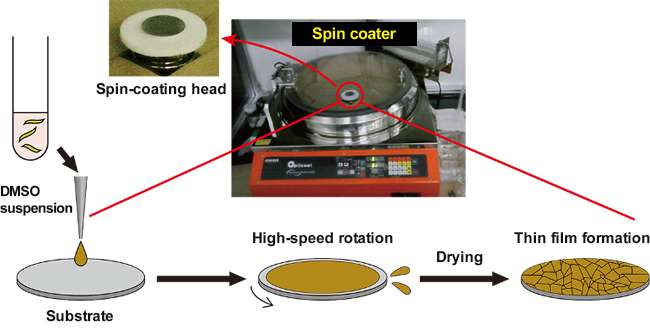
(Top) Photos showing spin-coating settings used to coat a substrate surface with a colloidal suspension of titanium oxide nanosheets. (Bottom) Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism of synthesizing a monolayer film composed of neatly tiled nanosheets. A thin layer of the suspension is first formed over the substrate surface. The thickness of the layer is then gradually reduced, which causes its interference colors to change. The layer eventually dries. (Credit: National Institute for Materials Science)
A NIMS research group has developed a novel technique to synthesize monolayer films composed of neatly tiled two-dimensional materials, such as oxide nanosheets and graphene, on substrate surfaces in as quickly as one minute.
A NIMS research group led by Takayoshi Sasaki has developed a novel technique to synthesize monolayer films composed of neatly tiled two-dimensional materials, such as oxide nanosheets and graphene, on substrate surfaces in approximately one minute. The technique may facilitate industrial production of various nanosheet-based devices as it offers a simpler and quicker alternative to the conventional, complicated film fabrication procedures.
Ultimate two-dimensional materials of atomic- or molecular-scale thickness—represented by graphene and oxide nanosheets—possess a number of extremely desirable properties (e.g., high conductivity, high dielectric and catalytic properties). For this reason, their potential to bring about technological innovation in a wide range of fields, including electronics, environmental and energy technology has been much anticipated, making them the subject of active R&D efforts worldwide. Many two-dimensional materials have been produced in colloidal form (i.e., sheet materials with widths within the micrometer range dispersed in solutions). In order to take full advantage of the properties of these materials for device applications, an important first step is to array them in an orderly manner—like playing cards—on the surfaces of various base materials. In other words, it is critical to develop a technique to eliminate gaps and overlapping between nanosheets arrayed in monolayer films. Once a monolayer film can be successfully synthesized, it will be feasible to synthesize multilayer films and superlattice films by repeating the monolayer film synthesis process. This approach could potentially lead to the development of devices with diverse functions. Currently, the Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) method is generally used to synthesize monolayers composed of neatly tiled nanosheets. However, this method is not practical for industrial-scale production as it requires skillful manipulation and complex conditions. In addition, the fabrication of films using this method normally takes about one hour. Because of these issues, there is strong demand for the development of simpler, quicker and more industrially practical film fabrication techniques.
The research group succeeded in using a simple spin-coating procedure to synthesize a monolayer film composed of neatly tiled nanosheets in approximately one minute—much more rapidly than the LB method. Specifically, the group applied a small amount of an organic suspension containing oxide nanosheets or graphene onto a substrate surface and spin-coated the substrate at appropriate rotational speeds. The balanced combination of centrifugal force generated by the rotating substrate and the force existing between the nanosheets and the substrate surface prevents the nanosheets from overlapping or forming gaps, resulting in the formation of smooth monolayer films at the atomic level. The group further confirmed that repetition of this coating procedure enables nanosheets to be progressively layered into multilayer films; therefore, the film thickness can be controlled in increments of nanosheet thickness. In addition, the group verified that this technique is applicable to two-dimensional materials varying in composition and structure, and can be used to fabricate films on the surfaces of substrates varying in shape, size and material. Therefore, this film fabrication technique can be considered very versatile.
In this study, the group succeeded in synthesizing films composed of neatly tiled two-dimensional nanosheets using a completely new mechanism. From this viewpoint, the accomplishment is valuable and academically novel. In addition, the technique enables quick and easy fabrication of monolayers and multilayers composed of neatly tiled nanosheets—a vital process in the application of nanosheet materials. Therefore, the development of the technique can be seen as a breakthrough in putting industrial production of nanosheet-based devices into practice.
Part of this study was supported by the MEXT Grant-in-Aid for a Scientific Research (A) project entitled “Pioneering novel functions of two-dimensional inorganic nanosheets by forming multilayer heterostructures.”
This study was published in the online version of Science Advances.




