For the first time, physicists at CERN have observed a benchmark atomic energy transition in anithydrogen, a major step toward cooling and manipulating the basic form of antimatter.
“The Lyman-alpha transition is the most basic, important transition in regular hydrogen atoms, and to capture the same phenomenon in antihydrogen opens up a new era in antimatter science,” says Takamasa Momose, the University of British Columbia chemist and physicist who led the development of the laser system used to manipulate the anithydrogen.
“This approach is a gateway to cooling down antihydrogen, which will greatly improve the precision of our measurements and allow us test how antimatter and gravity interact, which is still a mystery.”
The results were published in Nature.
Antimatter, annihilated on impact with matter, is notoriously tricky to capture and work with. But its study is key to solving one of the great mysteries of the universe: why anti-matter, which should have existed in equal amounts to matter at the time of the Big Bang, has all but disappeared.
“This gets us just a bit closer to answering some of these big questions in physics,” says Makoto Fujiwara, Canada’s spokesperson for CERN’s ALPHA antihydrogen research collaboration, and a physicist with TRIUMF, Canada’s particle accelerator centre. “Over the past decades, scientists have been able to revolutionize atomic physics using optical manipulation and laser cooling, and with this result we can begin applying the same tools to probing the mysteries of antimatter.”
An antihydrogen atom, consisting of an antiproton and positron, is the antimatter counterpart of a hydrogen atom, made of a single proton with an orbiting electron.
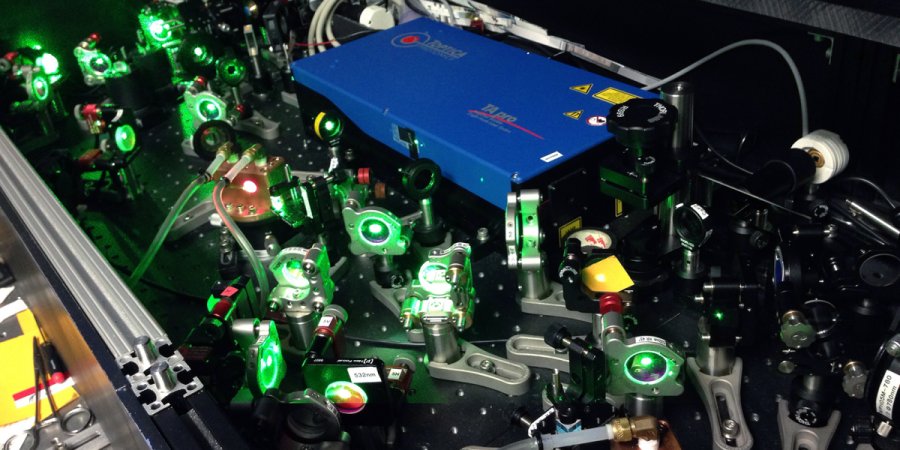
Ti:Sapphire laser system built at the University of British Columbia. Image: University of British Columbia
The so-called Lyman-alpha transition, first seen in hydrogen more than 100 years ago, is measured as a series of ultraviolet emissions when a hydrogen atom’s electron is prompted to shift from a low orbital to a high orbital. Using laser pulses lasting nano seconds, Momose, Fujiwara, Canadian colleagues, and the international ALPHA collaboration at CERN, were able to achieve the same transition in several hundred antihydrogen atoms magnetically trapped in a vacuum.
Aside from the very real challenge of trapping that many antihydrogen atoms long enough to work with them, fine-tuning the laser system components took years.
“You can’t actually see the laser pulses you’re using to excite the antihydrogen and shift the orbitals,” says Momose. “So, our team was essentially working and trouble-shooting the laser system in the blind!”
The team’s next step is to use the laser innovation to help produce cold and dense sample of anti-atoms for precision spectroscopy and gravity measurements.
Source: University of British Columbia


