Researchers at Washington State University, University of New Mexico, Eindhoven University of Technology, and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory have developed a catalyst that can both withstand high temperatures and convert pollutants at near room temperature – an important advance for reducing pollution in modern cars. They report on their work in the journal, Nature Communications.…
Catalyst Advance Could Lead to Economical Fuel Cells
Researchers at Washington State University have developed a new way to make low-cost, single-atom catalysts for fuel cells — an advance that could make important clean energy technology more economically viable. Their work is published in the Advanced Energy Materials journal. Hydrogen fuel cells are critical for the clean energy economy as they are more…
Researchers Find New Way to Estimate Magma Beneath Yellowstone Supervolcano
Researchers at Washington State University and the University of Idaho have found a new way to estimate how fast magma is recharging beneath the Yellowstone supervolcano. While their findings offer no help in predicting if the volcano will erupt, they can now get a better understanding of a key factor–a pool of basalt magma recharging…
One-Step, 3D Printing for Multimaterial Projects Developed by WSU Researchers
Similar to the advance from black and white to color printing, a Washington State University research team for the first time has used 3D printing technology in a one-step process to print structures made of two different materials. The advance could potentially help manufacturers reduce manufacturing steps and use one machine to make complex products…
Turmeric Increased Bone-Growing Capabilities on 3D-Printed Bone Scaffold
A WSU research team is bringing together natural medical cures with modern biomedical devices in hopes of bringing about better health outcomes for people with bone diseases. In this first-ever effort, the team improved bone-growing capabilities on 3D-printed, ceramic bone scaffolds by 30-45 percent when coated with curcumin, a compound found in the spice, turmeric.…
Researchers Extract Nicotine From Ancient Dental Plaque for the First Time
A team of scientists including researchers from Washington State University has shown for the first time that nicotine residue can be extracted from plaque, also known as “dental calculus”, on the teeth of ancient tobacco users. Their research provides a new method for determining who was consuming tobacco in the ancient world and could help…
Researchers Document Transformation of Graphite into Hexagonal Diamond
A new study by Washington State University researchers answers longstanding questions about the formation of a rare type of diamond during major meteorite strikes. Hexagonal diamond or lonsdaleite is harder than the type of diamond typically worn on an engagement ring and is thought to be naturally made when large, graphite-bearing meteorites slam into Earth.…
Computer Approaches Human Skill For First Time In Mapping Brain
Study Shows Muted Stress Response Linked to Long-Term Cannabis Use
Researchers Develop Alternative to Wasteful Methane Flaring
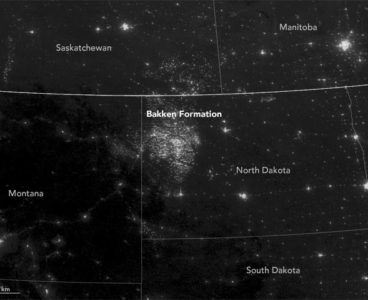
Jean-Sabin McEwen knocks out a web search for “North Dakota,” “night sky” and “flaring,” and quickly finds a picture from space showing a glowing cluster bigger than Minneapolis. It’s from oil and gas fields burning off methane, producing as much greenhouse gas in a year as 1 million cars. “It’s a big problem because not…
Researchers Develop Recycling For Carbon Fiber Composites
A WSU research team for the first time has developed a promising way to recycle the popular carbon fiber plastics that are used in everything from modern airplanes and sporting goods to the wind energy industry. The work, reported in Polymer Degradation and Stability, provides an efficient way to re-use the expensive carbon fiber and other…
Physicists Create ‘Negative Mass’
Mathematician Breaks Down How to Defend Against Quantum Computing Attacks
New Clues for Nuclear Waste Cleanup
Researchers Discover Unique Microbial Photosynthesis
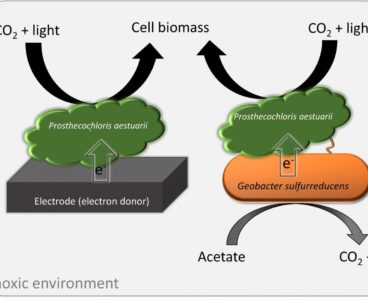
Researchers at Washington State University have discovered a new type of cooperative photosynthesis that could be used in engineering microbial communities for waste treatment and bioenergy production. They report today on the unique metabolic process seen for the first time in a pair of bacteria in Nature Communications. Photosynthetic bacteria account for nearly half of the…
Computer Models Find Ancient Solutions to Modern Problems
Washington State University archaeologists are at the helm of new research using sophisticated computer technology to learn how past societies responded to climate change. Their work, which links ancient climate and archaeological data, could help modern communities identify new crops and other adaptive strategies when threatened by drought, extreme weather and other environmental challenges. In…
Researchers Develop Novel Wound-Healing Technology
A WSU research team has successfully used a mild electric current to take on and beat drug-resistant bacterial infections, a technology that may eventually be used to treat chronic wound infections. The researchers report on their work in the online edition of npj Biofilms and Microbiomes. Led by Haluk Beyenal, Paul Hohenschuh Distinguished Professor in the…
Wireless Data-Center-On-A-Chip Aims to Cut Energy Use
Soybean Nitrogen Breakthrough Could Help Feed The World
Wireless ‘Data Center on a Chip’ Aims to Cut Energy Use
Tiny Data Chip Cuts Energy Use
A Washington State University research team has designed a tiny, wireless data center that someday could be as small as a hand-held device and dramatically reduce the energy needed to run such centers. Their idea is a paradigm shift in the management of big data, says Partha Pratim Pande, a computer engineering professor in the…
Reducing Expensive Noble Metals for Fuel Cell Reactions
Washington State University researchers have developed a novel nanomaterial that could improve the performance and lower the costs of fuel cells by using fewer precious metals like platinum or palladium. Led by Yuehe Lin, professor in the School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, the researchers used inexpensive metal to make a super low density material,…
Illuminating Sulfides’ Role in the Body
For the first time, researchers at Washington State University have created an injectable compound or “probe” that illuminates hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen polysulfides in different colors when they are present in cells. Hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen polysulfides are gases notorious as the source of rotten egg stench. They are produced and used for a wide…
Researcher Develops Gene Therapy for Muscle Wasting
Researchers Improve Catalyst Efficiency for Clean Industries
Researchers have developed a way to use less platinum in chemical reactions commonly used in the clean energy, green chemicals, and automotive industries, according to a paper in Science. Led by the University of New Mexico in collaboration with Washington State University, the researchers developed a unique approach for trapping platinum atoms that improves the efficiency…