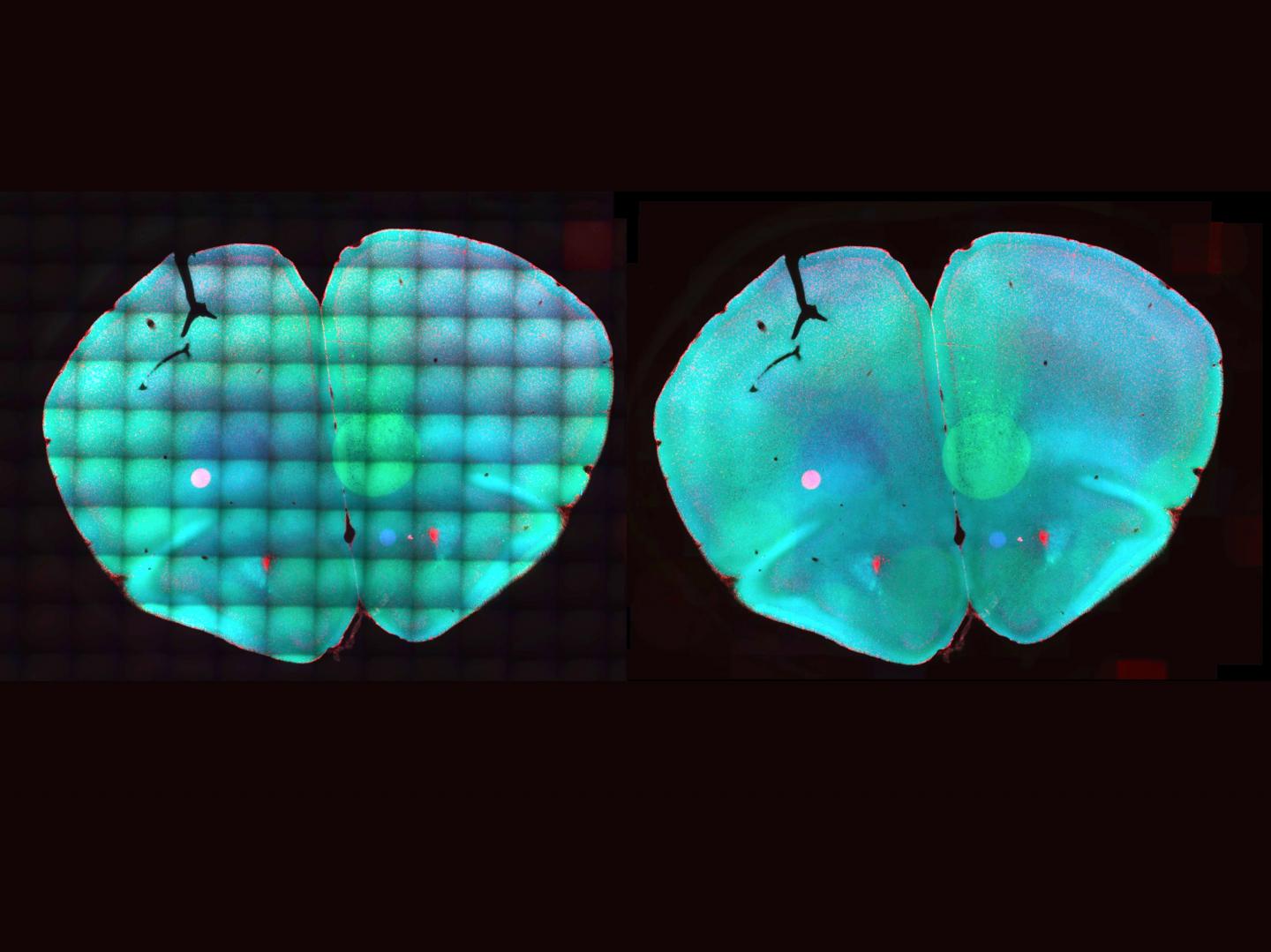
The software BaSiC improves microscope images, e.g., the mosaic image of a mouse brain thin section (left without, right with BaSiC correction). BaSiC’s image correction is also a valuable tool for stem cell researchers who want to detect the appearance of specific transcription factors early on. Source: Tingying Peng / TUM/HMGU
Today, tracking the development of individual cells and spotting the associated factors under the microscope is nothing unusual. However, impairments like shadows or changes in the background complicate the interpretation of data. Now, researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Helmholtz Zentrum München have developed a software that corrects images to make hitherto hidden development steps visible.
When stem cells develop into specialized cells, this happens in multiple steps. But which regulatory proteins are active during the decisive branching on the development path? Using so-called time-lapse microscopy, researchers can observe individual cells at very high time resolutions and, using fluorescent labelling, they can recognize precisely which of these proteins appear when in the cell.
Once a stem cell has been identified, it can be closely observed over several days using cell-tracking software. Yet, this “surveillance work” often turns out to be difficult. “The imaging data is frequently marred by irregular brightness and faded backgrounds in the time-lapse,” explains Dr. Carsten Marr, heading the workgroup Quantitative Single Cell Dynamics at the Institute of Computational Biology (ICB) of the Helmholtz Zentrum München. “This makes it difficult or impossible to detect proteins that are decisive when a cell opts for a specific development direction, so-called transcription factors.”
Algorithms that filter out these kinds of artefacts exist, but they require either specifically prepared reference images, many images per dataset or complex manual adjustments. Furthermore, none of the existing methods correct alterations in the background over time, which hamper the quantification of individual cells.
Algorithm eliminates background changes
Now, Dr. Tingying Peng, member of Dr. Carsten Marr’s group at the Helmholtz Zentrum München and Professor Nassir Navab, head of the Chair for Computer Aided Medical Procedures and Augmented Reality at TU Munich, present an algorithm that corrects these artefacts using only a few images per dataset.
The software is called “BaSiC” and is freely available. It is compatible with many image formats commonly used in bioimaging, including mosaics pieced together from numerous smaller images and used, for example, to render large tissue regions. “Contrary to other programs, however,” explains Dr. Peng, “BaSiC can correct changes in the background of time-lapse videos. This makes it a valuable tool for stem cell researchers who want to detect the appearance of specific transcription factors early on.”
Bringing significant details to light
How well the new image correction program improves the analysis of individual stem cell development steps the scientists demonstrated with time-lapse videos of blood stem cells. They recorded the videos to observe cells over a six-day time span. At a certain point during this observation period undifferentiated precursor cells choose between two possible tacks of development that lead to the formation of different mature blood cells.
In images corrected using BaSiC, the researchers could identify a substantial increase in the intensity of a specific transcription factor in one of the two cell lines, while the amount of his protein in the other cell line remained unchanged. Without the image correction, the difference was not ascertainable.
“Using BaSiC, we were able to make important decision factors visible that would otherwise have been drowned out by noise,” says Nassir Navab. “The long-term goal of this research is to facilitate influencing the development of stem cells in a targeted manner, for example to cultivate new heart muscle cells for heat-attack patients. The novel possibilities for observation are bringing us a step closer to this goal.”