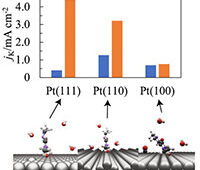
A new generation of higher-powered batteries for phones and cameras could result from ground-breaking research led by scientists at the University of Kent.
Researchers from the University’s School of Physical Sciences (SPS), working with scientists from other European institutions, formulated a recipe to increase the rate at which a solid material – an artificial mineral – can conduct charge.
The team found that a phenomenon known as geometric frustration can be used in this process to increase the charge transport rate in the solid material in a way that is comparable with heating that material.
Making use of this phenomenon, the team was able to ‘tune’ materials to be used in future batteries and fuel cells to speed up ionic conductivity.
Lead researcher Dr Dean Sayle and his team in SPS found that geometric frustration broke up the regimented formation of atoms in the material, leading to a more disordered pattern. This disordered pattern allowed the charge to pass through the material at a much higher rate.
Dr Sayle said: ‘Disorder can be created by geometric frustration which might be understood as randomly giving two kinds of differently sized umbrellas to a regimented parade of people and telling them to put them up and come as close together as the size of the umbrellas allow.
‘Naturally, this will lead to a destruction of the former formation towards a disordered formation exhibiting a large number of gaps. Similarly, we used geometric frustration to make the atoms disordered by mixing two differently sized atoms together which increased charge transport by 100,000’.
As well as more powerful batteries, the new technique may lead to the development of new energy materials with zero- emissions.