New Polymer Films Conduct Heat Instead of Trapping It
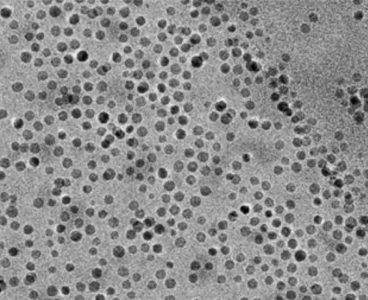
Polymers are usually the go-to material for thermal insulation. Think of a silicone oven mitt, or a Styrofoam coffee cup, both manufactured from polymer materials that are excellent at trapping heat. Now MIT engineers have flipped the picture of the standard polymer insulator, by fabricating thin polymer films that conduct heat — an ability normally…
Shrinking the Carbon Footprint of a Chemical in Everyday Objects
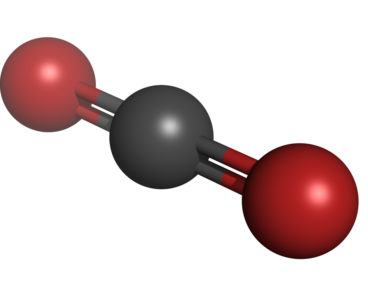
The biggest source of global energy consumption is the industrial manufacturing of products such as plastics, iron, and steel. Not only does manufacturing these materials require huge amounts of energy, but many of the reactions also directly emit carbon dioxide as a byproduct. In an effort to help reduce this energy use and the related…
Greener, More Efficient Natural Gas Filtration
Engineers Develop Concept For Hybrid Heavy-Duty Trucks
New Approach Could Boost Energy Capacity of Lithium Batteries
‘Particle Robot’ Works as a Cluster of Simple Units
Taking a cue from biological cells, researchers from MIT, Columbia University, and elsewhere have developed computationally simple robots that connect in large groups to move around, transport objects, and complete other tasks. This so-called “particle robotics” system — based on a project by MIT, Columbia Engineering, Cornell University, and Harvard University researchers — comprises many…
Kicking Neural Network Automation Into High Gear
A new area in artificial intelligence involves using algorithms to automatically design machine-learning systems known as neural networks, which are more accurate and efficient than those developed by human engineers. But this so-called neural architecture search (NAS) technique is computationally expensive. A state-of-the-art NAS algorithm recently developed by Google to run on a squad of…
Lobster’s Underbelly is as Tough as Industrial Rubber
Using Artificial Intelligence to Engineer Materials’ Properties
Tiny Satellites Could be ‘Guide Stars’ for Huge Next-Generation Telescopes
Sun-Soaking Device Turns Water into Superheated Steam
MIT engineers have built a device that soaks up enough heat from the sun to boil water and produce “superheated” steam hotter than 100 degrees Celsius, without any expensive optics. On a sunny day, the structure can passively pump out steam hot enough to sterilize medical equipment, as well as to use in cooking and…
Technique Inspired by Dolphin Chirps Could Improve Tests of Soft Materials
LIGO and Virgo Announce Four New Gravitational-Wave Detections
On Saturday, December 1, scientists attending the Gravitational Wave Physics and Astronomy Workshop in College Park, Maryland, presented new results from the National Science Foundation’s LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) and the European- based VIRGO gravitational-wave detector regarding their searches for coalescing cosmic objects, such as pairs of black holes and pairs of neutron stars.…
A New Way to Provide Cooling Without Power
Machine-Learning System Could Aid Critical Decisions in Sepsis Care
Chemical Synthesis Could Produce More Potent Antibiotics
Using a novel type of chemical reaction, MIT researchers have shown that they can modify antibiotics in a way that could potentially make them more effective against drug-resistant infections. By chemically linking the antibiotic vancomycin to an antimicrobial peptide, the researchers were able to dramatically enhance the drug’s effectiveness against two strains of drug-resistant bacteria.…
How to Mass Produce Cell-Sized Robots
Tiny robots no bigger than a cell could be mass-produced using a new method developed by researchers at MIT. The microscopic devices, which the team calls “syncells” (short for synthetic cells), might eventually be used to monitor conditions inside an oil or gas pipeline, or to search out disease while floating through the bloodstream. The…
Inexpensive Chip-Based Device may Transform Spectrometry
Spectrometers — devices that distinguish different wavelengths of light and are used to determine the chemical composition of everything from laboratory materials to distant stars — are large devices with six-figure price tags, and tend to be found in large university and industry labs or observatories. A new advance by researchers at MIT could make…
Machine-Learning Model Provides Risk Assessment for Complex Nonlinear Systems, Including Boats and Offshore Platforms
MIT Announces $1B Commitment to the Study of Computing and AI
MIT today announced a new $1 billion commitment to address the global opportunities and challenges presented by the prevalence of computing and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). The initiative marks the single largest investment in computing and AI by an American academic institution, and will help position the United States to lead the world…
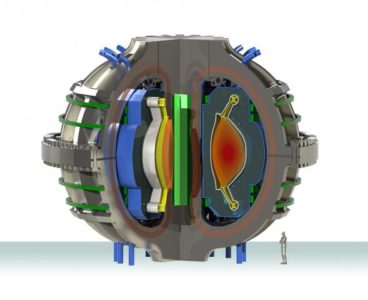
A New Path to Solving a Longstanding Fusion Challenge
A class exercise at MIT, aided by industry researchers, has led to an innovative solution to one of the longstanding challenges facing the development of practical fusion power plants: how to get rid of excess heat that would cause structural damage to the plant. The new solution was made possible by an innovative approach to…
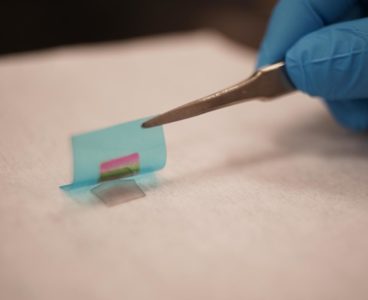
Study Opens Route to Flexible Electronics Made From Exotic Materials
The vast majority of computing devices today are made from silicon, the second most abundant element on Earth, after oxygen. Silicon can be found in various forms in rocks, clay, sand, and soil. And while it is not the best semiconducting material that exists on the planet, it is by far the most readily available.…
Chemists Discover Unexpected Enzyme Structure
Software Finds the Best Way to Stick a Mars Landing
Selecting a landing site for a rover headed to Mars is a lengthy process that normally involves large committees of scientists and engineers. These committees typically spend several years weighing a mission’s science objectives against a vehicle’s engineering constraints, to identify sites that are both scientifically interesting and safe to land on. For instance, a…