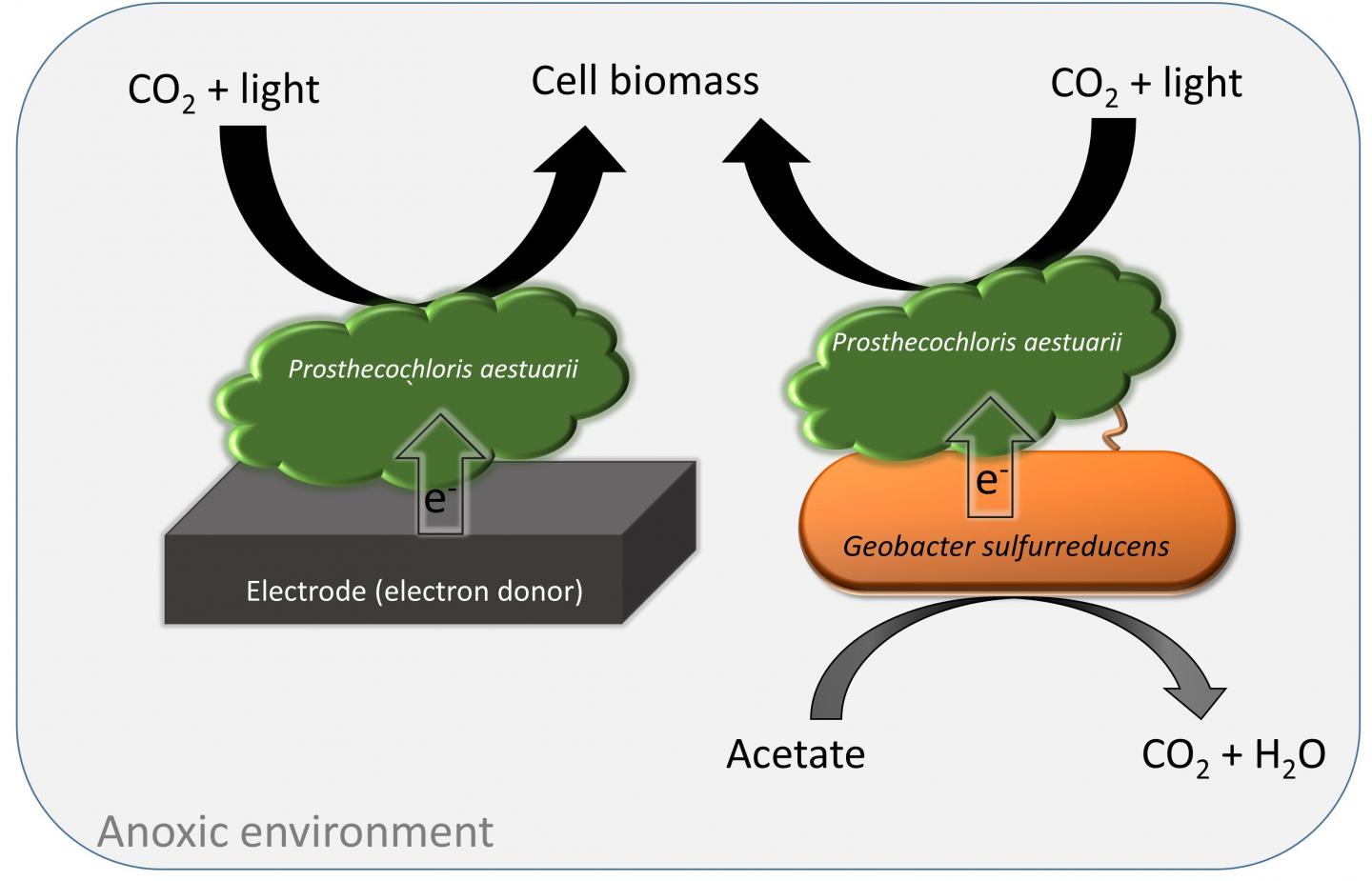
Conceptual model of a new type of anaerobic photosynthesis of G. sulfurreducens and P. aestuarii via direct, inter-species electron transfer. Source: Washington State University
Researchers at Washington State University have discovered a new type of cooperative photosynthesis that could be used in engineering microbial communities for waste treatment and bioenergy production.
They report today on the unique metabolic process seen for the first time in a pair of bacteria in Nature Communications.
Photosynthetic bacteria account for nearly half of the world’s food production and carbon-based organic material. The research could also improve understanding of lake ecology.
Phototroph + electron generator
Prosthecochloris aestaurii , a green-tinged, plant-like microbe, comes from the extreme environment of Hot Lake, a high salinity lake in northern Okanogan County near Oroville, Wash. Discovered and identified a few years ago by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and Southern Illinois University, the bacterium is able to photosynthesize, using sunlight along with elemental sulfur or hydrogen sulfide to grow.
The researchers noticed that P. aestuarii tended to gather around a carbon electrode, an electricity conductor that they were operating in Hot Lake. The researchers isolated and grew P. aestuarii and determined that, similar to the way half of a battery works, the bacterium is able to grab electrons from a solid electrode and use them for photosynthesis. The pink-colored Geobacter sulfurreducens meanwhile, is known for its ability to convert waste organic matter to electricity in microbial fuel cells. The bacterium is also used in environmental cleanup.
G. sulfurreducens, like animals and humans, can’t photosynthesize. It consumes organic compounds, such as acetate, and “breathes” out carbon dioxide.
The bacterium is known for its ability to donate electrons to a solid electrode. As it consumes acetate, it generates electrons, which can be collected as electricity.
Microbes paired up in WSU lab
Led by Haluk Beyenal, the Paul Hohenschuh Distinguished Professor in the WSU Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering, and postdoctoral researcher Phuc Ha, the research team surmised that the bacteria might be able to help each other grow and put them together in the lab.
The researchers found that P. aestuarii could accept electrons generated from G. sulfurreducens and use them in a new type of anaerobic photosynthesis never before seen. Similar to how a battery or fuel cell works, the bacteria transfer electrons. They feed off each other to grow under conditions in which neither could grow independently.
Ecology-friendly implications
From an ecological perspective, this new form of metabolism may play an important role in carbon cycling in oxygen free zones of poorly mixed freshwater lakes. It may also present new possibilities for engineering microbial communities for waste treatment and bioenergy production.
“We think this could be a common bio-electrochemical process in nature,” said Beyenal, whose team is working to better understand the electron transfer mechanism.




