A dash of salt can simplify the creation of two-dimensional materials, and thanks to Rice University scientists, the reason is becoming clear.
Boris Yakobson, a Rice professor of materials science and nanoengineering and of chemistry, was the go-to expert when a group of labs in Singapore, China, Japan and Taiwan used salt to make a “library” of 2-D materials that combined transition metals and chalcogens.
These compounds could lead to smaller and faster transistors, photovoltaics, sensors, and catalysts, according to the researchers.
Through first-principle molecular dynamics simulations and accurate energy computations, Yakobson and his colleagues determined that salt reduces the temperature at which some elements interact in a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) furnace. That makes it easier to form atom-thick layers similar to graphene but with the potential to customize their chemical composition for specific layer-material and accordingly electrical, optical, catalytic and other useful properties.
The research team including Yakobson and Rice postdoctoral researcher Yu Xie and graduate student Jincheng Lei reported its results in Nature.
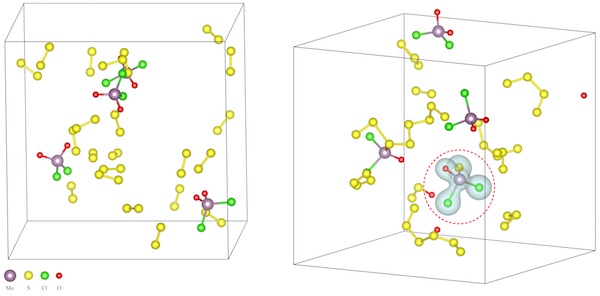
Rice University scientists built computer models of intermediate reactions to understand why salt lowers reaction temperatures in the synthesis of two-dimensional compounds. Above left, molybdenum oxychloride precursor molecules undergo sulfurization in which sulfur atoms replace oxygen atoms. That sets up the material to form new compounds. At right, the calculations show the charge densities of the new molecules. Image: Courtesy of the Yakobson Group
The team led by Zheng Liu of Nanyang Technological University in Singapore used its seasoned technique with CVD to create 47 compounds of metal chalcogenides (which contain a chalcogen and an electropositive metal). Most of the new compounds had two ingredients, but some were alloys of three, four and even five. Many of the materials had been imagined and even coveted, Yakobson says, but never made.
In the CVD process, atoms excited by temperatures — in this case between 600 and 850 degrees Celsius (1,112 and 1,562 degrees Fahrenheit) — form a gas and ultimately settle on a substrate, linking to atoms of complementary chemistry to form monolayer crystals.
Researchers already suspected salt could facilitate the process, Yakobson says. Liu came to him to request a molecular model analysis to learn why salt made it easier to melt metals with chalcogens and get them to react. That would help them learn if it might work within the broader palette of the periodic table.
“They did impressively broad work to make a lot of new materials and to characterize each of them comprehensively,” Yakobson says. “From our theoretical perspective, the novelty in this study is that we now have a better understanding of why adding plain salt lowers the melting point for these metal-oxides and especially reduces the energy barriers of the intermediates on the way to transforming them into chalcogenides.”
Source: Rice University




