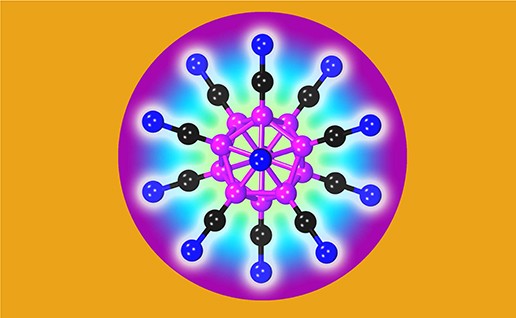
A recently predicted doubly ionized molecule with extraordinary stability could help make very safe and efficient batteries. The image shows the predicted structure of this boron (B) (pink), carbon (C) (black), nitrogen (N) (blue) molecule: B12(CN)122-. In the optimized geometry, CN moieties are bound radially to the icosahedron made of boron atoms with the carbon atoms attached to the boron atoms.Credit: Image courtesy of the authors and Angewandte Chemie International Edition 55, 3704 (2016).
The Science
Long-lasting, lightweight batteries could improve everything from electric cars to cell phones. The challenge in designing such batteries is getting the molecules to handle more electrons (electricity). Most small molecules cannot accommodate multiple extra electrons. Why? The repulsion between the electrons causes the molecule to disintegrate. The icosahedral-shaped molecule composed of 20 boron and 20 hydrogen atoms is one of the exceptions. Scientists made it more stable. They substituted a carbon-nitrogen (CN) atomic pair for hydrogen. The result is a six-fold increase in the molecular stability. If confirmed experimentally, this colossal improvement would make this the world’s most stable doubly ionized molecule and lead to better batteries.
The Impact
This study offers a powerful computational tool for energy storage that will accelerate discovery of novel molecules critically important for new batteries. For example, the researchers used this new complex to design a halogen-free electrolyte. Halogens are toxic. The new electrolyte in lithium- and magnesium-ion batteries could lead to safer, longer-lasting, lighter-weight, more efficient devices.
Summary
Powered by the state-of-the art computational tools and inspired by nature, researchers investigated the stability of ionic molecules for their potential electrolyte use in energy storage applications such as electrochemical cells. Initial research at Virginia Commonwealth University focused on the observed improved stability of smaller molecules like benzene (C6H6) and the improved stability observed when a carbon-nitrogen (CN) atomic pair was substituted for hydrogen. The research team then investigated a similar substitution on the much larger ionic icosahedral cluster of B12H122− using state-of-the-art computational energy calculations. In this configuration, a second electron binding energy of 5.28 eV leads to a stable dianion molecule resulting in a remarkable discovery—the new molecule B12(CN)122− was calculated to have a six-fold increase in the molecular stability compared to B12H122−, making it potentially the most stable doubly ionized molecule in nature. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulation confirmed that the molecular stability continued at high temperatures up to 1500 K.
Publications
H. Zhao, J. Zhou, and P. Jena, “Stability of B12(CN)122-: Implications for lithium and magnesium ion batteries.” Angewandte Chemie International Edition 55, 3704 (2016). [DOI: 10.1002/anie.201600275]