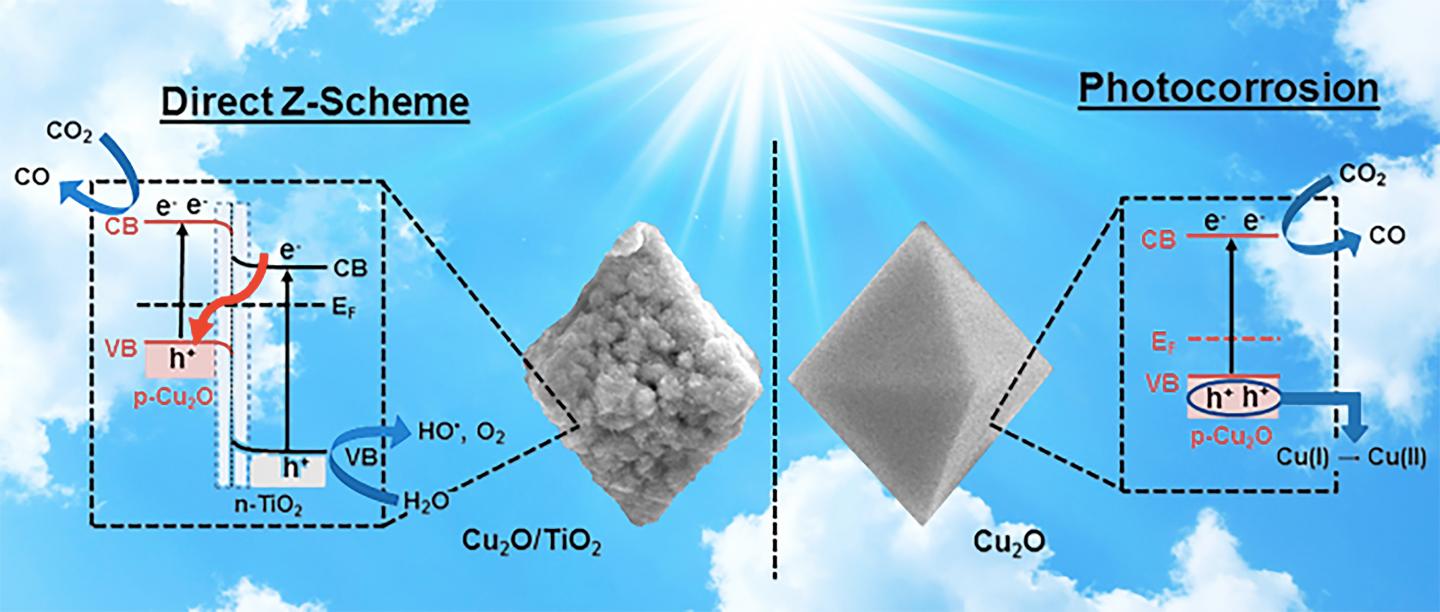
This is the Cu2O (right) that gets photocorrosion compared to Cu2O/TiO2 (left) that operates under a Z-scheme to reduce CO2. Credit: Ruixin Zhou, UK doctoral student of chemistry.
A team of chemists from the University of Kentucky and the Institute of Physics Research of Mar del Plata in Argentina has just reported a way to trigger a fundamental step in the mechanism of photosynthesis, providing a process with great potential for developing new technology to reduce carbon dioxide levels.
Led by Marcelo Guzman, an associate professor of chemistry in the UK College of Arts and Sciences, and Ruixin Zhou, a doctoral student working with Guzman, the researchers used a synthetic nanomaterial that combines the highly reducing power of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) with a coating of oxidizing titanium dioxide (TiO2) that prevents the loss of copper (I) ion in the catalyst. The catalyst made of Cu2O/TiO2 has the unique ability to transfer electrons for reducing the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) while simultaneously breaking the molecule of water (H2O). The unique feature of this catalyst for electron transfer mimics the so called “Z-scheme” mechanism from photosynthesis.
Published in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, the researchers demonstrated that if the catalyst is exposed to sunlight, electrons are transferred to CO2 in a process that resembles the way photosystems 1 and 2 operate in nature.
“Developing the materials that can be combined to reduce CO2 through a direct Z-scheme mechanism with sunlight is an important problem,” said Zhou. “However, it is even more difficult to demonstrate the process actually works. From this scientific viewpoint, the research is contributing to advance feature technology for carbon sequestration.”
This is a task that many scientists have been pursuing for a long time but the challenge is to prove that both components of the catalyst interact to enable the electronic properties of a Z-scheme mechanism. Although a variety of materials may be used, the key aspect of this research is that the catalyst is not made of scarce and very expensive elements such as rhenium and iridium to drive the reactions with sunlight energy reaching the Earth’s surface. The catalyst employed corrosion resistant TiO2 to apply a white protective coating to octahedral particles of red Cu2O.
The team designed a series of experiments to test out the hypothesis that the catalyst operates through a Z-scheme instead of using a double-charge transfer mechanism. The measured carbon monoxide (CO) production from CO2 reduction, the identification of hydroxyl radical (HO* ) intermediate from H2O oxidation en route to form oxygen (O2), and the characterized electronic and optical properties of the catalyst and individual components verified the proposed Z-scheme was operational.
The next goal of the research is to improve the approach by exploring a series of different catalysts and identify the most efficient one to transform CO2 into chemical fuels such as methane. This way, new technology will be created to supply clean and affordable alternative energy sources and to address the problem of continuous consumption of fossil fuels and rising levels of greenhouse gases.



