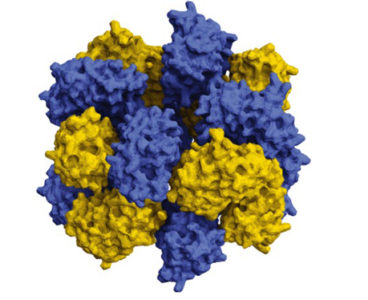
Red blood cells are amazing. They pick up oxygen from our lungs and carry it all over our body to keep us alive. The hemoglobin molecule in red blood cells transports oxygen by changing its shape in an all-or-nothing fashion. Four copies of the same protein in hemoglobin open and close like flower petals, structurally coupled to…
Supercomputers Help Design Mutant Enzyme That Eats Plastic Bottles
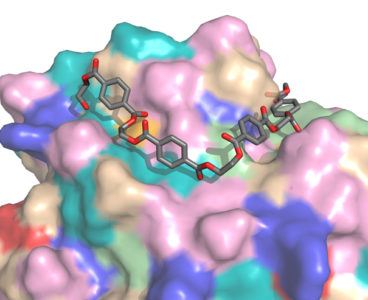
A dump truck’s worth of plastic empties into the ocean every minute. Worldwide, humankind produces over 300 million tons of plastic each year, much of which is predicted to last centuries to millennia and pollutes both aquatic and terrestrial environments. PET plastic, short for polyethylene terephthalate, is the fourth most-produced plastic and is used to…
An AI Oncologist to Help Cancer Patients Worldwide
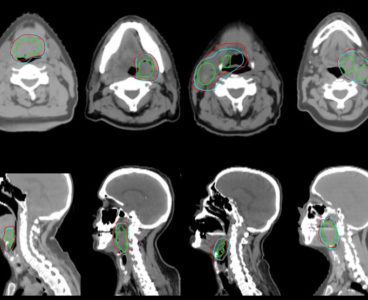
Before performing radiation therapy, radiation oncologists first carefully review medical images of the patient to identify the gross tumor volume, the observable portion of the disease. They then design patient-specific clinical target volumes that include surrounding tissues, since these regions can hide cancerous cells and provide pathways for metastasis. Known as contouring, this process establishes…
TACC Builds Seamless Software for Scientific Innovation
Big, impactful science requires a whole technological ecosystem to progress. This includes cutting-edge computing systems, high-capacity storage, high-speed networks, power, cooling… the list goes on and on. Critically, it also requires state-of-the-art software: programs that work together seamlessly to allow scientists and engineers to answer tough questions, share their solutions, and conduct research with the…
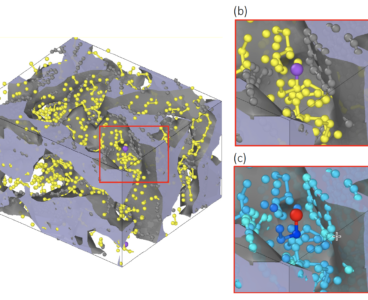
Overcoming a Battery’s Fatal Flaw
As renewable energy grows as a power source around the world, one key component still eludes the industry: large-scale, stable, efficient and affordable batteries. Lithium-ion batteries have proven successful for consumer electronics, but electric vehicles, wind turbines or smart grids require batteries with far greater energy capacity. A leading contender is the lithium-metal battery, which…
TACC, Lamont Observatory of Columbia University Host One of the Largest Earth Sciences Data Collections in the Country
The Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) at The University of Texas at Austin is partnering with the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) at Columbia University to host one of the largest data collections for Earth sciences of its type in the country. The data relates to the Ross Ice Shelf, a massive slab of floating ice that…
Supercomputing More Light Than Heat
Solar cells can’t stand the heat. Photovoltaics lose some energy as heat in converting sunlight to electricity. The reverse holds true for lights made with light-emitting diodes (LED), which convert electricity into light. Some scientists think there might be light at the end of the tunnel in the hunt for better semiconductor materials for solar…
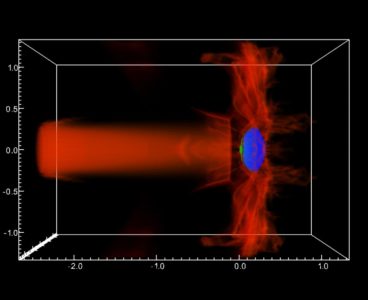
Cosmos Code Helps Probe Space Oddities
Black holes make for a great space mystery. They’re so massive that nothing, not even light, can escape a black hole once it gets close enough. A great mystery for scientists is that there’s evidence of powerful jets of electrons and protons that shoot out of the top and bottom of some black holes. Yet…
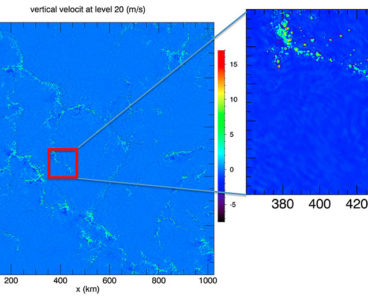
Anticipating Aftershocks
Cloud Computing Testbed Chameleon Renewed for Second Phase
Cloud computing lies behind many of today’s most popular technologies, from streaming video and music to e-mail and chat services to storing and sharing family photos. Since 2015, the Chameleon testbed has helped researchers push the potential of cloud computing even further, finding novel scientific applications and improving security and privacy. A new grant from the National Science Foundation…
More Precise Diagnostics for Improved Cancer Outcomes
An important factor in fighting cancer is the speed at which the disease can be identified, diagnosed and treated. The current standard involves a patient feeling ill or a physician seeing signs of a tumor. These indicators lead to more precise diagnoses via blood tests, x-rays or MRI imaging. But once the disease is far…
A New Paradigm for Training in Advanced Computing
The Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) has a long, rich history of providing training in advanced computing to researchers and students on and off The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin) campus. From the beginning, TACC has taught the basics of high performance computing (HPC) and scientific visualization. One of the center’s goals has…
Reaching for the Stormy Cloud With Chameleon
Some scientists dream about big data. The dream bridges two divided realms. One realm holds lofty peaks of number-crunching scientific computation. Endless waves of big data analysis line the other realm. A deep chasm separates the two. Discoveries await those who cross these estranged lands. Unfortunately, data cannot move seamlessly between Hadoop (HDFS) and parallel…
Targeted, High-Energy Cancer Treatments Get a Supercomputing Boost
Radiation therapy shoots high-energy particles into the body to destroy or damage cancer cells. Over the last century, the technologies used have constantly improved and it has become a highly effective way to treat cancer. However, physicians must still walk a fine line between delivering enough radiation to kill tumors, while sparing surrounding healthy tissue.…
New Hikari Supercomputer Starts Solar HDVC
The roar can be deafening. Cooling fans and power supplies whoosh and whine from rows and rows of supercomputers at the main data center of the Texas Advanced Computing Center in Austin. The power bill at TACC can reach over a million dollars a year to keep the machines humming. But there’s a stranger in…