Researchers have created a new drug delivery system that could improve the effectiveness of an emerging concept in cancer treatment — to dramatically slow and control tumors on a long-term, sustained basis, not necessarily aiming for their complete elimination.
The approach, called a “metronomic dosage regimen,” uses significantly lower doses of chemotherapeutic drugs but at more frequent time intervals. This would have multiple goals of killing cancer cells, creating a hostile biological environment for their growth, reducing toxicity from the drug regimen and avoiding the development of resistance to the cancer drugs being used.
A system just published in Chemistry of Materials by a group of researchers from Oregon and the United Kingdom offers an even more effective way to deliver such drugs and may be able to greatly improve this approach, scientists say. Further testing is needed in both animals and humans for safety and efficacy.
“This new system takes some existing cancer therapy drugs for ovarian cancer, delivers both of them at the same time and allows them to work synergistically,” says Adam Alani, an associate professor in the Oregon State University/Oregon Health & Science University College of Pharmacy, and lead author on the new study.
“Imagine if we could manage cancer on a long-term basis as a chronic condition, like we now do high blood pressure or diabetes. This could be a huge leap forward.”
This approach is still in trial stages, Alani says, but shows promise. In some prior work with related systems in animal tests, OSU and collaborating researchers have been able to completely eradicate tumors.
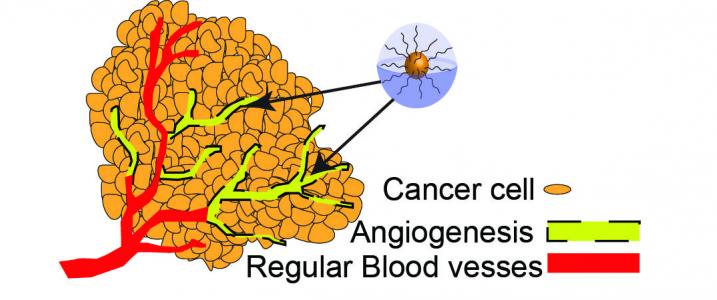
Total remission, Alani says, may be possible with metronomic dosage, but the initial goal is not only to kill cancer cells but to create an environment in which it’s very difficult for them to grow, largely by cutting off the large blood supply these types of cells often need.
Most conventional cancer chemotherapy is based on the use of “maximum tolerable doses” of a drug, in an attempt to completely eliminate cancer or tumors. In some cases such as ovarian cancer, however, drug-free intervals are needed to allow patient recovery from side effects, during which tumors can sometimes begin to grow again or develop resistance to the drugs being used.
The types of cancers this approach may best lend itself to are those that are quite complex and difficult to treat with conventional regimens based on “maximum tolerable dose.” This includes ovarian, sarcoma, breast, prostate, and lung cancers.
One example of the new metronomic regimen, in this instance, is use of two drugs already common in ovarian cancer treatment — paclitaxel and rapamycin — but at levels a tenth to a third of the maximum tolerable dose. One drug attacks cancer cells; the other inhibits cancer cell formation and the growth of blood vessels at tumor sites.
The new system developed in this research takes the process a step further. It attaches these drugs to polymer nanoparticles that migrate specifically into cancer cells and are designed to release the drugs at a particular level of acidity that is common to those cells. The low doses, careful targeting of the drugs and their ability to work in synergy at the same time appeared to greatly increase their effectiveness, while almost completely eliminating toxicity.
“Our goal is to significantly reduce tumors, slow or stop their regrowth, and allow a person’s body and immune system time to recover its health and natural abilities to fight cancer,” Alani says. “I’m very optimistic this is possible, and that it could provide an entirely new approach to cancer treatment.”
This research was supported by OSU, the Medical Research Foundation of Oregon, and the AACP New Pharmacy Faculty Research Award Program. It was done in collaboration with researchers from the Oregon Health & Science University, Pacific University, and Kingston University in the United Kingdom.
Source: Oregon State University




