In a recent experiment at EPFL, a microwave resonator, a circuit that supports electric signals oscillating at a resonance frequency, is coupled to the vibrations of a metallic micro-drum. By actively cooling the mechanical motion close to the lowest energy allowed by quantum mechanics, the micro-drum can be turned into a quantum reservoir – an…
Cameras Reveal Images Hidden to the Naked Eye
EPFL researchers took advantage of the limits of human vision to hide an image in a video. The image is invisible to the human eye, but not to a camera. Human visual perception works well and is very effective at seeing what’s important to us. But our eyes are not capable of averaging video images…
Cracking the Code of Huntington’s Disease
Huntington’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that causes patients to lose their ability to move, speak, and even think. It is caused by a gene mutation that produces an abnormal form of the protein huntingtin, which aggregates and builds up inside neurons of the cortex and striatum. Small chemical modifications on different parts of huntingtin…
Six-Legged Robots Exhibit Faster Gait Than Observed in Nature
Researchers at EPFL and UNIL have discovered a faster and more efficient gait, never observed in nature, for six-legged robots walking on flat ground. Bio-inspired gaits – less efficient for robots – are used by real insects since they have adhesive pads to walk in three dimensions. The results provide novel approaches for roboticists and…
A New Technique Speeds Up Genetics
Scientists at EPFL have developed a technique that can be a game-changer for genetics by making the characterization of DNA-binding proteins much faster, more accurate, and efficient. Genes hold the DNA code for producing all the proteins of the cell. To begin this process, genes must first be transcribed from DNA into RNA. This requires…
New Perovskite Could Lead The Next Generation of Data Storage
EPFL scientists have developed a new perovskite material with unique properties that can be used to build next-generation hard drives. As we generate more and more data, we need storage systems, e.g. hard drives, with higher density and efficiency. But this also requires materials whose magnetic properties can be quickly and easily manipulated in order…
New Hydrogel Can Take Organoids from Dish to Clinic
EPFL scientists have developed a gel for growing miniaturized body organs that can be used in clinical diagnostics and drug development. Organoids are miniature organs that can be grown in the lab from a person’s stem cells. They can be used to model diseases, and in the future could be used to test drugs or…
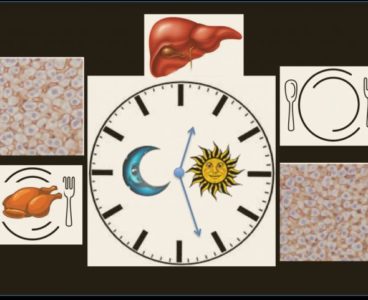
How The Liver Dances to a Day/Night Rhythm
Following the day-night cycle, the liver has its own metabolic rhythm. Using cutting-edge proteomics, scientists at EPFL and the Nestlé Institute of Health Sciences have now identified over 500 liver proteins that change in abundance over the course of the day in the cell nucleus, opening a new dimension of metabolism. Biological processes occurring in…
New Class of Materials Could Realize Quantum Computers
Soft Robots That Mimic Human Muscles
An EPFL team is developing soft, flexible and reconfigurable robots. Air-actuated, they behave like human muscles and may be used in physical rehabilitation. They are made of low-cost materials and could easily be produced on a large scale. Robots are usually expected to be rigid, fast and efficient. But researchers at EPFL’s Reconfigurable Robotics Lab…
A Deep-Learning App Diagnoses Crop Diseases
Scientists at EPFL and Penn State have trained a computer-learning algorithm to identify crop diseases with extremely high accuracy. The algorithm will be incorporated in a smartphone app to help farmers prevent future food shortages. Crop diseases, which threaten the world’s food security, can be fought with the help of artificial intelligence systems. Scientists from…
Several Thousand Suns in a Laboratory
Eighteen light sources arranged in a half-sphere can mimic the equivalent of several thousand times the sun’s radiation received on earth, with unparalleled power and precision. This system, developed by an EPFL laboratory, can be used to test various materials in extreme conditions. An article on this topic was published today in Optics Express. A…
Effective, Low-Cost Solution for Storing Solar Energy
How can we store solar energy for period when the sun doesn’t shine? One solution is to convert it into hydrogen through water electrolysis. The idea is to use the electrical current produced by a solar panel to ‘split’ water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Clean hydrogen can then be stored away for future use…