Some animals, such as geckos, can easily climb up walls and across ceilings. But currently, no material exists that allows everyday people to scale walls or transverse ceilings as effortlessly. Now, scientists report in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces a dry adhesive that could someday make it easier to defy gravity.
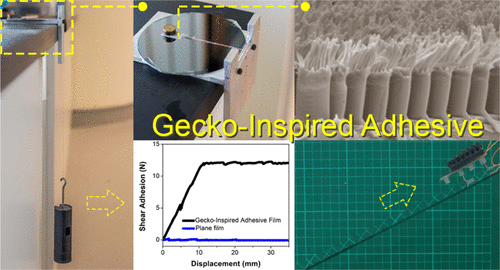
Geckos can scale walls because of their unique toe pads that help them quickly attach and detach from surfaces. Interestingly, gecko toe pads are covered with bristle-like layers of a stiff material called keratin. The bristle-like structure of the keratin in a toe pad helps it to stick — each pad is covered with microscopic pillars, which then branch out at the tips into even smaller structures. Scientists have manufactured dry adhesives with similar properties, but they haven’t been as sticky as gecko toes. And some methods involve the use of layers, but the first layer is usually damaged as successive ones are applied. Other methods are not easily scaled up. Hemant Kumar Raut, Hong Yee Low and colleagues wanted create a dry adhesive that was ultra-sticky but also simple to fabricate in large batches.
The researchers made a dry adhesive with stiff polycarbonate using a nanoimprinting technique to build web-like layers. This method is cost-effective, easy to perform and is scalable. To prevent damage to the first layer, the team used a sacrificial layer, which was dissolved away after the second layer was applied. In repetitive attachment and detachment tests, only a 20 percent decline in stickiness occurred after 50 cycles. This level of adhesion lasted for up to 200 cycles. The researchers say that their film’s adhesion was comparable to that of a gecko. The team also placed the adhesive film on the feet of a miniature robot, which moved with ease up a 30-degree incline.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Temasek Laboratories at Singapore University of Technology and Design and SUTD-MIT International Design Centre.
The abstract that accompanies this study is available here.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a not-for-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C. and Columbus, Ohio.




