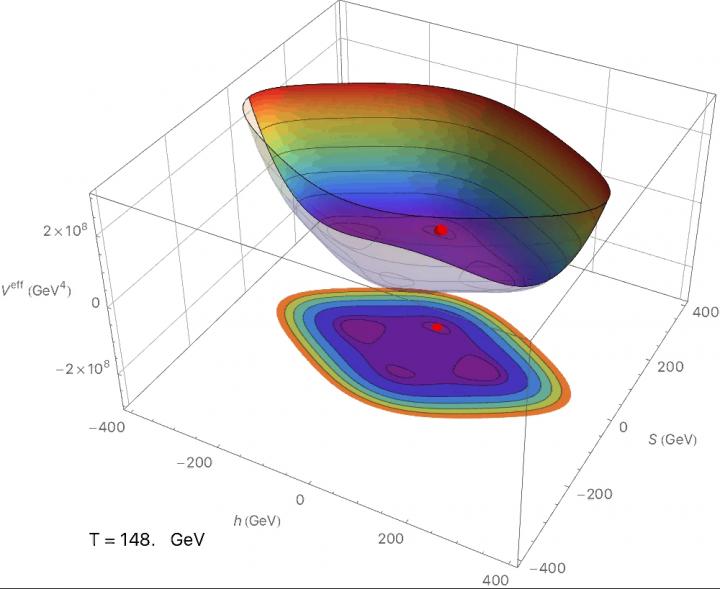
In the new dark matter model, the Higgs particle has different properties to those in the standard model of particle physics. The figure shows the energy of the Higgs particle as a function of the model parameters. Source: Ill./©: Michael Baker, JGU
Only a small part of the universe consists of visible matter. By far the largest part is invisible and consists of dark matter and dark energy. Very little is known about dark energy, but there are many theories and experiments on the existence of dark matter designed to find these as yet unknown particles. Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany have now come up with a new theory on how dark matter may have been formed shortly after the origin of the universe. This new model proposes an alternative to the WIMP paradigm that is the subject of various experiments in current research.
Dark matter is present throughout the universe, forming galaxies and the largest known structures in the cosmos. It makes up around 23 percent of our universe, whereas the particles visible to us that make up the stars, planets, and even life on Earth represent only about four percent of it. The current assumption is that dark matter is a cosmological relic that has essentially remained stable since its creation. “We have called this assumption into question, showing that at the beginning of the universe dark matter may have been unstable,” explained Dr. Michael Baker from the Theoretical High Energy Physics (THEP) group at the JGU Institute of Physics. This instability also indicates the existence of a new mechanism that explains the observed quantity of dark matter in the cosmos.
The stability of dark matter is usually explained by a symmetry principle. However, in their paper, Dr. Michael Baker and Prof. Joachim Kopp demonstrate that the universe may have gone through a phase during which this symmetry was broken. This would mean that it is possible for the hypothetical dark matter particle to decay. During the electroweak phase transition, the symmetry that stabilizes dark matter would have been re-established, enabling it to continue to exist in the universe to the present day.
With their new theory, Baker and Kopp have introduced a new principle into the debate about the nature of dark matter that offers an alternative to the widely accepted WIMP theory. Up to now, WIMPs, or weakly interacting massive particles, have been regarded as the most likely components of dark matter, and experiments involving heavily shielded underground detectors have been carried out to look for them. “The absence of any convincing signals caused us to start looking for alternatives to the WIMP paradigm,” said Kopp.
The two physicists claim that the new mechanism they propose may be connected with the apparent imbalance between matter and antimatter in the cosmos and could leave an imprint which would be detected in future experiments on gravitational waves. In their paper published in the scientific journal Physical Review Letters, Baker and Kopp also indicate the prospects of finding proof of their new principle at CERN’s LHC particle accelerator and other experimental facilities.




