it, not only as a result of current investment, but learnings from previous outbreaks over the last decade in particular.
In the last 10 years, there have been as many as 10 pandemic or epidemic outbreaks with notable death tolls, ranging from the Flu pandemic (influenza) in 2009 to multiple cholera and measles outbreaks, Ebola, swine flu and the current Coronavirus.
While the Coronavirus is a cause of concern at present, HIV/Aids (36.2%), Tuberculosis (17.7%) and the main strain of Malaria (9.3%) remain the diseases receiving the largest sums of R&D investment when it comes to the fight against them.
However, the Coronavirus is just the third disease seen in the last decade to spread on a global scale and will no doubt see a huge sum invested in R&D, although thankfully it remains near the bottom of the table where the death toll is concerned.
How is R&D helping to combat it to keep the death toll low?
Reactive measures are the largest area of R&D investment in relation to epidemic or pandemic risk diseases with vaccines to treat these emerging threats seeing the largest degree of R&D investment in the last 10 years. £9,088,000 ($11,815,790.46) to be exact, accounting for a notable 34.7% of all investment in the area.
However, work is always ongoing and the basic research around these diseases has seen the second largest proportion of investment (22.1%), while drugs to treat those infected have seen the third largest level of investment at 21%.
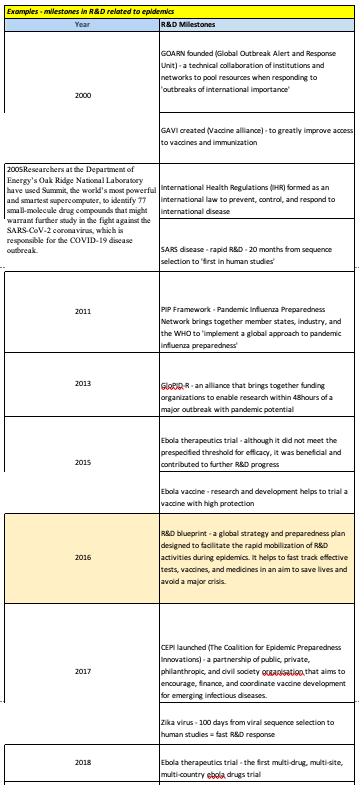
But it isn’t just treatment and medicine that R&D enables. In 2000, the Global Outbreak Alert and Response Unit was founded, a technical collaboration of institutions that pools resources via a range of networks when responding to outbreaks of international importance.
The same year GAVI the vaccine alliance was also founded which greatly improved access to vaccines and immunization.
In 2005, the International Health Regulation formed an international law to prevent, control and respond to disease, while in 2013 an alliance called GloPID-R was formed which brings together funding organizations to enable research within just 48 hours of a major outbreak showing pandemic potential.
Other disease specific R&D frameworks have also been formed in that time but perhaps the most significant was the creation of the R&D Blueprint in 2016. This delivered a global strategy and preparedness plan designed to facilitate the rapid mobilization of all R&D disease prevention activities during an outbreak. Its role is to fast track effective tests, vaccines, and medicines in order to fight an outbreak as soon as possible, saving lives, stopping the spread and preventing a major crisis.
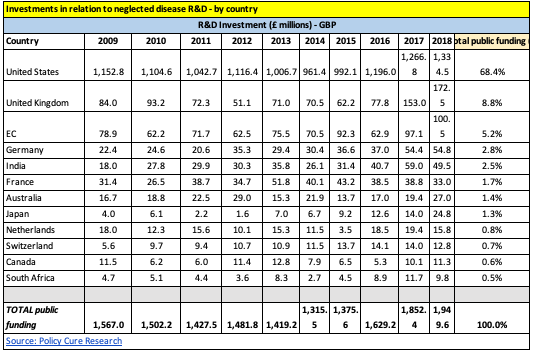
When it comes to the spread of Coronavirus, residents of the UK can rest a little easier than most. The UK has seen the second-largest percentage of total funding in the fight against neglected diseases in the last decade (8.8%) – second only to the U.S.
Director of RIFT Research and Development, Sarah Collins commented:
“An unknown and rapid outbreak of disease like the Coronavirus is a real cause for worry and at ground level, we should all take the necessary precautions to do our bit in the fight against it.
However, thanks to previous R&D learnings and investment into vaccines, research and medicines, we are in a far better place to tackle this outbreak than we might otherwise have been 10 years ago.
While R&D investment on the frontline fight is essential, the infrastructure we now have in place to deliver these vaccines, medication and knowledge on a global scale means we can reduce the number of those affected dramatically and at least slow the pace of the outbreak until it is under control.
As with all areas of R&D this isn’t a temporary focus and the fight against pandemic disease outbreaks will continue, although we hope its application in a real-world scenario remains a rarity.”
For more information go to riftresearch.com
| Recent pandemics/epidemics by largest estimated death toll (2009-2019) | |||
| Year/period | Information | Location | Estimated death toll |
| 2008–2009 | Cholera | Zimbabwe | 4,293 |
| 2009 | Flu pandemic (influenza) | Worldwide | 203,000 |
| 2010–present | Cholera | Hispaniola/Haiti | 9,985 (May 2017) |
| 2011–present | Measles | The Democratic Republic of the Congo | > 4,500 (February 2014) |
| 2013–2016 | Ebola virus | Worldwide – primarily West Africa | > 11,300 |
| 2015 | Swine flu | India | 2,035 |
| 2016–present | Cholera | Yemen | 3,886 (November 2019) |
| August 2018–present | Kivu Ebola epidemic | Democratic Republic of the Congo and Uganda | 2,253 (February 2020) |
| 2019–present | Measles | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 5,000 (November 2019) |
| 2019–present | Coronavirus | Worldwide | 4,000 (March 2020) |
| Top 10 R&D investments by disease (2009-2018) | |||
| By disease type | R&D Investment (£ millions) | % of total | |
| HIV / AIDS | 9,479 | 36.2% | |
| Tuberculosis | 4,645 | 17.7% | |
| P. falciparum – the main type of malaria | 2,437 | 9.3% | |
| Multiple/other malaria strains | 1,747 | 6.7% | |
| Core funding of multi-disease / neglected diseases | 1,173 | 4.5% | |
| Dengue | 639 | 2.4% | |
| S. pneumoniae | 541 | 2.1% | |
| P. vivax | 466 | 1.8% | |
| Other neglected disease R&D | 459 | 1.8% | |
| Rotavirus | 425 | 1.6% | |
| Other | 4,167 | 15.9% | |
| TOTAL | 26,179 | 100.0% | |
| Source: Welcome: Advancing R&D to keep up with a changing world | |||
| Top 10 investments by type of R&D in relation to epidemic risk diseases (2009-2019) | |||
| Type of R&D | R&D Investment (£ millions) | % of total | |
| Vaccines | 9,088 | 34.7% | |
| Basic Research | 5,774 | 22.1% | |
| Drugs | 5,496 | 21.0% | |
| Unspecified | 2,514 | 9.6% | |
| Microbicides | 1,358 | 5.2% | |
| Diagnostics | 1,147 | 4.4% | |
| Chemical vector control products | 241 | 0.9% | |
| Biological vector control products | 189 | 0.7% | |
| Adjuvants and immunomodulators | 108 | 0.4% | |
| General diagnostic platforms | 106 | 0.4% | |
| Other | 158 | 0.6% | |
| TOTAL | 26,179 | 100.0% | |
| Source: Welcome: Advancing R&D to keep up with a changing world | |||
Sources: Welcome: Advancing R&D to keep up with a changing world
World Health Organization: Prioritizing diseases for research and development in emergency contexts
Source: Policy Cure Research





Good Job, thoughtful, mature planning structures. Thank you for your diligence.