Rutgers University-New Brunswick engineers have created a 3D-printed smart gel that walks underwater and grabs objects and moves them.
The watery creation could lead to soft robots that mimic sea animals like the octopus, which can walk underwater and bump into things without damaging them. It may also lead to artificial heart, stomach and other muscles, along with devices for diagnosing diseases, detecting and delivering drugs and performing underwater inspections.
Soft materials like the smart gel are flexible, often cheaper to manufacture than hard materials and can be miniaturized. Devices made of soft materials typically are simple to design and control compared with mechanically more complex hard devices.
“Our 3D-printed smart gel has great potential in biomedical engineering because it resembles tissues in the human body that also contain lots of water and are very soft,” says Howon Lee, senior author of a new study and an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. “It can be used for many different types of underwater devices that mimic aquatic life like the octopus.”
The study, published online in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, focuses on a 3D-printed hydrogel that moves and changes shape when activated by electricity. Hydrogels, which stay solid despite their 70-plus percent water content, are found in the human body, diapers, contact lenses, Jell-O, and many other things.
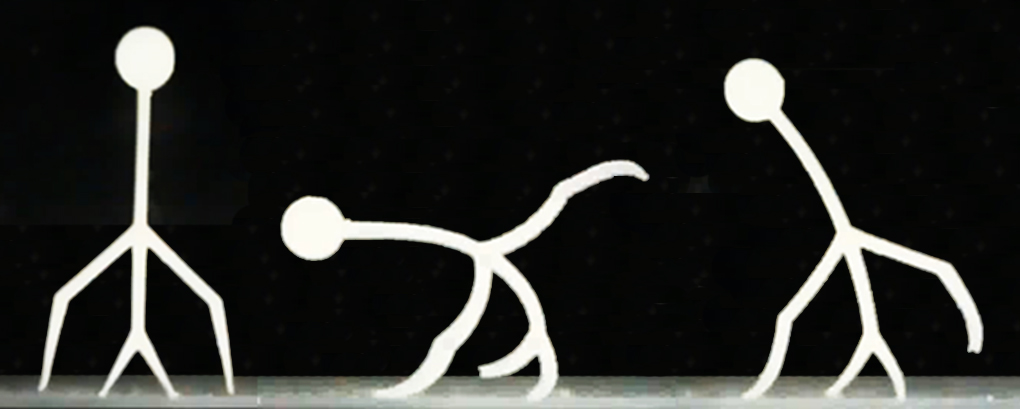

A human-like 3D-printed smart gel walks underwater. Image: Daehoon Han/Rutgers University-New Brunswick
During the 3D-printing process, light is projected on a light-sensitive solution that becomes a gel. The hydrogel is placed in a salty water solution (or electrolyte) and two thin wires apply electricity to trigger motion: walking forward, reversing course and grabbing and moving objects, says Lee. The human-like walker that the team created is about one inch tall.
The speed of the smart gel’s movement is controlled by changing its dimensions (thin is faster than thick), and the gel bends or changes shape depending on the strength of the salty water solution and electric field. The gel resembles muscles that contract because it’s made of soft material, has more than 70 percent water and responds to electrical stimulation, Lee says.
“This study demonstrates how our 3D-printing technique can expand the design, size and versatility of this smart gel,” he says. “Our microscale 3D-printing technique allowed us to create unprecedented motions.”
The study’s lead author is Daehoon Han, a doctoral student in mechanical and aerospace engineering in Rutgers’ School of Graduate Studies. Co-authors include former Rutgers undergraduate student Cindy Farino; Chen Yang, a doctoral student in mechanical and aerospace engineering; Tracy Scott, a former postdoc; Daniel Browe, a doctoral student in biomedical engineering; Joseph W. Freeman, an associate professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering; and Wonjoon Choi, an associate professor in the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University in Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Source: Rutgers University