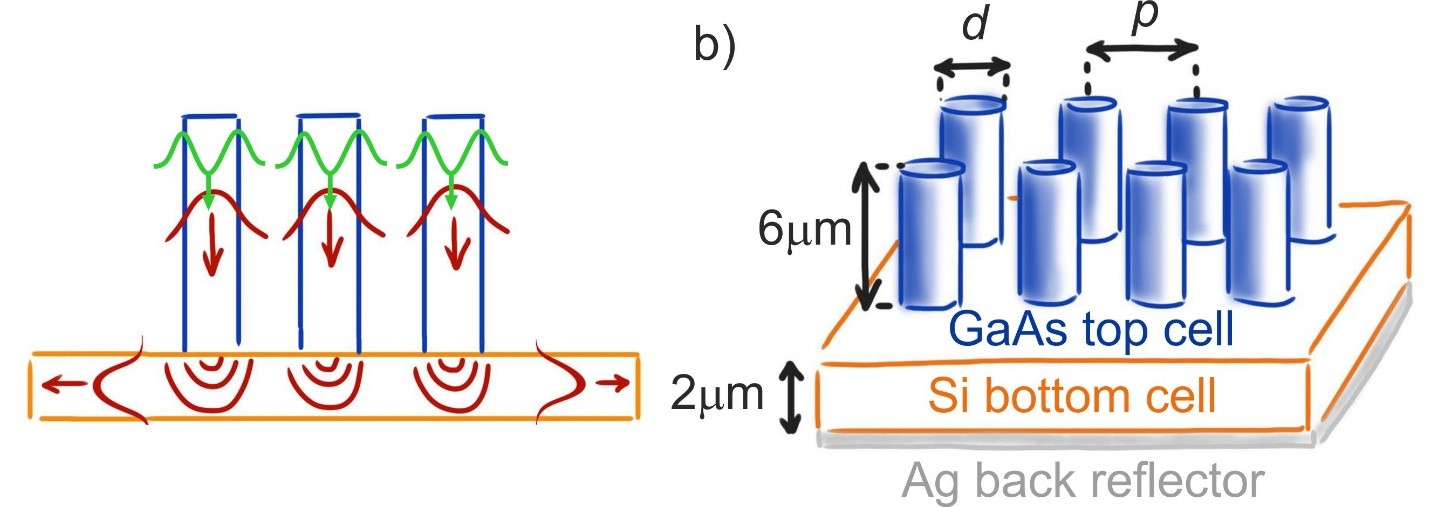
Optically coupled tandem of GaAs nanowires (6um tall) on silicon ultrathin film (2um). Sunlight is efficiently absorbed in each nanowire, and the array will transmit infrared light to be trapped into silicon film.
Capturing and manipulating light at nanoscale is a key factor to build high efficiency solar cells. Researchers in the 3D Photovoltaics group have recently presented a promising new design. Their simulations show that vertically stacked nanowires on top of ultrathin silicon films reduces the total amount of material needed by 90 percent while increasing the efficiency of the solar cell.
These promising simulation results are an important step towards new generation solar cells that are used in myriad ways in our buildings and landscape.
The results were published on May 23 in Optics Express.
A fascinating strategy to reduce both cost and rigidity is to combine ultrathin silicon photovoltaic films with semiconductor nanowire solar cells. The mechanical flexibility and resilience of micrometer thin cells make them well suited to apply on curved surfaces.
The idea is to optically couple the two materials stacked on top of each other as a tandem cell: a Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) nanowire array on top of an ultrathin silicon (2um-thick) film. GaAs vertical nanowires are well-known semiconductor components in photovoltaic applications.
Earlier experimental research in the 3D photovoltaics group has shown that such nanowires are able to absorb light ten to hundred times their geometrical cross section. Silicon, the second material in the tandem cell, is a highly desirable component thanks to the mature understanding of its optical and electronic properties as well as its widely available fabrication technologies.
The challenge researchers typically encounter when trying to downscale silicon to a few micrometers in thickness is that it compromises the solar cell’s performance due to poor absorption of infrared light. Light management strategies are therefore needed to compensate.
The research team decided to add vertically standing nanowires on top of silicon film and thereby make it up to four times more efficient in trapping infrared light in the silicon bottom cell.