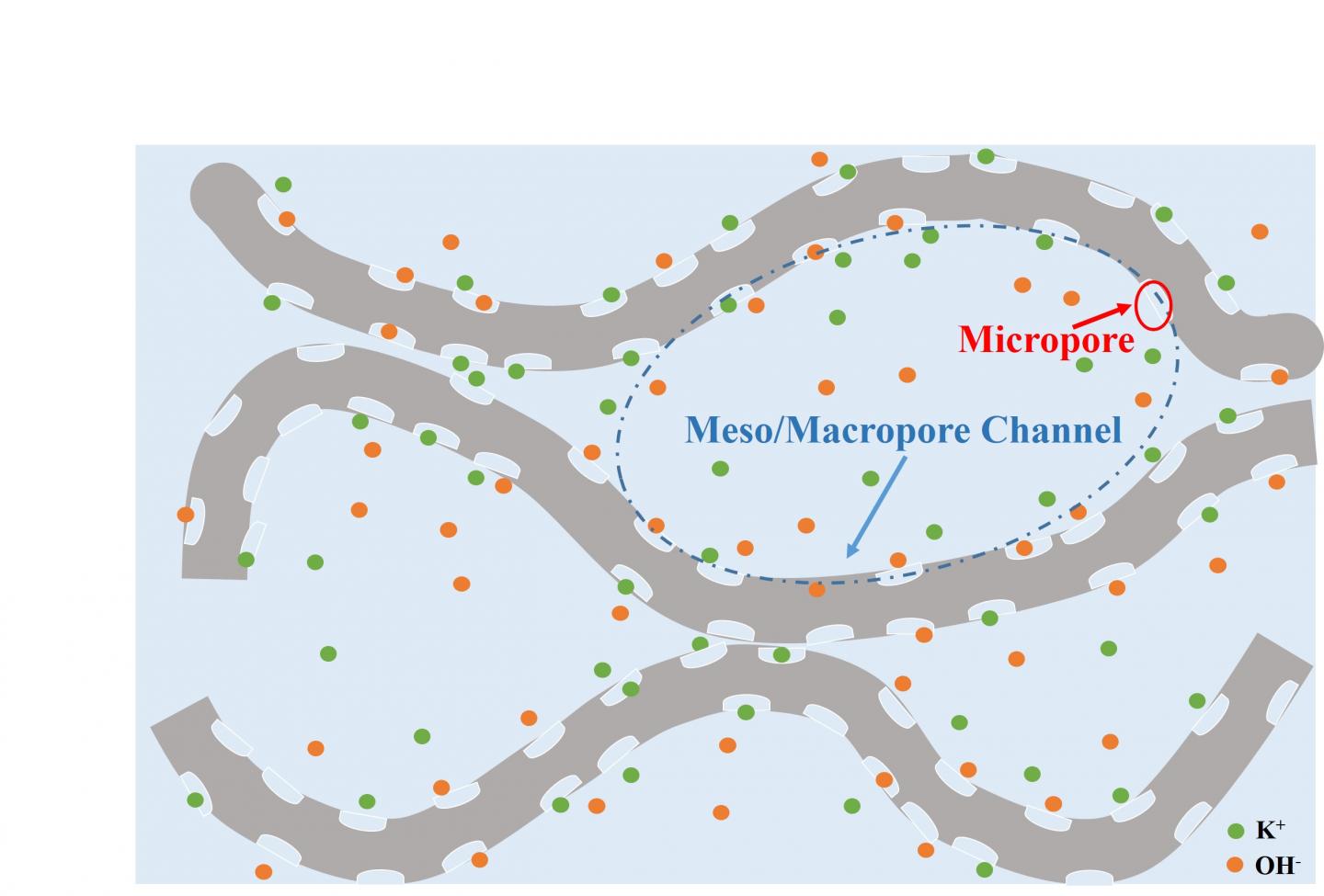
The folds of 3-D graphene make mesopore channels that work with the surface’s micropores to increase the material’s supercapacitive properties. Credit: Yun Hang Hu/Michigan Tech
Tiny dents in the surface of graphene greatly enhances its potential as a supercapacitor. Even better, it can be made from carbon dioxide.
A material scientist at Michigan Technological University invented a novel approach to take carbon dioxide and turn it into 3-D graphene with micropores across its surface. The process is the focus of a new study published in the American Chemical Society’s Applied Materials & Interfaces.
The conversion of carbon dioxide to useful materials usually requires high energy input due to its ultrahigh stability. However, materials science professor Yun Hang Hu and his research team created a heat-releasing reaction between carbon dioxide and sodium to synthesize 3-D surface-microporous graphene.
“3-D surface-microporous graphene is a brand-new material,” Hu says, explaining the material’s surface is pockmarked with micropores and folds into larger mesopores, which both increase the surface area available for adsorption of electrolyte ions. “It would be an excellent electrode material for energy storage devices.”
Holey Supercapacitors
Basically, a supercapacitor material needs to store — and release — a charge. The limiting factor is how quickly ions can move through the material.
The supercapacitive properties of the unique structure of 3-D surface-microporous graphene make it suitable for elevators, buses, cranes and any application that requires a rapid charge/discharge cycle. Supercapacitors are an important type of energy storage device and have been widely used for regenerative braking systems in hybrid vehicles.
Current commercialized supercapacitors employ activated carbon using swaths of micropores to provide efficient charge accumulation. However, electrolyte ions have difficulty diffusing into or through activated carbon’s deep micropores, increasing the charging time.
“The new 3-D surface-microporous graphene solves this,” Hu says. “The interconnected mesopores are channels that can act as an electrolyte reservoir and the surface-micropores adsorb electrolyte ions without needing to pull the ions deep inside the micropore.”
The mesopore is like a harbor and the electrolyte ions are ships that can dock in the micropores. The ions don’t have to travel a great distance between sailing and docking, which greatly improves charge/discharge cycles they can steer through. As a result, the material exhibited an ultrahigh areal capacitance of 1.28 F/cm2, which is considered an excellent rate capability as well as superb cycling stability for supercapacitors.
From Thin Air
To synthesize the material from carbon dioxide, Hu’s team added carbon dioxide to sodium, followed by increasing temperature to 520 degrees Celsius. The reaction can release heat instead of require energy input.
During the process, carbon dioxide not only forms 3-D graphene sheets, but also digs the micropores. The tiny dents are only 0.54 nanometers deep in the surface layers of graphene.




