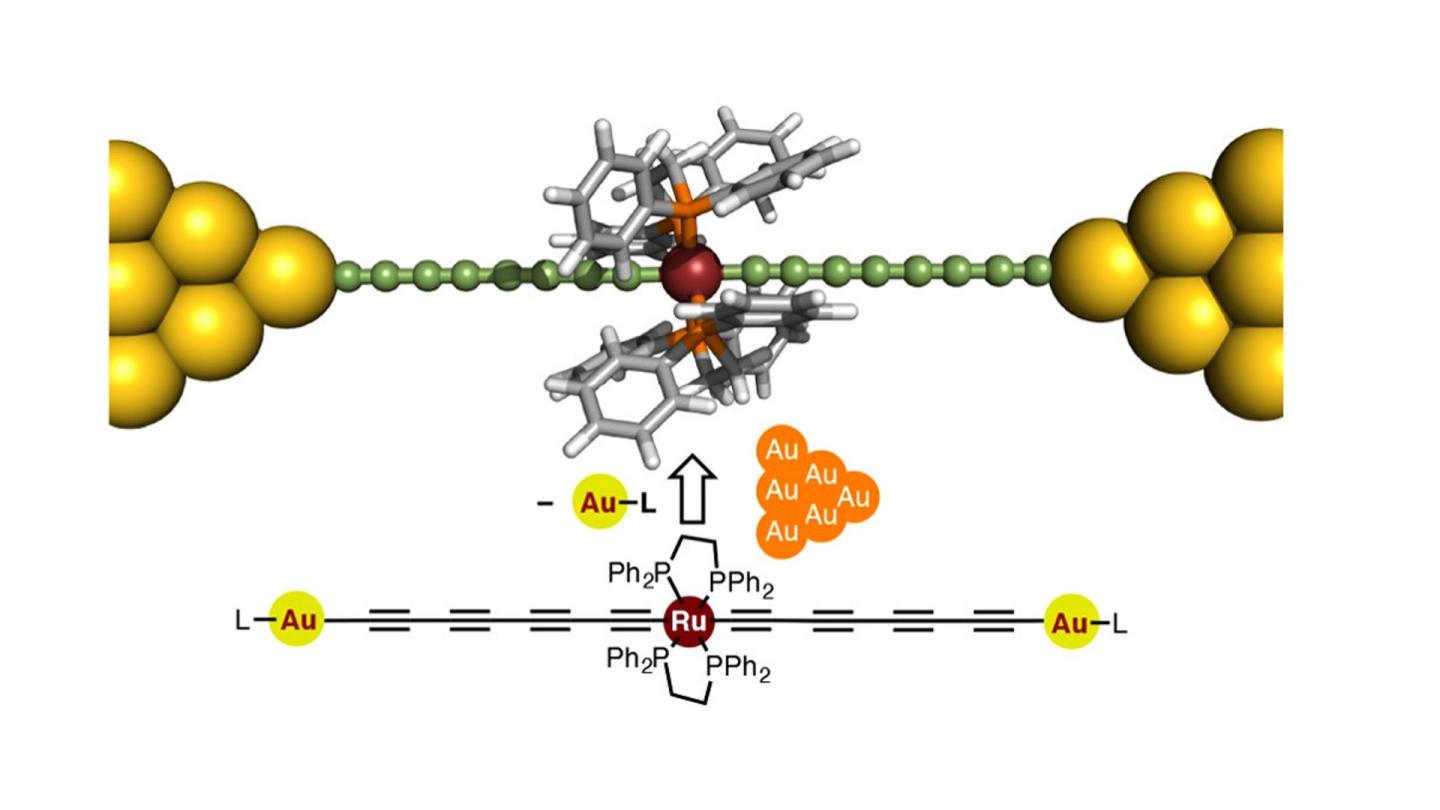
The proposed wire is ‘doped’ with a ruthenium unit that enhances its conductance to unprecedented levels compared with previously reported similar molecular wires. Credit: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology designed a new type of molecular wire doped with organometallic ruthenium to achieve unprecedentedly higher conductance than earlier molecular wires. The origin of high conductance in these wires is fundamentally different from similar molecular devices and suggests a potential strategy for developing highly conducting “doped” molecular wires.
Since their conception, researchers have tried to shrink electronic devices to unprecedented sizes, even to the point of fabricating them from a few molecules. Molecular wires are one of the building blocks of such minuscule contraptions, and many researchers have been developing strategies to synthesize highly conductive, stable wires from carefully designed molecules.
A team of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology, including Yuya Tanaka, designed a novel molecular wire in the form of a metal electrode-molecule-metal electrode (MMM) junction including a polyyne, an organic chain-like molecule, “doped” with a ruthenium-based unit Ru(dppe)2. The proposed design, featured in the cover of the Journal of the American Chemical Society, is based on engineering the energy levels of the conducting orbitals of the atoms of the wire, considering the characteristics of gold electrodes.
Using scanning tunneling microscopy, the team confirmed that the conductance of these molecular wires was equal to or higher than those of previously reported organic molecular wires, including similar wires “doped” with iron units. Motivated by these results, the researchers then went on to investigate the origin of the proposed wire’s superior conductance. They found that the observed conducting properties were fundamentally different from previously reported similar MMM junctions and were derived from orbital splitting. In other words, orbital splitting induces changes in the original electron orbitals of the atoms to define a new “hybrid” orbital facilitating electron transfer between the metal electrodes and the wire molecules. According to Tanaka, “such orbital splitting behavior has rarely been reported for any other MMM junction”.
Since a narrow gap between the highest and lowest occupied molecular orbitals is a crucial factor for enhancing conductance of molecular wires, the proposed synthesis protocol adopts a new technique to exploit this knowledge, as Tanaka adds “The present study reveals a new strategy to realize molecular wires with an extremely narrow gap via MMM junction formation.”
This explanation for the fundamentally different conducting properties of the proposed wires facilitate the strategic development of novel molecular components, which could be the building blocks of future minuscule electronic devices.