Advances in the technology of material growth allow fabricating sandwiches of materials with atomic precision. The interface between the two materials can sometimes exhibit physical phenomena which do not exist in both parent materials. For example, a magnetic interface found between two non-magnetic materials. A new discovery, published today in Nature Physics, shows a new way of controlling this emergent magnetism which may be the basis for new types of magnetic electronic devices.
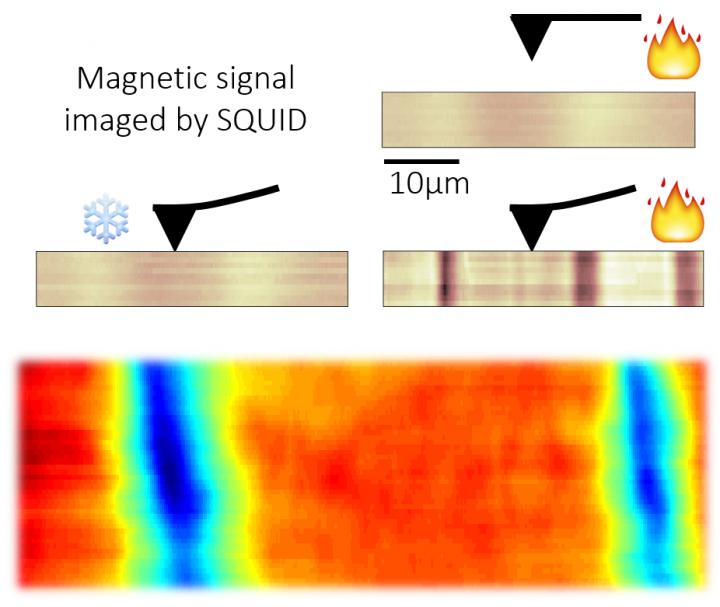
Using very sensitive magnetic probes, an international team of researchers led by Prof. Beena Kalisky, of Bar-Ilan University’s Department of Physics and Institute of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials (BINA), has found surprising evidence that magnetism which emerges at the interfaces between non-magnetic oxide thin layers can be easily tuned by exerting tiny mechanical forces. The team also includes Prof. Lior Klein, of Bar-Ilan’s Department of Physics and BINA, and researchers from DTU (Denmark) and Stanford University (USA).
Magnetism already plays a central role in storing the increasing amount of data produced by humanity. Much of our data storage today is based on tiny magnets crammed into our memory drive. One of the promising means in the race to improve memory, in terms of quantity and speed, is the use of smaller magnets. Until today the size of memory cells can be as small as a few tens of nanometers — almost a millionth of the width of a strand of hair! Further reduction in size is challenging in three main respects: the stability of the magnetic cell, the ability to read it, and the ability to write into it without affecting its neighboring cells. This recent discovery provides a new and unexpected handle to control magnetism, thus enabling denser magnetic memory.
These oxide interfaces combine a number of interesting physical phenomena, such as two-dimensional conductance and superconductivity. “Coexistence of physical phenomena is fascinating because they do not always go hand in hand. Magnetism and superconductivity, for example, are not expected to coexist,” says Kalisky. “The magnetism we saw did not extend throughout the material but appeared in well-defined areas dominated by the structure of the materials. Surprisingly, we discovered that the strength of magnetism can be controlled by applying pressure to the material”.
Coexistence between magnetism and conductivity has great technological potential. For example, magnetic fields can affect the current flow in certain materials and, by manipulating magnetism, we can control the electrical behavior of electronic devices. An entire field called Spintronics is dedicated to this subject. The discovery that tiny mechanical pressures can effectively tune the emerging magnetism at the studied interfaces opens new and unexpected routes for developing novel oxide-based spintronic devices.




