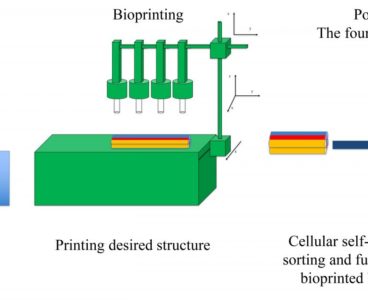
3D printers can be used to make a variety of useful objects by building up a shape, layer by layer. Scientists have used this same technique to “bioprint” living tissues, including muscle and bone. Bioprinting is a relatively new technology that has advanced mostly by trial and error. Scientists are now using the laws of…
Autonomous Weed Control Via Smart Robots
Discovery Opens the Door to Better Magnetic Field Sensors
Magnetic field sensors can enhance applications that require efficient electric energy management. Improving magnetic field sensors below the picoTesla range could enable a technique to measure brain activity at room temperature with millisecond resolution — called magnetic encephalography — without superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) technology, which requires cryogenic temperatures to work. A group of…
Scientists Unravel the Mysteries of Polymer Strands in Fuel Cells
Reservoir Computer Marks Revolutionary Neural Network Application
As artificial intelligence has become increasingly sophisticated, it has inspired renewed efforts to develop computers whose physical architecture mimics the human brain. One approach, called reservoir computing, allows hardware devices to achieve the higher-dimension calculations required by emerging artificial intelligence. One new device highlights the potential of extremely small mechanical systems to achieve these calculations.…
New Memristor Boosts Accuracy and Efficiency for Neural Networks on an Atomic Scale
New Model Helps Define Optimal Temperature and Pressure to Forge Nanoscale Diamonds
Nanodiamonds, bits of crystalline carbon hundreds of thousands of times smaller than a grain of sand, have intriguing surface and chemical properties with potential applications in medicine, optoelectronics and quantum computing. To forge these nanoscopic gemstones, researchers expose organic explosive molecules to powerful detonations in a controlled environment. These explosive forces, however, make it difficult…
Novel Use of NMR Sheds Light on Easy-to-Make Electropolymerized Catalysts
A New Brain-Inspired Architecture Could Improve How Computers Handle Data and Advance AI
IBM researchers are developing a new computer architecture, better equipped to handle increased data loads from artificial intelligence. Their designs draw on concepts from the human brain and significantly outperform conventional computers in comparative studies. They report on their recent findings in the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing. Today’s computers are built on…
A ‘Recipe Book’ that Creates Color Centers in Silicon Carbide Crystals
Silicon carbide (SiC), a material known for its toughness with applications from abrasives to car brakes, to high-temperature power electronics, has enjoyed renewed interest for its potential in quantum technology. Its ability to house optically excitable defects, called color centers, has made it a strong candidate material to become the building block of quantum computing.…
Researchers Challenge our Assumptions on the Effects of Planetary Rotation
The earth’s rotation causes the Coriolis effect, which deflects massive air and water flows toward the right in the Northern Hemisphere and toward the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This phenomenon greatly impacts global wind patterns and ocean currents, and is only significant for large-scale and long-duration geophysical phenomena such as hurricanes. The magnitude of…
Method to Determine Oxidative Age Could Show How Aging Affects Nanomaterial’s Properties
Iron oxide nanoparticles are used in sentinel node detection, iron replacement therapy and other biomedical applications. New work looks to understand how these materials age, and how aging may change their functional or safety profiles. For the first time, by combining lab-based Mössbauer spectroscopy with “center of gravity” analysis, researchers can quantify the diffusive oxidation…
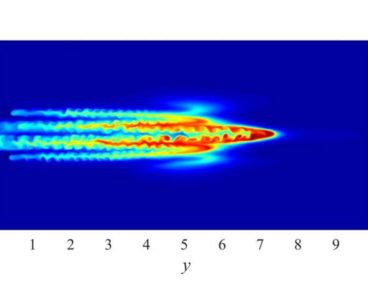
Separating the Sound from the Noise in Hot Plasma Fusion
In the search for abundant clean energy, scientists around the globe look to fusion power, where isotopes of hydrogen combine to form a larger particle, helium, and release large amounts of energy in the process. For fusion power plants to be effective, however, scientists must find a way to trigger the low-to-high confinement transition, or…
Carbon Nanodots do an Ultrafine Job With In Vitro Lung Tissue
Epidemiological studies have established a strong correlation between inhaling ultrafine particles from incomplete combustion and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Still, relatively little is known about the mechanisms behind how air particulates affect human health. New work with carbon nanodots seeks to provide the first model of how ultrafine carbon-based particles interact with the lung tissues.…
Researchers Develop a New Method to Detect Nucleation
Lasers Blast Tiny Craters into Glass
Modern communication systems often employ optical fibers to carry signals across or between devices. The integrated optics in these devices combine more than one function into a single circuit. However, signal transmission requires long optical fibers, which makes it difficult to miniaturize the device. Instead of long optical fibers, scientists have started testing planar waveguides.…
Blasting Tiny Craters in Glass, Creating Material to Miniaturize Telecommunication Devices
Modern communication systems often employ optical fibers to carry signals across or between devices. The integrated optics in these devices combine more than one function into a single circuit. However, signal transmission requires long optical fibers, which makes it difficult to miniaturize the device. Instead of long optical fibers, scientists have started testing planar waveguides.…
Computer Model Predicts How Fracturing Metallic Glass Releases Energy at the Atomic Level
Metallic glasses — alloys lacking the crystalline structure normally found in metals — are an exciting research target for tantalizing applications, including artificial joints and other medical implant devices. However, the difficulties associated with predicting how much energy these materials release when they fracture is slowing down development of metallic glass-based products. Recently, a pair…
Underlying Mechanism Discovered for Magnetic Effect in Superconducting Spintronics
The emerging field of spintronics leverages electron spin and magnetization. This could enhance the storage capacity of computer hard drives and potentially play an important role in quantum computing’s future. Superconductor-ferromagnet (SF) structures are widely regarded as the building blocks of this superconducting spintronic technology. More conventional spintronic devices typically require large currents, so researchers…
Newly Discovered Properties of Ferroelectric Crystal Shed Light on Branch of Materials
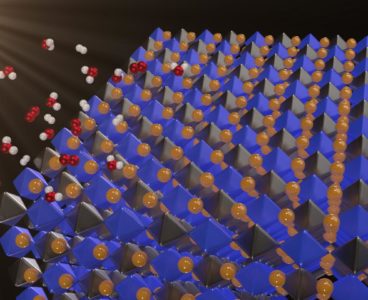
Water Does the Splits
Solar energy is clean and abundant. But when the sun isn’t shining, you must store the energy in batteries or through a process called photocatalysis — in which solar energy is used to make fuels. In photocatalytic water splitting, sunlight separates water into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen can then be recombined in…
New Material For Splitting Water
Solar energy is clean and abundant. But when the sun isn’t shining, you must store the energy in batteries or through a process called photocatalysis — in which solar energy is used to make fuels. In photocatalytic water splitting, sunlight separates water into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen can then be recombined in…
Microbubbles Delivered Via Gas Embolotherapy Could Provide a Vehicle For Cutting Off Blood Supply and Delivering Drugs
Embolization—the use of various techniques to cut off the blood vessels that feed tissue growth—has gained traction over the past few decades to treat cancerous tumors. This method of starving tumors of blood supply and nutrients is less invasive than surgery and typically involves injecting drugs (chemoembolization) or lodging nanoscopic beads directly into blood vessels.…
Nanomaterials Clear the Way for Next-Generation Computing
Nanoscientists at Northwestern University have developed a blueprint to fabricate new heterostructures from different types of 2-D materials. 2-D materials are single atom layers that can be stacked together like “nano-interlocking building blocks.” Materials scientists and physicists are excited about the properties of 2-D materials and their potential applications. The researchers describe their blueprint in…
Nanorobots Assemble World’s Smallest House, Too Tiny for a Mite
A French nanorobotics team from the Femto-ST Institute in Besançon, France, assembled a new microrobotics system that pushes forward the frontiers of optical nanotechnologies. Combining several existing technologies, the µRobotex nanofactory builds microstructures in a large vacuum chamber and fixes components onto optical fiber tips with nanometer accuracy. The microhouse construction, reported in the Journal…