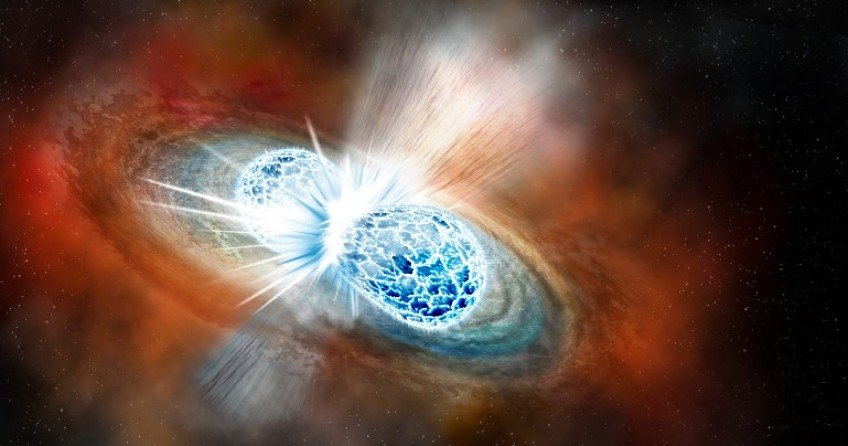
Artist’s conception of two neutron stars colliding. A University of Alberta researcher has created a 3-D computer simulation that gives scientists a clearer picture of what happens in the aftermath of the collision. (Credit: Robin Dienel, Carnegie Institution for Science)
Unprecedented detail of the aftermath of a collision between two neutron stars depicted in a 3D computer model created by a University of Alberta astrophysicist provides a better understanding of how some of the universe’s fundamental elements form in cosmic collisions.
“The collision creates heavy elements including gold and lead,” said Rodrigo Fernández, who worked with an international research team using supercomputers at the U.S. National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center and data from a collision scientists detected in August of 2017—the first such collision ever observed.
“We also saw for the first time a gamma-ray burst from two neutron stars colliding. There’s a large amount of science coming out of that discovery,” he added, including helping researchers calculate the mass of the neutron stars and even confirm how fast the universe is expanding.
Neutron stars are the smallest and densest stars, packing more mass than Earth’s sun into an area the size of a city. When two of them collide, they merge in a flash of light and debris known as a kilonova, as material explodes outward.
Until now, computer simulations of the collisions haven’t been sophisticated enough to account for where all that material ends up.
For example, the new 3D model shows that the accretion disk—the collection of leftover debris that orbits the combined star—ejects twice the amount of material and at higher speeds compared with previous 2D models.
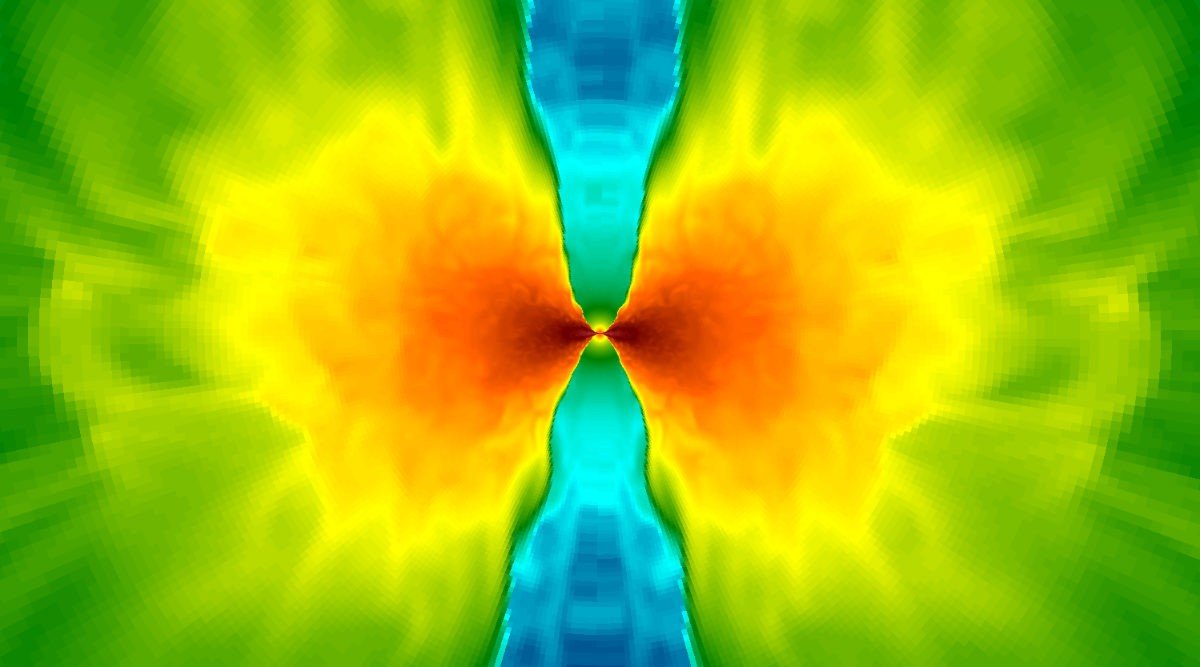
A cross-section of the model of two colliding neutron stars shows the accretion disk in red around the black hole at the center. The astrophysical jet is the blue funnel above and below the black hole. (Credit: Rodrigo Fernández)
“While our results do not fully reconcile all discrepancies, they bring the numbers closer together,” Fernández said, adding that his model provides a better understanding of how heavy elements are created and ejected into space.
By modelling the aftermath of the collision in such detail, Fernández and the team were also able to account for another way matter is ejected from the collision: on an astrophysical jet, a narrow plume of particles and radiation shot out at nearly the speed of light as the stars collide. The jet is also thought to be the source of the gamma-ray burst.
“It was expected that we could find jets, but this is the first time we’ve been able to model this in enough detail to see this effect emerge,” explained Fernández.
Modelling the event in 3D was no easy task, he added. Although a neutron star collision happens in just milliseconds, the accretion disk can last for seconds. Its formation also involves complex physics and many physical processes all happening at once, making it far harder for computers to simulate.
“Among the processes at work, the main culprit is actually the magnetic field acting on the matter,” noted Fernández. “We know the equations that describe that process, but the only way that we can properly describe them is in 3D. So, not only do you have to run the simulation for a long time, you also have to model it in three dimensions, which is computationally very expensive.
“The simulation’s technical aspects are impressive from a scientific standpoint because the interactions are so complex.”
The study, “Long-Term GRMHD Simulations of Neutron Star Merger Accretion Disks: Implications for Electromagnetic Counterparts,” was published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.