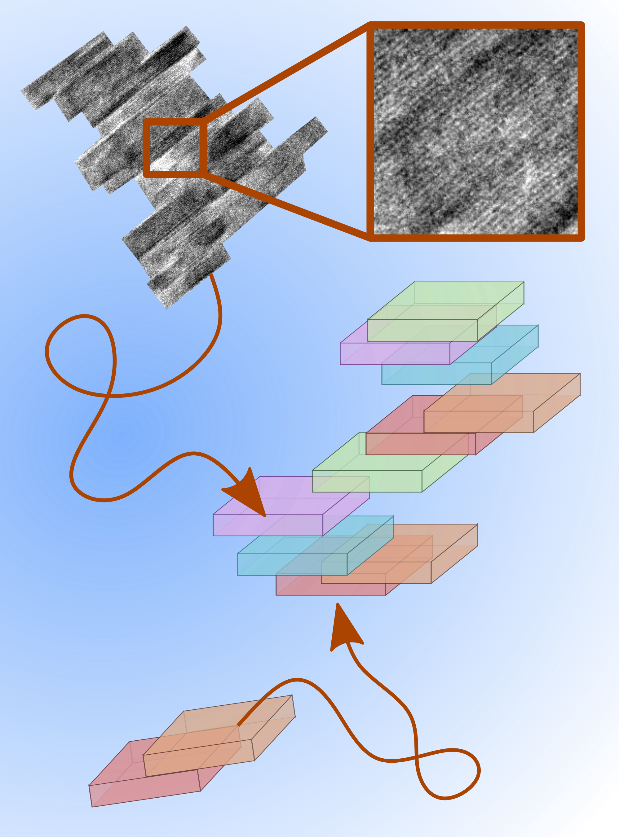
Scheme of transport and aggregation of boehmite nanoplatelets. Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy shows platelet stacks that align and merge into single crystals.
Particles in solution can grow, transport, collide, interact, and aggregate into complex shapes and structures. Predicting the outcome of these events is very challenging, especially for irregularly shaped particles in extreme solution conditions.
New research from scientists at the Interfacial Dynamics in Radioactive Environments and Materials (IDREAM) Energy Frontier Research Center has found that aluminum oxyhydroxide (boehmite) nanoplatelets align and attach to form neatly ordered stacks, a novel findings that involved both experimental and computational research.
The work, led by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory scientists in collaboration with scientists at Washington State University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was featured in ACS Nano in a paper titled, “Impact of Solution Chemistry and Particle Anisotropy on the Collective Dynamics of Oriented Aggregation.”
The study provides key details on the structure and dynamics of boehmite platelets in salt solutions at high pH, conditions relevant to high-level radioactive waste such as that found at Hanford nuclear site.
When nanocrystal stacks were placed in salt solutions at high pH, they aggregated rapidly into larger microstructures. These platelet stacks further aggregate at rates that increase with pH and [NaNO3], crossing from reaction-limited to diffusion-limited regimes. To help explain this behavior, the researchers calculated the transport properties of nanoplatelets, specifically their rotational and translational modes of motion. Calculations of translational/rotational diffusivities and colloidal stability ratios demonstrated importance of considering irregular particle shapes.
Monte Carlo simulations connected the shape of the seed nanoparticles to the structure and growth behavior of the emerging aggregates. Moreover, the researchers determined that platelets interact differently at edges, faces, or corners, which complicates the use of typical models based on spherical particles. These results are important steps towards a predictive understanding of nanoparticle transport and aggregation that will solve problems in geochemistry, biology, materials science, and beyond.
These new insights into the growth, assembly, and aggregation for boehmite and other aluminum bearing systems will inform the development of predictive models applied to process control schemes.




