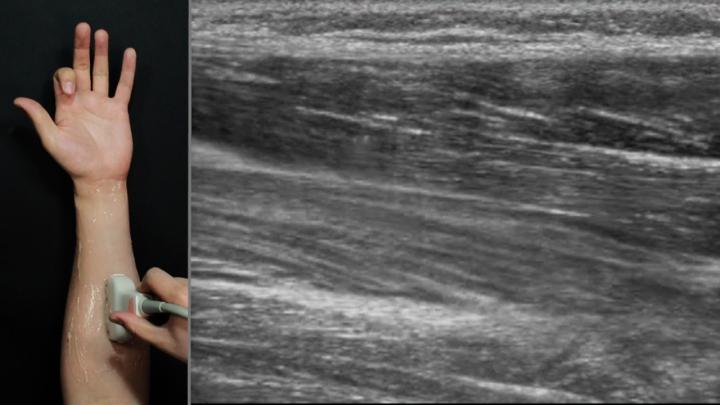
New research has shown future wearable devices, such as smartwatches, could use ultrasound imaging to sense hand gestures.
The research team led by Professor Mike Fraser, Asier Marzo and Jess McIntosh from the Bristol Interaction Group (BIG) at the University of Bristol, together with University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust (UH Bristol), presented their paper this summer [8-11 May] at one of the world’s most important conferences on human-computer interfaces, ACM CHI 2017 held in Denver, USA.
Computers are growing in number and wearable computers, such as smartwatches, are gaining popularity. Devices around the home, such as WiFi light bulbs and smart thermostats, are also on the increase. However, current technology limits the capability to interact with these devices.
Hand gestures have been suggested as an intuitive and easy way of interacting with and controlling smart devices in different surroundings. For instance, a gesture could be used to dim the lights in the living room, or to open or close a window. Hand gesture recognition can be achieved in many ways, but the placement of a sensor is a major restriction and often rules out certain techniques. However, with smartwatches becoming the leading wearable device this allows sensors to be put in the watch to sense hand movement.
The research team propose ultrasonic imaging of the forearm could be used to recognise hand gestures. Ultrasonic imaging is already used in medicine, such as pregnancy scans along with muscle and tendon movement, and the researchers saw the potential for this to be used as a way of understanding hand movement.
The team used image processing algorithms and machine learning to classify muscle movement as gestures. The researchers also carried out a user study to find the best sensor placement for this technique.
The team’s findings showed a very high recognition accuracy, and importantly this sensing method worked well at the wrist, which is ideal as it allows future wearable devices, such as smartwatches, to combine this ultrasonic technique to sense gestures.
Jess McIntosh, PhD student in the Department of Computer Science and BIG Group, said: “With current technologies, there are many practical issues that prevent a small, portable ultrasonic imaging sensor integrated into a smartwatch. Nevertheless, our research is a first step towards what could be the most accurate method for detecting hand gestures in smartwatches.”




