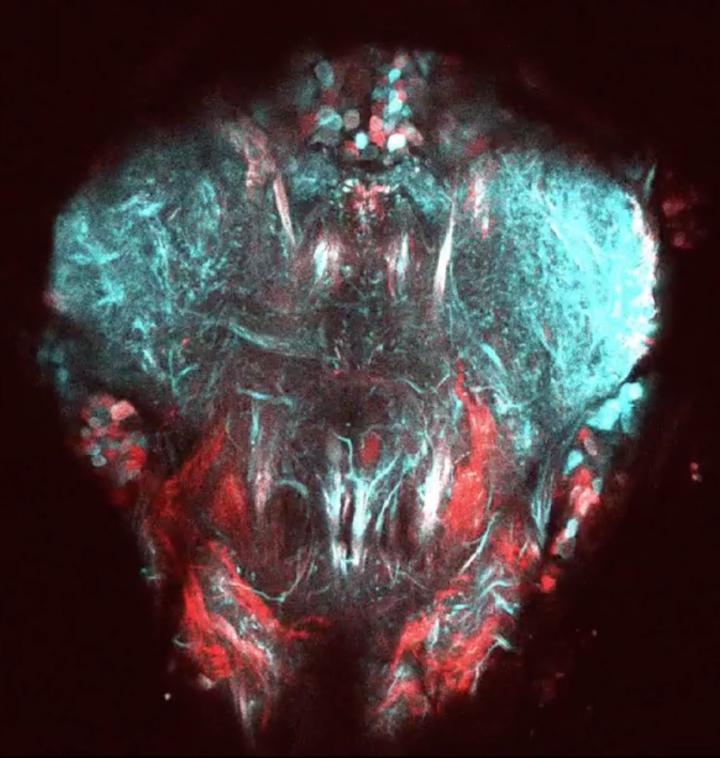
Two-photon image of neural tissue controlling the front legs of the fly. Neurons express fluorescent proteins to visualize neural activity (cyan) and neural anatomy (red). Credit: Pavan Ramdya, EPFL
One of the major goals of biology, medicine, and robotics is to understand how limbs are controlled by circuits of neurons working together. And as if that is not complex enough, a meaningful study of limb activity also has to take place while animals are behaving and moving. The problem is that it is virtually impossible to get a complete view of the activity of motor and premotor circuits that control limbs during behavior, in either vertebrates or invertebrates.
Scientists from the lab of Pavan Ramdya at EPFL’s Brain Mind Institute and Interfaculty Institute of Bioengineering have developed a new method for recording the activity of limb control neural circuits in the popular model organism, the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. The method uses an advanced imaging technique called “two-photon microscopy” to observe the firing of fluorescently labeled neurons that become brighter when they are active.
The scientists focused on the fly’s ventral nerve cord, which is a major neural circuit controlling the legs, neck, wings, and two dumbbell-shaped organs that the insect uses to orient itself, called the “halteres”. But most importantly, they were able to image the fly’s ventral nerve cord while the animal was carrying out specific behaviors.
The scientists discovered different patterns of activity across populations of neurons in the cord during movement and behavior. Specifically, the researchers looked at grooming and walking, which allowed them to study neurons involved in the fly’s ability to walk forward, backwards, or to turn while navigating complex environments.
Finally, the team developed a genetic technique that makes it easier to access to the ventral nerve cord. This can help future studies that directly investigate circuits associated with complex limb movements.
“I am very excited about our new recording approach,” says Professor Pavan Ramdya. “Combined with the powerful genetic tools available for studying the fly, I believe we can rapidly make an impact on understanding how we move our limbs and how we might build robots that move around the world just as effectively as animals.”




