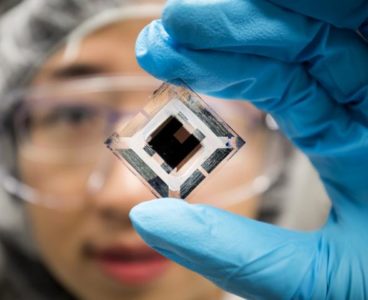
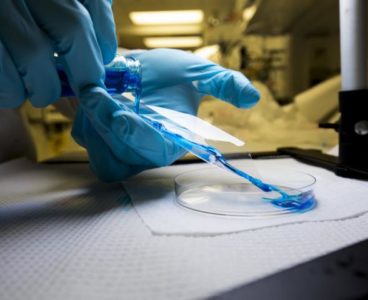
A prototype wearable device, tested in animal models, can continuously collect live cancer cells directly from a patient’s blood. Developed by a team of engineers and doctors at the University of Michigan, it could help doctors diagnose and treat cancer more effectively. “Nobody wants to have a biopsy. If we could get enough cancer cells…
Researchers Confirm Massive Hyper-Runaway Star Ejected From the Milky Way Disk
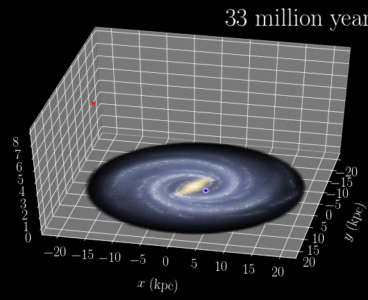
A fast-moving star may have been ejected from the Milky Way’s stellar disk by a cluster of young stars, according to researchers from the University of Michigan who say the star did not originate from the middle of the galaxy, as previously believed by astronomers. “This discovery dramatically changes our view on the origin of…
Running an LED in Reverse Could Cool Future Computers
Toward Brain-like Computing: New Memristor Better Mimics Synapses
A new electronic device developed at the University of Michigan can directly model the behaviors of a synapse, which is a connection between two neurons. For the first time, the way that neurons share or compete for resources can be explored in hardware without the need for complicated circuits. “Neuroscientists have argued that competition and…
Revealing Hidden Information in Sound Waves
Laser Device Sniffs Out Gas in Under a Second
University of Michigan researchers have refined a gas-sniffing device so that it can detect poisonous gases and explosives in less than half a second. The laser-based method could be used as a security device in airports or to monitoring for pollutants or toxins in the environment. The physicists’ findings build upon a method they developed…
Fewer Biofuels, More Green Space: Climate Action Researcher Calls for Urgent Shift
Battery Breakthrough: Doubling Performance With Lithium Metal That Doesn’t Catch Fire
A rechargeable battery technology developed at the University of Michigan could double the output of today’s lithium ion cells–drastically extending electric vehicle ranges and time between cell phone charges–without taking up any added space. By using a ceramic, solid-state electrolyte, engineers can harness the power of lithium metal batteries without the historic issues of poor…
Big-Data Study Pinpoints More Than 150 Genes Associated With Atrial Fibrillation
How Even One Automated, Connected Vehicle Can Improve Safety and Save Energy in Traffic
Artificial Photosynthesis Creates Clean Hydrogen Fuel
A new, stable artificial photosynthesis device doubles the efficiency of harnessing sunlight to break apart both fresh and salt water, generating hydrogen that can then be used in fuel cells. The device could also be reconfigured to turn carbon dioxide back into fuel. Hydrogen is the cleanest-burning fuel, with water as its only emission. But…
Semiconductor Computers Could Be a Million Times Faster
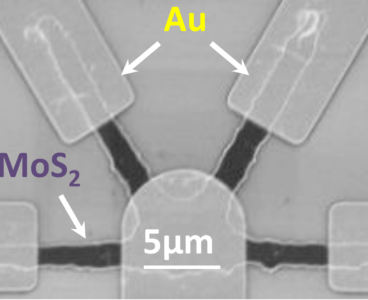
A technique to manipulate electrons with light could bring quantum computing up to room temperature. A team of researchers in Germany and at the University of Michigan have demonstrated how infrared laser pulses can shift electrons between two different states, the classic 1 and 0, in a thin sheet of semiconductor. “Ordinary electronics are in…
Harvesting Clean Hydrogen Fuel Through Artificial Photosynthesis
A new, stable artificial photosynthesis device doubles the efficiency of harnessing sunlight to break apart both fresh and salt water, generating hydrogen that can then be used in fuel cells. The device could also be reconfigured to turn carbon dioxide back into fuel. Hydrogen is the cleanest-burning fuel, with water as its only emission. But…
Organic Solar Cells Reach Record Efficiency, Benchmark for Commercialization
In an advance that makes a more flexible, inexpensive type of solar cell commercially viable, University of Michigan researchers have demonstrated organic solar cells that can achieve 15 percent efficiency. This level of efficiency is in the range of many solar panels, or photovoltaics, currently on the market. “Organic photovoltaics can potentially cut way down…
‘Everything-Repellent’ Coating Could Kidproof Phones, Homes
In an advance that could grime-proof phone screens, countertops, camera lenses and countless other everyday items, a materials science researcher at the University of Michigan has demonstrated a smooth, durable, clear coating that swiftly sheds water, oils, alcohols and, yes, peanut butter. Called “omniphobic” in materials science parlance, the new coating repels just about every…
Semiconductor Breakthrough May be Game-Changer for Organic Solar Cells
Semiconductor Discovery is Game-Changer for Organic Solar Cells
In an advance that could push cheap, ubiquitous solar power closer to reality, University of Michigan researchers have found a way to coax electrons to travel much further than was previously thought possible in the materials often used for organic solar cells and other organic semiconductors. “For years, people had treated the poor conductivity of…
Nanoparticle Gel Uses Magnetism to Control Twisted Light
“Help me, Obi Wan Kenobi. You’re my only hope.” For many of those around at the release of Star Wars in 1977, that scene was a first introduction to holograms — a real technology that had been around for roughly 15 years. So why aren’t holograms or related optical devices part of our everyday lives…
A Shoebox-Sized Chemical Detector
Nanodiscs Catch Misfolding Proteins in the Act
When proteins misfold, accumulate and clump around insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, they kill cells. Now, researchers, including University of Michigan biophysicists, have obtained a structural snapshot of these proteins when they are most toxic, detailing them down to the atomic level. The researchers hope this kind of detail can help in the search for…
Nanofibers Used to Create Kevlar-Based Artificial Cartilage
The unparalleled liquid strength of cartilage, which is about 80 percent water, withstands some of the toughest forces on our bodies. Synthetic materials couldn’t match it — until “Kevlartilage” was developed by researchers at the University of Michigan and Jiangnan University. “We know that we consist mostly of water — all life does — and…
Nanoparticles Provide Distraction to Limit Immune System Inflammation
A surprise finding suggests that an injection of nanoparticles may be able to help fight the immune system when it goes haywire, researchers at the University of Michigan have shown. The nanoparticles divert immune cells that cause inflammation away from an injury site. Inflammation is a double-edged sword. When it works, it helps the body…