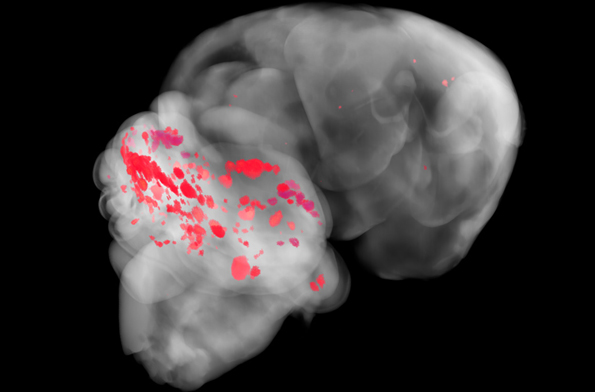
CCMs in a mouse using microCT Credit: Issam Awad, University of Chicago
Bacteria in the gut microbiome drive the formation of cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), clusters of dilated, thin-walled blood vessels in the brain that can cause stroke and seizures, according to new research published this week in Nature by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Led by Mark Kahn, MD, a professor of Cardiovascular Medicine, the team’s research suggests that altering the microbiome in CCM patients may be an effective therapy for this cerebrovascular disease.
CCM disease, which occurs in about one in 100 to 200 people, can present in two forms. One is sporadic, accounting for 80 percent of cases, and is most frequent in older individuals. The remaining 20 percent are familial, inherited cases.
In 2016, the Kahn lab discovered the molecular mechanism in endothelial cells that underlies the formation of CCMs. In the current Nature study, the team discovered that this molecular pathway is activated by TLR4, a receptor for the bacterial molecule lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Activation of TLR4 on brain endothelial cells by LPS vastly accelerated CCM formation. Conversely, if TLR4 was removed from endothelial cells genetically, or if the mice were treated with drugs that block TLR4 function, CCM formation is prevented.
Since TLR4 primarily responds to LPS from Gram-negative bacteria, Alan Tang, an MD-PhD student in the Kahn lab, proposed that bacteria from the animal’s gut microbiome may drive CCM formation. To test this theory, he examined CCM formation in mice that were housed under germ-free conditions (in collaboration with the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia through the PennCHOP Microbiome Program Core Facility) or treated with antibiotics to reduce the number of bacteria living in the gut. In both cases, CCM formation was dramatically reduced, demonstrating a key role for bacteria in the pathology of CCM disease.
The team next sought evidence that bacterial LPS-TLR4 signaling might also support CCM formation in human patients. They worked with researchers at the University of New Mexico (UNM) and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) who have studied several hundred patients who carry an identical mutation in one CCM gene but display a widely variable disease course.
“Some of these patients experience severe stroke by the age of two and others have no symptoms over their lifetime,” Kahn said. “What makes the disease outcome so variable?”
Working with the team from UNM and UCSF, they discovered that genetic variations that raise the amount of TLR4 that is produced are associated with higher numbers of CCM lesions, suggesting that the key role for LPS-TLR4 signaling identified in mice is also present in humans.
These studies identify an unexpected, direct link between the microbiome and a common cerebrovascular disease. “This suggests that treatments designed to block TLR4 signaling or alter the microbiome may be used to treat this disease,” Kahn said.




