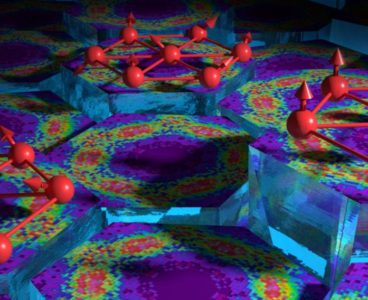
A unique combination of imaging tools and atomic-level simulations has allowed a team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory to solve a longstanding debate about the properties of a promising material that can harvest energy from light. The researchers used multimodal imaging to “see” nanoscale interactions within a thin film of…
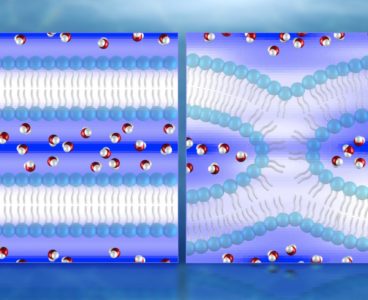
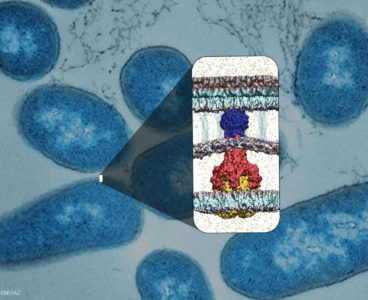
Neutrons Produce First Direct 3D Maps of Water During Cell Membrane Fusion
New 3D maps of water distribution during cellular membrane fusion are accelerating scientific understanding of cell development, which could lead to new treatments for diseases associated with cell fusion. Using neutron diffraction at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, researchers have made the first direct observations of water in lipid bilayers used to…
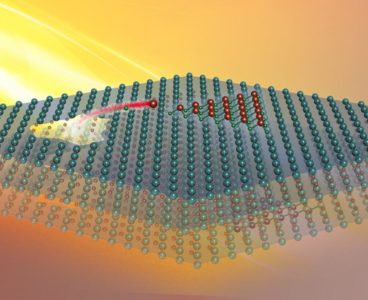
Cannibalistic Materials Feed on Themselves to Grow New Nanostructures
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory induced a two-dimensional material to cannibalize itself for atomic “building blocks” from which stable structures formed. The findings, reported in Nature Communications, provide insights that may improve design of 2D materials for fast-charging energy-storage and electronic devices. “Under our experimental conditions, titanium and carbon atoms…
Critical Plant Gene Takes Unexpected Detour That Could Boost Biofuel Yields
For decades, biologists have believed a key enzyme in plants had one function–produce amino acids, which are vital to plant survival and also essential to human diets. But for Wellington Muchero, Meng Xie and their colleagues, this enzyme does more than advertised. They had run a series of experiments on poplar plants that consistently revealed…
With Supercomputing Power, Scientists Solve a Next-Generation Physics Problem
Nuclear Physicists Leap into Quantum Computing with First Simulations of Atomic Nucleus
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are the first to successfully simulate an atomic nucleus using a quantum computer. The results, published in Physical Review Letters, demonstrate the ability of quantum systems to compute nuclear physics problems and serve as a benchmark for future calculations. Quantum computing, in which computations are…
Supersonic Waves May Help Electronics Beat the Heat
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory made the first observations of waves of atomic rearrangements, known as phasons, propagating supersonically through a vibrating crystal lattice–a discovery that may dramatically improve heat transport in insulators and enable new strategies for heat management in future electronics devices. “The discovery gives you a different…
Putting Quantum Scientists in the Driver’s Seat
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are conducting fundamental physics research that will lead to more control over mercurial quantum systems and materials. Their studies will enable advancements in quantum computing, sensing, simulation, and materials development. The researchers’ experimental results were recently published in Physical Review B Rapid Communication and Optics…
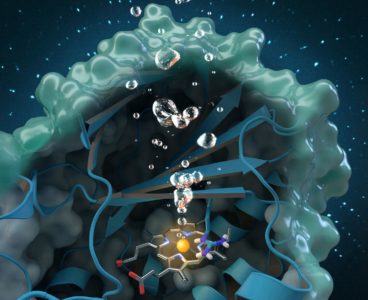
Neutrons Probe Oxygen-Generating Enzyme for a Greener Approach To Clean Water
A new study sheds light on a unique enzyme that could provide an eco-friendly treatment for chlorite-contaminated water supplies and improve water quality worldwide. An international team of researchers led by Christian Obinger from the University of Vienna used neutron analysis at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, x-ray crystallography and other techniques to study the chlorite…
3D Models Help Scientists Gauge Flood Impact
Heavy rainfall can cause rivers and drainage systems to overflow or dams to break, leading to flood events that bring damage to property and road systems as well potential loss of human life. One such event in 2008 cost $10 billion in damages for the entire state of Iowa. After the flood, the Iowa Flood…
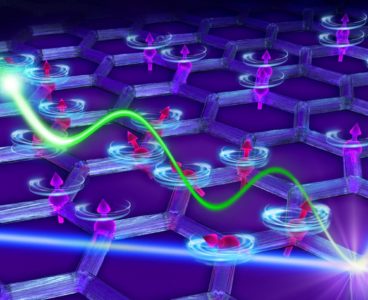
Neutrons Detect Elusive Higgs Amplitude Mode in Quantum Material
A team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory has used sophisticated neutron scattering techniques to detect an elusive quantum state known as the Higgs amplitude mode in a two-dimensional material. The Higgs amplitude mode is a condensed matter cousin of the Higgs boson, the storied quantum particle theorized in the 1960s…
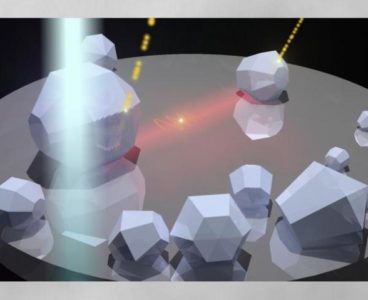
Neutrons Zero In On Elusive Magnetic Majorana Fermion
Neutron scattering has revealed in unprecedented detail new insights into the exotic magnetic behavior of a material that, with a fuller understanding, could pave the way for quantum calculations far beyond the limits of the ones and zeros of a computer’s binary code. A research team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National…
Automated Measurement System Enhances Quality, Reduces Handling in Pu-238 Production
Under a collaborative partnership between the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the Department of Energy, a new automated measurement system developed at DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory will ensure quality production of plutonium-238 while reducing handling by workers. NASA has funded ORNL and other national laboratories to develop a process that will restore U.S.…
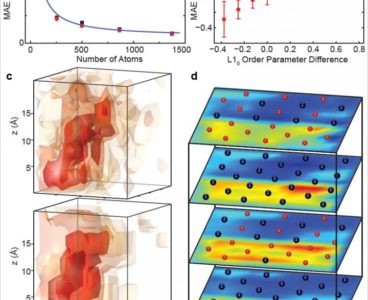
Supercomputing, Experiment Combine for First Look at Magnetism of Real Nanoparticle
Barely wider than a strand of human DNA, magnetic nanoparticles — such as those made from iron and platinum atoms — are promising materials for next-generation recording and storage devices like hard drives. Building these devices from nanoparticles should increase storage capacity and density, but understanding how magnetism works at the level of individual atoms…
The Shape of Melting in Two Dimensions
Crystallization Method Offers New Option for Carbon Capture from Ambient Air
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have found a simple, reliable process to capture carbon dioxide directly from ambient air, offering a new option for carbon capture and storage strategies to combat global warming. Initially, the ORNL team was studying methods to remove environmental contaminants such as sulfate, chromate or phosphate…
Neutrons Identify Key Ingredients of Quantum Spin Liquid Recipe
Neutron scattering studies of a rare earth metal oxide have identified fundamental pieces to the quantum spin liquid puzzle, revealing a better understanding of how and why the magnetic moments within these materials exhibit exotic behaviors such as failing to freeze into an ordered arrangement even near absolute zero temperatures. In a paper published in Nature…
Supercomputer Simulations Help Develop New Approach to Fight Antibiotic Resistance
Supercomputer simulations at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have played a key role in discovering a new class of drug candidates that hold promise to combat antibiotic resistance. In a study led by the University of Oklahoma with ORNL, the University of Tennessee and Saint Louis University, lab experiments were combined with…
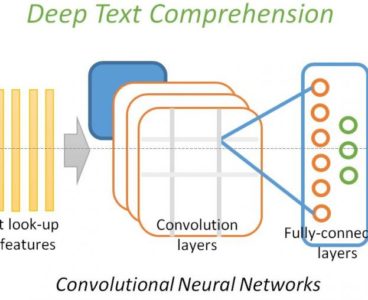
Accelerating Cancer Research With Deep Learning
Despite steady progress in detection and treatment in recent decades, cancer remains the second leading cause of death in the United States, cutting short the lives of approximately 500,000 people each year. To better understand and combat this disease, medical researchers rely on cancer registry programs–a national network of organizations that systematically collect demographic and…
Accelerating Cancer Research with Deep Learning
Scientists Isolate, Culture Elusive Yellowstone Microbe
A microbial partnership thriving in an acidic hot spring in Yellowstone National Park has surrendered some of its lifestyle secrets to researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Mircea Podar of ORNL’s Biosciences Division led a team that isolated the archaeonNanopusillus acidilobi, cultured these tiny microbes – just 100 to 300 billionths…
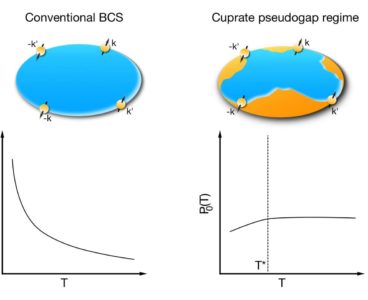
Titan Shines Light on High-Temperature Superconductor Pathway
When physicists Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Muller discovered the first high-temperature superconductors in 1986, it didn’t take much imagination to envision the potential technological benefits of harnessing such materials. High-temperature superconductors are materials that can transport electricity with perfect efficiency at or near liquid nitrogen temperatures (-196 degrees Celsius). Though their operating temperature may…
Drying Arctic Soils Could Accelerate Greenhouse Gas Emissions
A new study published in Nature Climate Change indicates soil moisture levels will determine how much carbon is released to the atmosphere as rising temperatures thaw Arctic lands. An international team led by Northern Arizona University scientists analyzed the results of 25 experiments from multiple research groups including the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National…