Our brain does not work like a typical computer memory storing just ones and zeroes: thanks to a much larger variation in memory states, it can calculate faster consuming less energy. Scientists of the MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology of the University of Twente (The Netherlands) now developed a ferro-electric material with a memory function resembling synapses and neurons in the brain, resulting in a multistate memory. They publish their results in this week’s Advanced Functional Materials.
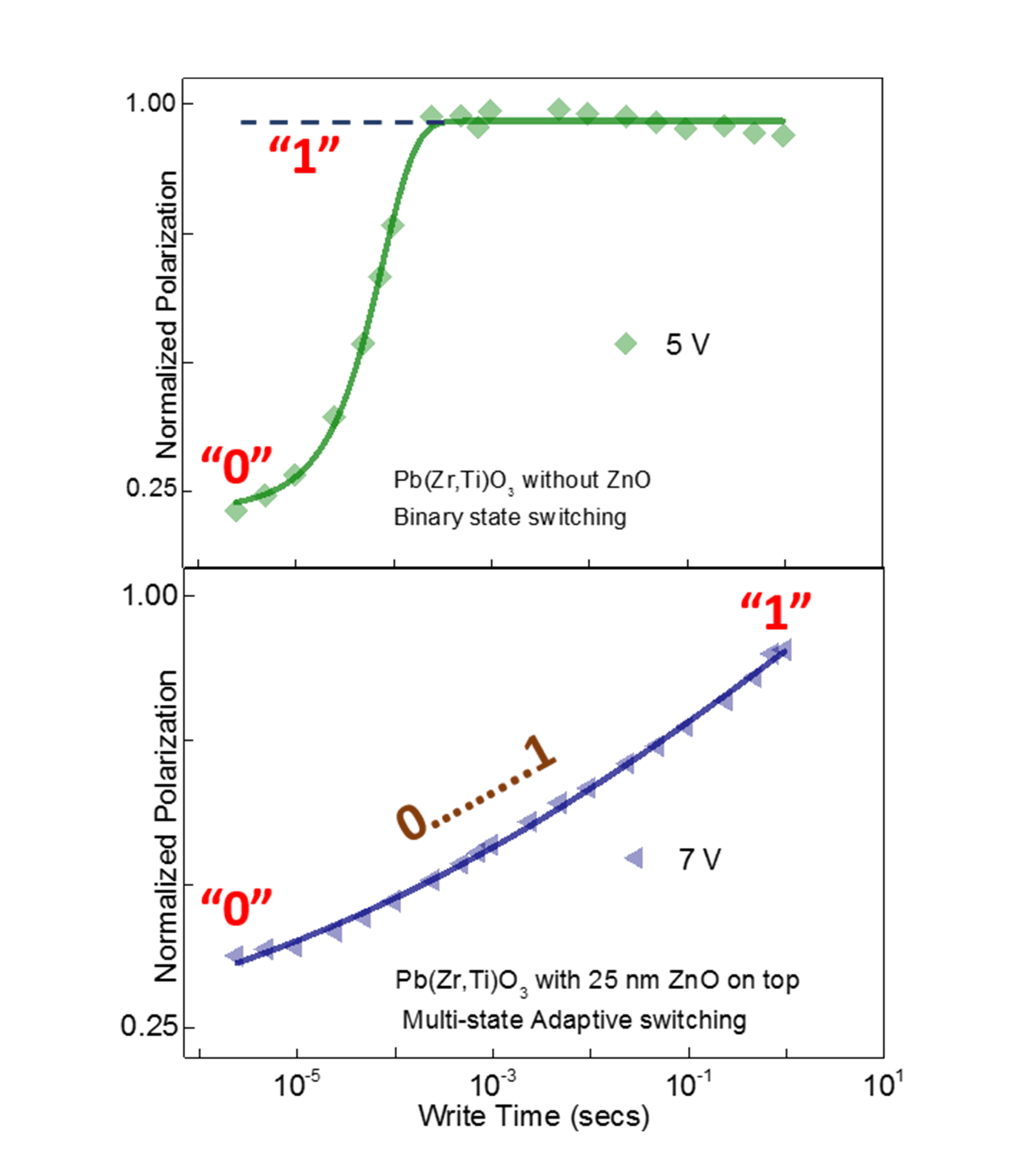
The material that could be the basic building block for ‘brain-inspired computing’ is lead-zirconium-titanate (PZT): a sandwich of materials with several attractive properties. One of them is that it is ferro-electric: you can switch it to a desired state, this state remains stable after the electric field is gone. This is called polarization: it leads to a fast memory function that is non-volatile. Combined with processor chips, a computer could be designed that starts much faster, for example. The UT scientists now added a thin layer of zinc oxide to the PZT, 25 nanometer thickness. They discovered that switching from one state to another not only happens from ‘zero’ to ‘one’ vice versa. It is possible to control smaller areas within the crystal: will they be polarized (‘flip’) or not?
Multi-state
By using variable writing times in those smaller areas, the result is that many states can be stored anywhere between zero and one. This resembles the way synapses and neurons ‘weigh’ signals in our brain. Multistate memories, coupled to transistors, could drastically improve the speed of pattern recognition, for example: our brain performs this kind of tasks consuming only a fraction of the energy a computer system needs. Looking at the graphs, the writing times seem quite long compared to nowaday’s processor speeds, but it is possible to create many memories in parallel. The function of the brain has already been mimicked in software like neurale networks, but in that case conventional digital hardware is still a limitation. The new material is a first step towards electronic hardware with a brain-like memory. Finding solutions for combining PZT with semiconductors, or even developing new kinds of semiconductors for this, is one of the next steps.
This research has been done within the Inorganic Materials Science group, of UT’s MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology. Within this group, also other attractive properties of PZT have been found, like piezo-electrical behavior: the material can expand using an electric voltage, pressing it can also generate a voltage, in turn.




