Australian researchers from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Nanoscale BioPhotonics (CNBP) have developed a 3D printable “clip-on” that can turn any smartphone into a fully functional microscope.
Reported in the research journal Scientific Reports, the smartphone microscope is powerful enough to visualize specimens as small as 1/200th of a millimeter, including microscopic organisms, animal and plant cells, blood cells, cell nuclei, and more.
The clip-on technology is unique in that it requires no external power or light source to work yet offers high-powered microscopic performance in a robust and mobile handheld package.
And the researchers are making the technology freely available, sharing the 3D printing files publicly so anyone — from scientists to the scientifically curious — can turn their own smartphones into microscopes.
Lead developer and CNBP Research Fellow at RMIT University, Dr. Antony Orth, believes the technology has immense potential as a scientific tool, one that is ideal for use in remote areas and for field-work where larger standalone microscopes are unavailable or impractical.
“We’ve designed a simple mobile phone microscope that takes advantage of the integrated illumination available with nearly all smartphone cameras,” says Orth.
The clip-on has been engineered with internal illumination tunnels that guide light from the camera flash to illuminate the sample from behind. This overcomes issues seen with other microscopy-enabled mobile phone devices, says Orth.
“Almost all other phone-based microscopes use externally powered light sources while there’s a perfectly good flash on the phone itself,” he explains. “External LEDs and power sources can make these other systems surprisingly complex, bulky and difficult to assemble.”
“The beauty of our design is that the microscope is useable after one simple assembly step and requires no additional illumination optics, reducing significantly the cost and complexity of assembly. The clip-on is also able to be 3D printed making the device accessible to anyone with basic 3D printing capabilities.”
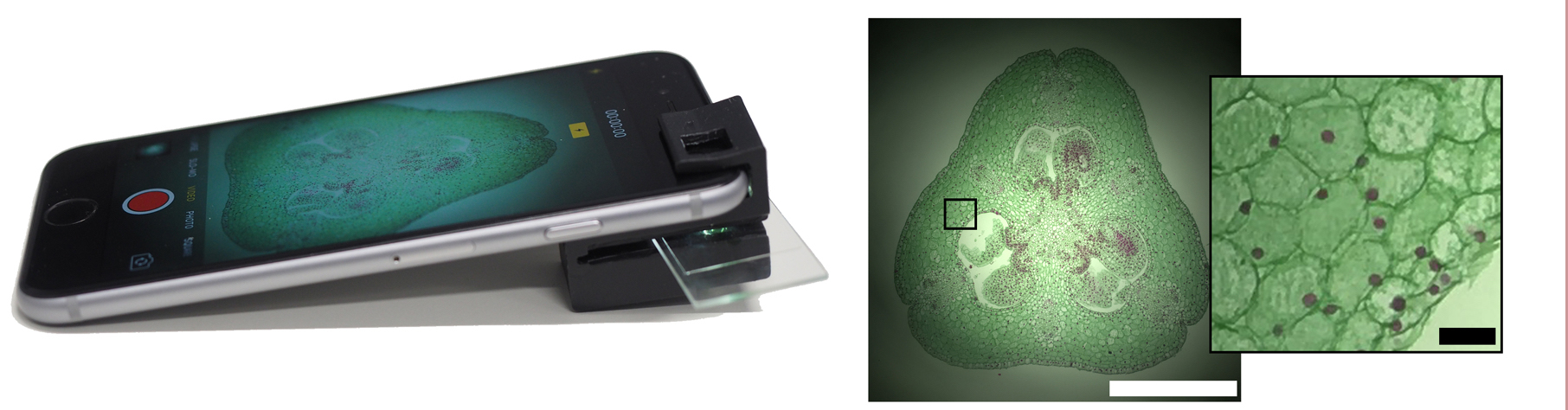
Cells being viewed by an add-on clip that turns a smartphone into a fully operational microscope.
A further advantage, notes Orth, is that the clip-on enables both bright-field and dark-field microscopy techniques to be undertaken. Bright-field microscopy is where a specimen is observed on a bright background. Conversely, dark-field shows the specimen illuminated on a dark background.
“The added dark-field functionality lets us observe samples that are nearly invisible under conventional bright-field operation such as cells in media,” he says. “Having both capabilities in such a small device is extremely beneficial and increases the range of activity that the microscope can be successfully used for.”
Orth believes the potential applications for the smartphone microscope are enormous.
“Our mobile microscope can be used as an inexpensive and portable tool for all types of on-site or remote area monitoring.”
“Water quality, blood samples, environmental observation, early disease detection and diagnosis — these are all areas where our technology can be easily used to good effect.”
Orth sees significant benefit in developing countries for the device.
“Powerful microscopes can be few and far between in some regions,” says Orth. “They’re often only found in larger population centers and not in remote or smaller communities. Yet their use in these areas can be essential — for determining water quality for drinking, through to analyzing blood samples for parasites, or for disease diagnosis including malaria.”
To ensure that this technology can be utilized the world over, the files for the 3D printing of the microscope clip-on are being made freely available. They are available for download at the CNBP web site: http://cnbp.org.au/online-tools
“Ideally, a phone microscope should take advantage of the integrated flash found in nearly every modern mobile, avoiding the need for external lighting and power. It should also be as compact and easy to assemble as possible. It is this design philosophy that inspired us in the development of this add-on clip,” says Orth.
The new phone microscope has already been tested by Orth and his CNBP colleagues in a number of areas, successfully visualizing samples ranging from cell culture, to zooplankton to live cattle semen in support of livestock fertility testing.