Brown University researchers have made a discovery about the way things stick together at tiny scales that could be helpful in engineering micro- and nanoscale devices. In a series of papers, the latest of which is published in Scientific Reports, the researchers show that miniscule differences in the roughness of a surface can cause surprising…
Graphene Crinkles Function as ‘Molecular Zippers’
A decade ago, scientists noticed something very strange happening when buckyballs—soccer ball shaped carbon molecules—were dumped onto a certain type of multilayer graphene, a flat carbon nanomaterial. Rather than rolling around randomly like marbles on a hardwood floor, the buckyballs spontaneously assembled into single-file chains that stretched across the graphene surface. Now, researchers from Brown…
Huge New Dark Matter Detector Receives its ‘Eyes’
The LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) dark matter detector, which will soon start its search for the elusive particles thought to account for a majority of matter in the universe, had the first of its “eyes” delivered late last week. The first of two large arrays of photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) — powerful light sensors that can detect the…
Researchers Create New ‘Smart’ Material With Potential Biomedical, Environmental Uses
Brown University researchers have shown a way to use graphene oxide (GO) to add some backbone to hydrogel materials made from alginate, a natural material derived from seaweed that’s currently used in a variety of biomedical applications. In a paper published in the journal Carbon, the researchers describe a 3-D printing method for making intricate and…
New, Durable Catalyst for Key Fuel Cell Reaction May Prove Useful in Eco-Friendly Vehicles
One factor holding back the widespread use of eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cells in cars, trucks and other vehicles is the cost of the platinum catalysts that make the cells work. One approach to using less precious platinum is to combine it with other cheaper metals, but those alloy catalysts tend to degrade quickly in fuel…
Brown Researchers Teach Computers to See Optical Illusions
Is that circle green or gray? Are the center lines straight or tilted? Optical illusions can be fun to experience and debate, but understanding how human brains perceive these different phenomena remains an active area of scientific research. For one class of optical illusions, called contextual phenomena, those perceptions are known to depend on context.…
Research Identifies Key Weakness in Modern Computer Vision Systems
Computer vision algorithms have come a long way in the past decade. They’ve been shown to be as good or better than people at tasks like categorizing dog or cat breeds, and they have the remarkable ability to identify specific faces out of a sea of millions. But research by Brown University scientists shows that…
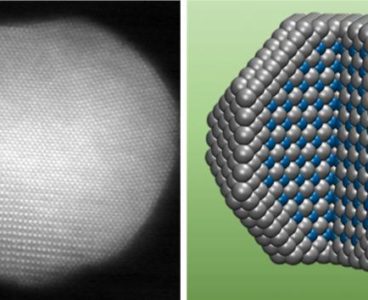
Researchers Find New Molecular Structures in Boron-Based Nanoclusters
Brown University researchers and collaborators from Tsinghua University in China have shown that nanoclusters made from boron and lanthanide elements form highly stable and symmetric structures with interesting magnetic properties. The findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that these nanoclusters may be useful as molecular magnets or assembled into magnetic…
Graphene Crinkles Up to Carry an Electric Charge
Researchers from Brown University have discovered another peculiar and potentially useful property of graphene, one-atom-thick sheets of carbon, that could be useful in guiding nanoscale self-assembly or in analyzing DNA or other biomolecules. A study published in Proceedings of the Royal Society A demonstrates mathematically what happens to stacks of graphene sheets under slight lateral…
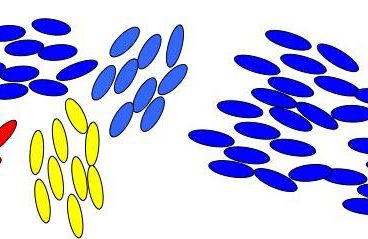
Research Reveals How Order First Appears in Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystals undergo a peculiar type of phase change. At a certain temperature, their cigar-shaped molecules go from a disordered jumble to a more orderly arrangement in which they all point more or less in the same direction. LCD televisions take advantage of that phase change to project different colors in moving images. For years,…
Projectile Cannon Experiments Show How Asteroids Can Deliver Water
Experiments using a high-powered projectile cannon show how impacts by water-rich asteroids can deliver surprising amounts of water to planetary bodies. The research, by scientists from Brown University, could shed light on how water got to the early Earth and help account for some trace water detections on the Moon and elsewhere. “The origin and…
New Theory Shows how Strain Makes for Better Catalysts
Brown University researchers have developed a new theory to explain why stretching or compressing metal catalysts can make them perform better. The theory, described in the journal Nature Catalysis, could open new design possibilities for new catalysts with new capabilities. Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions. The vast majority of industrial catalysis involves…
ADHD Drugs Increase Brain Glutamate, Predict Positive Emotion in Healthy People
A new study shows that healthy people who take attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) drugs experience a surge in the neurotransmitter glutamate in key parts of the brain. And that increase in glutamate is associated with subsequent changes in positive emotion. The findings, published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology, not only provide clues about how these drugs…
New Stickiness Measuring Technique Helps Micro-Device Design
Brown University engineers have devised a new method of measuring the stickiness of micro-scale surfaces. The technique, described in Proceedings of the Royal Society A, could be useful in designing and building micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS), devices with microscopic moving parts. At the scale of bridges or buildings, the most important force that engineered structures need…
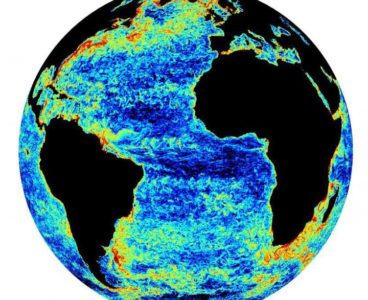
New Understanding of Ocean Turbulence Could Improve Climate Models
Brown University researchers have made a key insight into how high-resolution ocean models simulate the dissipation of turbulence in the global ocean. Their research, published in Physical Review Letters, could be helpful in developing new climate models that better capture ocean dynamics. The study was focused on a form of turbulence known as mesoscale eddies,…
Researchers Discover New Lead-Free Perovskite Material for Solar Cells
A class of materials called perovskites has emerged as a promising alternative to silicon for making inexpensive and efficient solar cells. But for all their promise, perovskites are not without their downsides. Most contain lead, which is highly toxic, and include organic materials that are not particularly stable when exposed to the environment. Now a…
Researchers Help Robots Think and Plan in the Abstract
Researchers from Brown University and MIT have developed a method for helping robots plan for multi-step tasks by constructing abstract representations of the world around them. Their study, published in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, is a step toward building robots that can think and act more like people. Planning is a monumentally difficult…
Gravitational Waves Could Shed Light on the Origin of Black Holes
Nanoscale Patterning Cuts Down on Metal Fatigue
A new study in the journal Nature shows how metals can be patterned at the nanoscale to be more resistant to fatigue, the slow accumulation of internal damage from repetitive strain. The research focused on metal manufactured with nanotwins, tiny linear boundaries in a metal’s atomic lattice that have identical crystalline structures on either side.…
New Research Suggests Mercury’s Poles Are Icier Than Scientists Thought
The scorching hot surface of Mercury seems like an unlikely place to find ice, but research over the past three decades has suggested that water is frozen on the first rock from the sun, hidden away on crater floors that are permanently shadowed from the sun’s blistering rays. Now, a new study led by Brown…
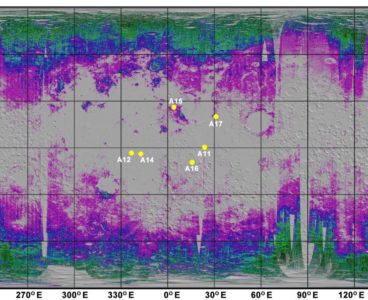
Researchers Create First Global Map of Water in Moon’s Soil
In research that may prove useful to future lunar explorers, scientists from Brown University have created the first quantitative map of water and its chemical building blocks trapped in the uppermost portion of the Moon’s soil. The study, published in Science Advances, builds on the initial discovery in 2009 of water and a related molecule — hydroxyl, which…
Brown Awarded $1.5M to Establish Data Science Research Institute
– Less than one year after launching its Data Science Initiative (DSI), Brown University has been awarded a $1.5 million grant by the National Science Foundation to establish a new research institute aimed at developing mathematical and computational tools for data-driven discovery. Brown’s award is one of 12 nationwide Transdisciplinary Research in Principles of Data Science…
3D Printed Biomaterials Degrade on Demand
Brown University engineers have demonstrated a technique for making 3-D-printed biomaterials that can degrade on demand, which can be useful in making intricately patterned microfluidic devices or in making cell cultures than can change dynamically during experiments. “It’s a bit like Legos,” said Ian Wong, an assistant professor in Brown’s School of Engineering and co-author…
Researchers Develop 3-D-printed Biomaterials That Degrade on Demand
Brown University engineers have demonstrated a technique for making 3-D-printed biomaterials that can degrade on demand, which can be useful in making intricately patterned microfluidic devices or in making cell cultures than can change dynamically during experiments. “It’s a bit like Legos,” said Ian Wong, an assistant professor in Brown’s School of Engineering and co-author…
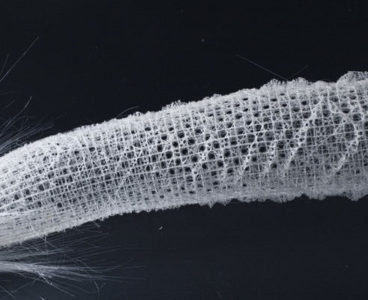
Bendy Glass Lets These Sea Sponges Hang Tight
Sea sponges known as Venus’ flower baskets remain fixed to the sea floor with nothing more than an array of thin, hair-like anchors that are essentially glass. A new study suggests it’s the internal architecture of those anchors, known as basalia spicules, that helps them to do it. The spicules, each about half the diameter…