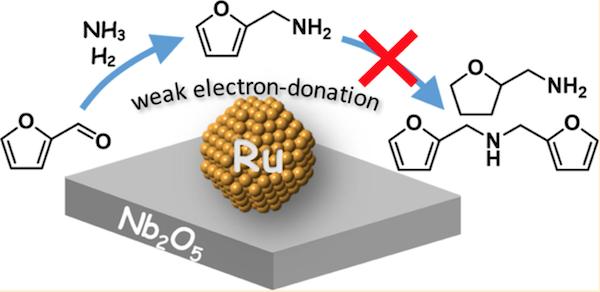
The weak electron-donating capability of ruthenium (Ru) nanoparticles supported on niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5) is thought to promote reductive amination while preventing the formation of undesirable by-products.
Known for their outstanding versatility, primary amines (derivatives of ammonia) are industrially important compounds used in the preparation of a wide range of dyes, detergents and medicines. Although many attempts have been made to improve their synthesis using catalysts containing nickel, palladium and platinum, for example, few have succeeded in reducing the formation of secondary and tertiary amines and other undesired by-products.
Now, researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have developed a highly selective catalyst consisting of ruthenium nanoparticles supported on niobium pentoxide (Ru/Nb2O5). In a study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the team demonstrated that Ru/Nb2O5 is capable of producing primary amines from carbonyl compounds with ammonia (NH3) and dihydrogen (H2), with negligible formation of by-products.
The study compared the extent to which different catalysts could convert furfural to furfurylamine in a process known as reductive amination1. This reaction is one of the most useful methods for producing primary amines on an industrial scale. The Ru/Nb2O5 catalyst outperformed all other types tested — remarkably, a yield of 99% was attained when ammonia was used in excess quantity.
Even after three recycles, the Ru/Nb2O5 catalyst achieved consistent results, with consecutive yields of over 90%. The superior catalytic efficiency is thought to be due to ruthenium’s weak electron-donating properties on the Nb2O5 surface (see Figure 1).
Michikazu Hara of Tokyo Tech’s Laboratory for Materials and Structures and his co-workers then explored how effectively the new catalyst could break down biomass (in the form of glucose) into 2,5-bis(aminomethyl)furan, a monomer for aramid production. Previous experiments using a nickel-based catalyst led to a yield of around 50% from glucose-derived feedstock (5-hydroxymethylfurfural). The new catalyst used in combination with a so-called ruthenium-xantphos complex produced a yield of 93%. With little to no by-products observed, Ru/Nb2O5 represents a major breakthrough in the clean, large-scale production of biomass-derived materials.
Further studies to expand on these initial findings are already underway. By pushing the boundaries of material design, the researchers say that Ru/Nb2O5 may accelerate the production of environmentally friendly plastics, rubber and heat-resistant aramid fibers2. In future, the Ru/Nb2O5 catalyst may also impact the development of novel anti-cancer drugs, anti-bacterials, pesticides, agrochemicals, fertilizers, bio-oils and biofuels.



