The potential for photon entanglement in quantum computing and communications has been known for decades. One of the issues impeding its immediate application is the fact that many photon entanglement platforms do not operate within the range used by most forms of telecommunication. An international team of researchers has started to unravel the mysteries of…
Enhancing the Sensing Capabilities of Diamonds With Quantum Properties
Pure diamond consists of carbon atoms in a perfect crystal lattice. But remove a few carbons and swap some others for nitrogen, and you get a diamond with special quantum-sensing properties. These properties are useful for quantum information applications and sensing magnetic fields, and as a platform for probing the mysteries of quantum physics. When…
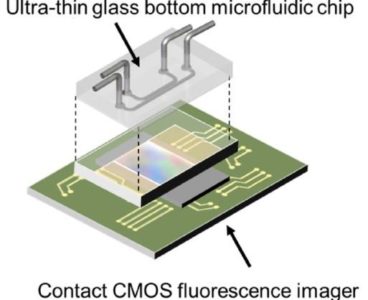
Fluorescence Microscopy On a Chip – No Lenses Required
Fluorescence microscopy gives researchers incredible power to illuminate the tiniest structures and capture the real-time activities of live cells by tagging biological molecules with a veritable rainbow of fluorescent dyes. This power comes at a cost: The technology can be expensive and time-consuming and, so far, has resisted attempts at automation. This situation may be…
Nanosensor Uses Torque for Signal Processing
The world of nanosensors may be physically small, but the demand is large and growing, with little sign of slowing. As electronic devices get smaller, their ability to provide precise, chip-based sensing of dynamic physical properties such as motion become challenging to develop. An international group of researchers have put a literal twist on this…
High-Tech Electronics Made From Autumn Leaves
Bond Dissociation Energies for Transition Metal Silicides Accurately Determined
Nanotechnology Gives Green Energy a Green Color
Solar panels have tremendous potential to provide affordable renewable energy, but many people see traditional black and blue panels as an eyesore. Architects, homeowners and city planners may be more open to the technology if they could install green panels that melt into the landscape, red panels on rooftops and white ones camouflaged as walls.…
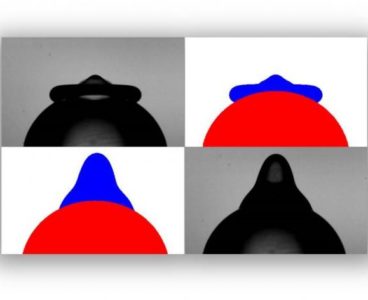
Researchers Study Dynamics of Drop Impact
For the most part, fluid dynamics researchers have focused efforts to understand the details of impacting drops on flat rigid surfaces; the effect of curved, convex or compliant surfaces on the dynamics of impacting drops is still relatively unknown. This is despite its extreme relevance to modern-day applications, such as 3-D ink-jet printing and the…
Bioprinted Veins Reveal New Drug Diffusion Details
Pulses of Electrons Manipulate Nanomagnets and Store Information
Thinking Thin Brings New Layering and Thermal Abilities to the Semiconductor Industry
What would a simple technique to remove thin layers from otherwise thick, rigid semiconductor crystals mean for the semiconductor industry? This concept has been actively explored for years, as integrated circuits made on thin layers hold promise for developments including improved thermal characteristics, lightweight stackability and a high degree of flexibility compared to conventionally thick…
Strange Silk: Why Rappelling Spiders Don’t Spin Out of Control
Getting the Biggest Bang Out of Plasma Jets
Atomic Structure of Irradiated Materials is More Akin to Liquid than Glass
Materials exposed to neutron radiation tend to experience significant damage, leading to the containment challenges involved in immobilizing nuclear waste or nuclear plant confinements. At the nanoscale, these incident neutrons collide with a material’s atoms that, in turn, then collide with each other somewhat akin to billiards. The resulting disordered atomic network and its physical…
Laser-Controlled Touch Displays on the Horizon
Characters in some of the more futuristic science fiction films, like Minority Report and Iron Man, control computer displays with slick and deliberate hand motions. In Minority Report, the protagonist, played by Tom Cruise, uses gloves that glow at the fingertips and give him the power of virtual manipulation. The light seems to allow him to control the…
How Fluids Flow Through Shale
Most of the world’s oil and natural gas reserves may be locked up inside the tiny pores comprising shale rock. But current drilling and fracturing methods can’t extract this fuel very well, recovering only an estimated 5 percent of oil and 20 percent of gas from shale. That’s partly due to a poor understanding of…
‘GAMERS’ Method Creates Unique 4D Molecular Spectral Maps
Researchers at Northwestern University have created a new method to extract the static and dynamic structure of complex chemical systems. In this context, “structure” doesn’t just mean the 3-D arrangement of atoms that make up a molecule, but rather time-dependent quantum-mechanical degrees of freedom that dictate the optical, chemical and physical properties of the system.…
Putting a Spin on Logic Gates
Computer electronics are shrinking to small-enough sizes that the very electrical currents underlying their functions can no longer be used for logic computations in the ways of their larger-scale ancestors. A traditional semiconductor-based logic gate called a majority gate, for instance, outputs current to match either the “0” or “1” state that comprise at least…
‘Going Deep’ to Measure Earth’s Rotational Effects
Researchers in Italy hope to measure Earth’s rotation using a laser-based gyroscope housed deep underground, with enough experimental precision to reveal measurable effects of Einstein’s general theory of relativity. The ring laser gyroscope (RLG) technology enabling these Earth-based measurements provide, unlike those made by referencing celestial objects, inertial rotation information, revealing fluctuations in the rotation…
Smoothing Thin Film Surfaces Improves Electronics
Surface roughness reduction is a really big deal when it comes to fundamental surface physics and while fabricating electronic and optical devices. As transistor dimensions within integrated circuits continue to shrink, smooth metallic lines are required to interconnect these devices. If the surfaces of these tiny metal lines aren’t smooth enough, it substantially reduces their…
Sunlight, Heat, and Movement Simultaneously Turn into Electricity
Many forms of energy surround you: sunlight, the heat in your room and even your own movements. All that energy — normally wasted — can potentially help power your portable and wearable gadgets, from biometric sensors to smart watches. Now, researchers from the University of Oulu in Finland have found that a mineral with the…
Zeroing in on The True Nature of Fluids with Nanocappillaries
Shrinking the investigation of objects down to the nanometer scale often reveals new properties of matter that have no equivalent for their bulk analysis. This phenomenon is motivating many current studies of nanomaterials which can reveal fascinating new phenomena. It inspired a group of researchers at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) to…
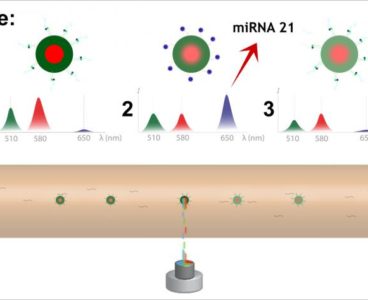
Detection System Reads Biomolecules in Barcoded Microgels
Single-stranded, noncoding micro-ribonucleic acids (microRNAs), consisting of 18-23 nucleotides, play a key role in regulating gene expression. Levels of microRNAs circulating within blood can be correlated to different states of diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and cardiovascular conditions. Many microRNAs within the blood are encapsulated within exosomes, nanoscale vesicles released by the cells. Accurate…
Lab-on-a-Chip Provides Easier Cancer Biomarker Detection
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the U.S., making early, reliable diagnosis and treatment a priority for researchers. Genomic biomarkers offer great potential for diagnostics and new forms of treatment, such as immunotherapy. Miniaturized lab-on-chip approaches are prime candidates for developing viable diagnostic tests and instruments because they are small, need only…
Blocks of Ice Demonstrate Levitated & Directed Motion
Resembling the Leidenfrost effect seen in rapidly boiling water droplets, a disk of ice becomes highly mobile due to a levitating layer of water between it and the smooth surface on which it rests and melts. The otherwise random rotation and translation (sliding) of the ice block can be directed by controlling the flow dynamics…