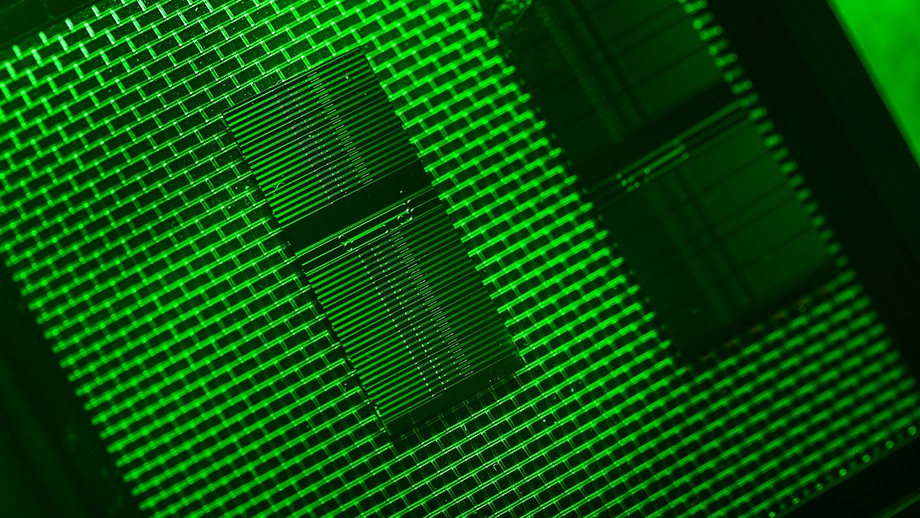
The new telescope chip. Source: Stuart Hay, ANU
Scientists have developed a new optical chip for a telescope that enables astronomers to have a clear view of alien planets that may support life.
Seeing a planet outside the solar system which is close to its host sun, similar to Earth, is very difficult with today’s standard astronomical instruments due to the brightness of the sun.
Associate Professor Steve Madden from The Australian National University (ANU) said the new chip removes light from the host sun, allowing astronomers for the first time to take a clear image of the planet.
“The ultimate aim of our work with astronomers is to be able to find a planet like Earth that could support life,” said Dr Madden from the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
“To do this we need to understand how and where planets form inside dust clouds, and then use this experience to search for planets with an atmosphere containing ozone, which is a strong indicator of life.”
Physicists and astronomers at ANU worked on the optical chip with researchers at the University of Sydney and the Australian Astronomical Observatory.
Dr Madden said the optical chip worked in a similar way to noise cancelling headphones.
“This chip is an interferometer that adds equal but opposite light waves from a host sun which cancels out the light from the sun, allowing the much weaker planet light to be seen,” he said.
PhD student Harry-Dean Kenchington Goldsmith, who built the chip at the ANU Laser Physics Centre, said the technology works like thermal imaging that fire fighters rely on to see through smoke.
“The chip uses the heat emitted from the planet to peer through dust clouds and see planets forming. Ultimately the same technology will allow us to detect ozone on alien planets that could support life,” said Mr Kenchington Goldsmith from the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
The innovation builds on over 10 years of research on specialised optical materials and devices that has been supported through CUDOS, a centre of excellence funded by the Australian Research Council.
The research is being presented at the Australian Institute of Physics Congress in Brisbane this week.