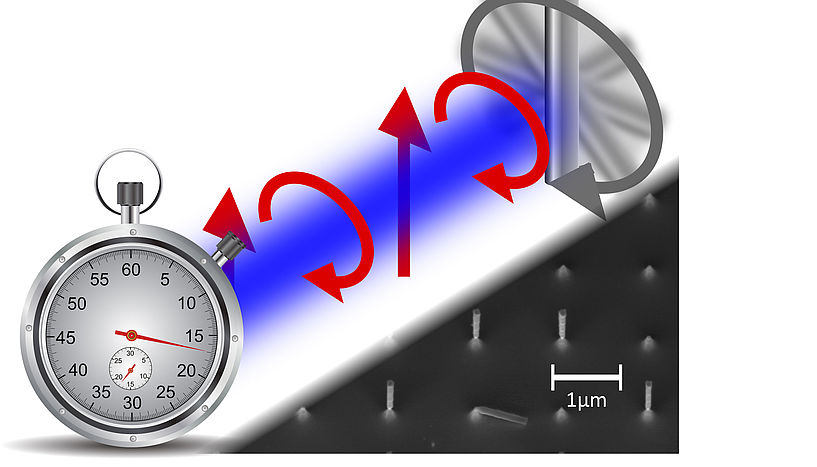
An international team of researches from the Universities of Vienna, Duisburg-Essen and Tel Aviv use tiny silicon nano-cylinders as the ultra-stable hands of a clock. Using a laser to levitate the tiny rod, they make the nano-hands tick with pulses of polarized light. Image: James Millen/University of Vienna
Tick … tock…
Very regular clocks are essential in our everyday lives. They enable us to navigate, from the marine chronometers used to determine longitude, to GPS. Stable clocks power the Internet, defining the speed with which information can be sent and received.
If your timepiece is very precise, it is easy to detect even small changes to its regularity. By measuring the motion of a physical object which is keeping time, such as the pendulum of a grandfather clock, and comparing it to an electronic reference, then we can detect disturbances, such as vibrations of the case.
In research published in Nature Communications, Stefan Kuhn at the University of Vienna and col-leagues have created an amazingly stable, material hand for an electronic clock, realized by the rotations of a micrometer-sized silicon cylinder, which is levitated by light. The team use the clock to kick the tiny rotor with pulses of polarized light, causing it to spin one million times a second.
“It is amazing that we can take an electronic signal, and use it to perfectly drive the motion of a physical object, without any loss of stability. Our clock only lost one-millionth of a second over four days,” says co-author James Millen. Other such tiny mechanical devices are limited in precision through contact with their environment, but when levitated the nano-rotor remains extremely stable for very long times.
Preparing such nanomechanical devices relies on the art of making pristine silicon pillars on a chip, as done in the group of Fernando Patolsky at Tel Aviv University. The Vienna team uses a “laser hammer” to knock out individual rods and traps them in tweezers made of light.
Describing the ensuing dynamics is a theoretical challenge that has been solved by the theoretical physicists Benjamin Stickler and Klaus Hornberger at the University of Duisburg-Essen. The motion of the spinning nano-rod is chaotic, a behavior also found in weather patterns and road traffic. This may not sound promising for technological application, but it is possible to find islands of calm in the chaos, where the ticking of the nano-hands of the clock become ultra-stable.
The ticking of a material, rather than electronic, clock is very sensitive to its environment. This highly accurate, tiny hand of a watch can be used to precisely measure properties of the world on the nanoscale, for instance pressure variations over sub-millimeter distances. The levitated cylinder could be moved through a gas flow to measure turbulence, or through a beam of atoms or light to discern its properties.
It may one day even be possible to use this method to test the limits of quantum physics: “At high rotation rates, this is an environmental sensor of stunning precision. At low frequencies it can open a new range of experiments on the quantum mechanics of rotation,” says Markus Arndt.
Source: University of Vienna




