Although rechargeable batteries in smartphones, cars and tablets can be charged again and again, they don’t last forever. Old batteries often wind up in landfills or incinerators, potentially harming the environment. And valuable materials remain locked inside.
Now, a team of researchers is turning to naturally occurring fungi to drive an environmentally friendly recycling process to extract cobalt and lithium from tons of waste batteries.
“The idea first came from a student who had experience extracting some metals from waste slag left over from smelting operations,” says Jeffrey A. Cunningham, Ph.D., the project’s team leader. “We were watching the huge growth in smartphones and all the other products with rechargeable batteries, so we shifted our focus. The demand for lithium is rising rapidly, and it is not sustainable to keep mining new lithium resources,” he adds.
Although a global problem, the U.S. leads the way as the largest generator of electronic waste. It is unclear how many electronic products are recycled. Most likely, many head to a landfill to slowly break down in the environment or go to an incinerator to be burned, generating potentially toxic air emissions.
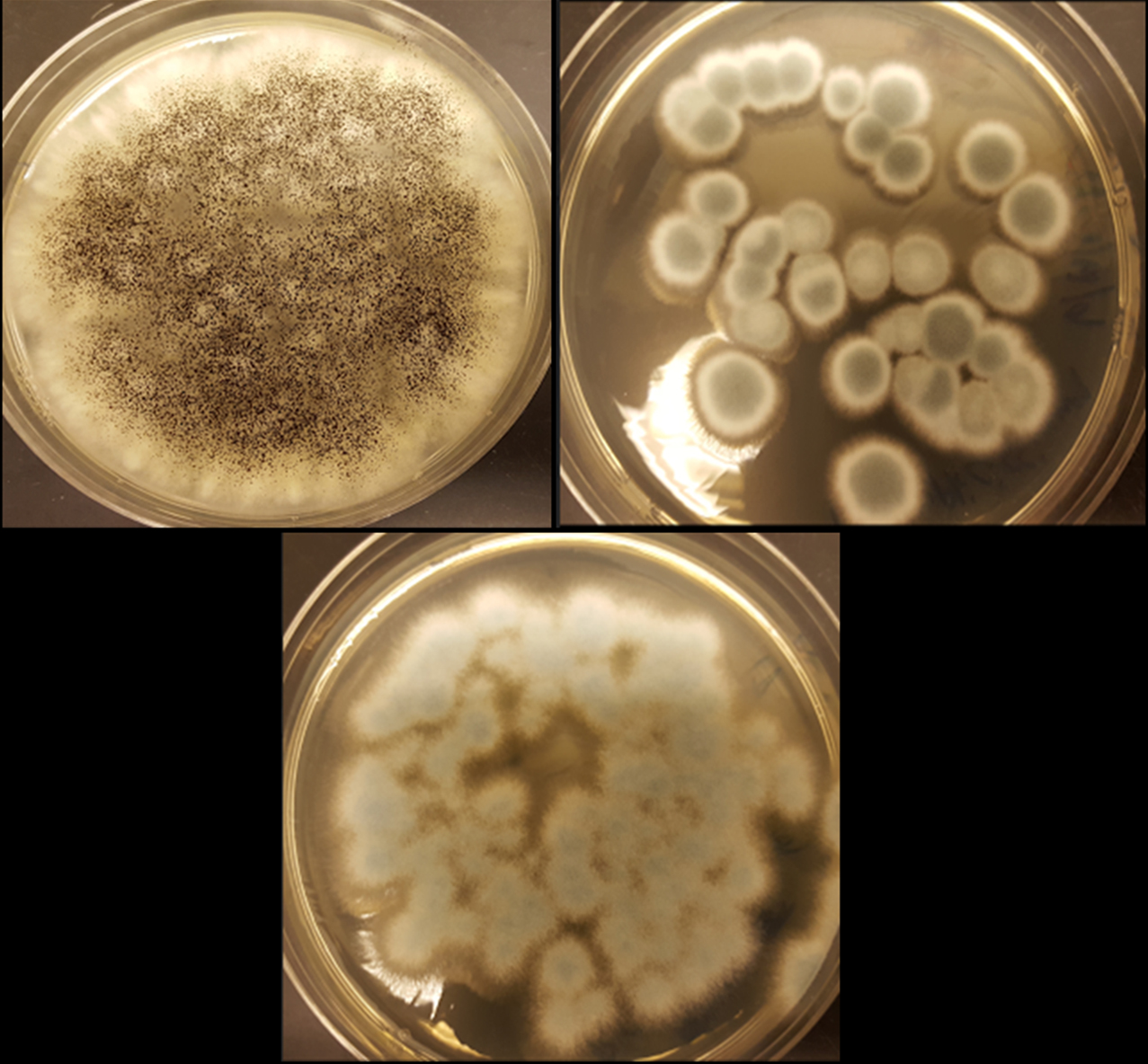
The fungi Aspergillus niger (top left), Penicillium simplicissimum (top right) and Penicillium chrysogenum (bottom) can recycle cobalt and lithium from rechargeable batteries. Image: Aldo Lobos
While other methods exist to separate lithium, cobalt, and other metals, they require high temperatures and harsh chemicals. Cunningham’s team is developing an environmentally safe way to do this with organisms found in nature — fungi in this case — and putting them in an environment where they can do their work. “Fungi are a very cheap source of labor,” he points out.
To drive the process, Cunningham and Valerie Harwood, Ph.D., both at the University of South Florida, are using three strains of fungi — Aspergillus niger, Penicillium simplicissimum, and Penicillium chrysogenum. “We selected these strains of fungi because they have been observed to be effective at extracting metals from other types of waste products,” Cunningham says. “We reasoned that the extraction mechanisms should be similar, and, if they are, these fungi could probably work to extract lithium and cobalt from spent batteries.”
The team first dismantles the batteries and pulverizes the cathodes. Then, they expose the remaining pulp to the fungus. “Fungi naturally generate organic acids, and the acids work to leach out the metals,” Cunningham explains. “Through the interaction of the fungus, acid and pulverized cathode, we can extract the valuable cobalt and lithium. We are aiming to recover nearly all of the original material.”
Results so far show that using oxalic acid and citric acid, two of the organic acids generated by the fungi, up to 85 percent of the lithium and up to 48 percent of the cobalt from the cathodes of spent batteries were extracted. Gluconic acid, however, was not effective for extracting either metal.
The cobalt and lithium remain in a liquid acidic medium after fungal exposure, Cunningham notes. Now his focus is on how to get the two elements out of that liquid.
“We have ideas about how to remove cobalt and lithium from the acid, but at this point, they remain ideas,” he says. “However, figuring out the initial extraction with fungi was a big step forward.”
Other researchers are also using fungi to extract metals from electronic scrap, but Cunningham believes his team is the only one studying fungal bioleaching for spent rechargeable batteries.
Cunningham, Harwood, and graduate student Aldo Lobos are now exploring different fungal strains, the acids they produce, and the acids’ efficiencies at extracting metals in different environments.
The team has received funding for this project from the National Science Foundation.
Source: American Chemical Society




