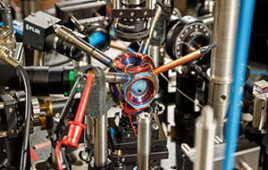
A new form of solar-powered supercapacitor could help make future wearable technologies lighter and more energy-efficient, scientists say.
In a paper published in the journal Nano Energy, researchers from the University of Glasgow’s Bendable Electronics and Sensing Technologies (BEST) group describe how they have developed a promising new type of graphene supercapacitor, which could be used in the next generation of wearable health sensors.
Currently, wearable systems generally rely on relatively heavy, inflexible batteries, which can be uncomfortable for long-term users. The BEST team, led by Professor Ravinder Dahiya, have built on their previous success in developing flexible sensors by developing a supercapacitor which could power health sensors capable of conforming to wearer’s bodies, offering more comfort and a more consistent contact with skin to better collect health data.
Their new supercapacitor uses layers of flexible, three-dimensional porous foam formed from graphene and silver to produce a device capable of storing and releasing around three times more power than any similar flexible supercapacitor. The team demonstrated the durability of the supercapacitor, showing that it provided power consistently across 25,000 charging and discharging cycles.
They have also found a way to charge the system by integrating it with flexible solar powered skin already developed by the BEST group, effectively creating an entirely self-charging system, as well as a pH sensor which uses wearer’s sweat to monitor their health.
Dahiya says, “We’re very pleased by the progress this new form of solar-powered supercapacitor represents. A flexible, wearable health monitoring system which only requires exposure to sunlight to charge has a lot of obvious commercial appeal, but the underlying technology has a great deal of additional potential.
“This research could take the wearable systems for health monitoring to remote parts of the world where solar power is often the most reliable source of energy, and it could also increase the efficiency of hybrid electric vehicles. We’re already looking at further integrating the technology into flexible synthetic skin which we’re developing for use in advanced prosthetics.”
The team’s paper, titled “Flexible Self-Charging Supercapacitor Based on Graphene-Ag-3D Graphene Foam Electrodes,” is published in Nano Energy.
The research was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and Scottish Funding Council (SFC).
Source: University of Glasgow