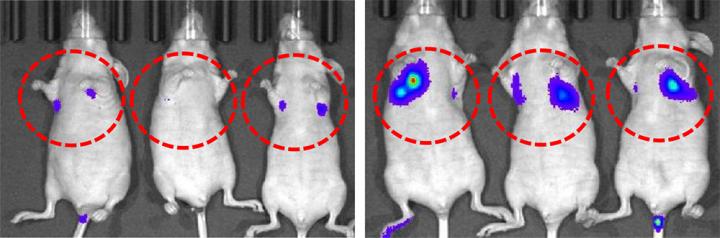
TRIM29 knockdown increases the metastatic potential of human squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). SCC cells were injected to mice with (right) or without (left) knocking down TRIM29 gene. Images were taken 23 days after the injection. Credit: Yanagi T. et al., Cancer Research, November 2, 2018
Loss of a protein called TRIM29 promotes cancer cell invasion in a common type of skin cancer, suggesting a novel diagnostic marker and a possible therapeutic target.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a common type of skin cancer, usually affecting skin that is exposed to the damaging ultraviolet rays of the sun. A protein that normally helps repair DNA, called TRIM29, is also involved in cancers of the breast, pancreas, prostate, lungs, bladder and stomach. Its role in squamous cell carcinoma, however, was unknown until now.
A research team led by dermatologist Teruki Yanagi and Professor Shigetsugu Hatakeyama at Hokkaido University found that human squamous carcinoma cells with lower levels of TRIM29 were more mobile and invasive, and thus correlated with a worse prognosis. This study was published in Cancer Research.
TRIM29 expression was highest in normal skin cells. It was lower in squamous cell carcinomas, and even lower in tumors that metastasized, migrating from the main cancer site to other parts of the body, such as the lungs. The researchers also determined that turning off the gene made the cancer cells more mobile and invasive, both in cell cultures and mice.
Interestingly, they found that TRIM29 interacts with another protein inside cells called keratin, which plays numerous roles in forming a protective structural framework within cells and also in cell motility and signalling.
When TRIM29 levels are normal in a cell, it makes sure keratin is widely distributed within the cytoplasm. On the other hand, when TRIM29 levels are low, keratin distributes mainly around the cell nucleus, resulting in altered cell shapes.
Previous studies had shown that TRIM29 suppressed breast and prostate cancer development, because the protein is spread throughout the cytoplasm in these types of cells. But it promoted development of pancreatic, lung, bladder and stomach cancers, where it is localized in the nucleus. In skin cells, TRIM29 is normally positioned throughout the cytoplasm, reinforcing its protective role in suppressing skin cancer.
“Our findings suggest that TRIM29 could be a novel diagnostic and prognostic marker in squamous cell cancers common in skin, neck and head. The TRIM-29/keratin interaction could also be a therapeutic target for treating advanced and metastatic squamous cell cancers,” says Teruki Yanagi.




