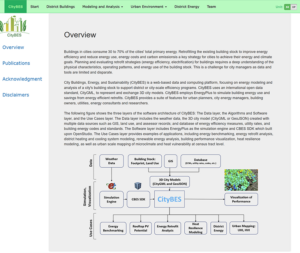
 Buildings generate 39% of global CO2 emissions. Decarbonizing the building sector and improving the climate resilience of buildings are essential to the global clean economy. However, evaluating and prioritizing cost-effective technical solutions for individual buildings at city scale poses a significant challenge for city stakeholders. City Buildings, Energy and Sustainability (CityBES), developed by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, is a powerful tool that helps users address this challenge. This innovative, easy, and free-to-use powerful modeling and analysis tool enables quick and quantitative assessments of actionable recommendations for decarbonizing buildings and improving their thermal resilience against extreme weather at the urban scale. CityBES builds upon open city datasets, international data standards, the powerful EnergyPlus engine, a library of 104 mitigation measures, and 3D-GIS visualization to inform decision-making on city buildings, energy, and sustainability. It also can be integrated with other urban analysis tools through its API. Its potential for carbon reductions is substantial — in U.S. cities alone, it can provide energy efficiency and decarbonization pathways to save 3.994 quads of annual primary energy and reduce 591 million metric tons of CO2 emission.
Buildings generate 39% of global CO2 emissions. Decarbonizing the building sector and improving the climate resilience of buildings are essential to the global clean economy. However, evaluating and prioritizing cost-effective technical solutions for individual buildings at city scale poses a significant challenge for city stakeholders. City Buildings, Energy and Sustainability (CityBES), developed by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, is a powerful tool that helps users address this challenge. This innovative, easy, and free-to-use powerful modeling and analysis tool enables quick and quantitative assessments of actionable recommendations for decarbonizing buildings and improving their thermal resilience against extreme weather at the urban scale. CityBES builds upon open city datasets, international data standards, the powerful EnergyPlus engine, a library of 104 mitigation measures, and 3D-GIS visualization to inform decision-making on city buildings, energy, and sustainability. It also can be integrated with other urban analysis tools through its API. Its potential for carbon reductions is substantial — in U.S. cities alone, it can provide energy efficiency and decarbonization pathways to save 3.994 quads of annual primary energy and reduce 591 million metric tons of CO2 emission.




Tell Us What You Think!