The discovery of green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is made by a jellyfish, transformed cell biology. It allowed scientists to stitch the GFP sequence to proteins from other organisms to trace their movements and interactions in living cells. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have designed peptide nanoparticles that can each glow…
Lonza to host webinar: “Bioreactor Aseptic Sampling and Process Control”
On June 23, Lonza will host a free 60-minute webinar on how to gain control of bioprocesses through automated, aseptic sampling of bioreactors. Dr. Clint Pepper, director, MAST Products, will present three case studies demonstrating cost savings and enhanced throughput and Product Quality Attribute (PQA) optimization using the MAST Aseptic Sampling System, while maintaining bioreactor…
Accurate and reliable real-time protein titer monitoring in biopharma
By Maxwell Geiger, Associate Product Solutions Manager for the BioProcess Analytics group within IDEX Health & Science Recently, regulators have encouraged pharma and biopharma companies to incorporate the concepts of Quality by Design (QbD) and Process Analytical Technology (PAT) into drug development and manufacturing processes (1). This encouragement is part of a drive for scientists…
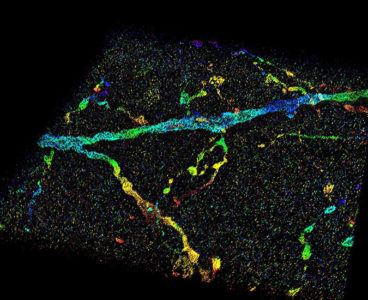
New imaging technology allows visualization of nanoscale structures inside whole cells and tissues
Since Robert Hooke’s first description of a cell in Micrographia 350 years ago, microscopy has played an important role in understanding the rules of life. However, the smallest resolvable feature, the resolution, is restricted by the wave nature of light. This century-old barrier has restricted understanding of cellular functions, interactions and dynamics, particularly at the…
New test will rapidly identify body fluids at crime scenes
By Holly Ober Engineers at UC Riverside’s Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering have received a $600,000 grant from the National Institute of Justice to develop a test kit that can rapidly identify body fluids at crime scenes. Existing tests to detect body fluids are not very sensitive and consume relatively large amounts of…
Qosina provides single-use bioprocessing components
Qosina carries a broad selection of in-stock, single-use bioprocessing components. The company provides 3D CAD models and comprehensive technical specifications, such as material safety data sheets, technical data sheets, material certification and compatibility information on most of these products. Qosina is ISO 13485, ISO 9001, ISO 22301 and ISO 14001 certified, reflecting its unwavering commitment…
Here’s the science behind face mask materials
[Republished from our sister publication, Design World] By Lee Teschler, Executive Editor It looks as though the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) may end up strongly suggesting that Americans cover their faces in public until the coronavirus pandemic plays out. The Washington Post reports the recommendations now being floated would call for…
Upgrading biomass with selective surface-modified catalysts
Scientists have designed a catalyst composed of very low concentrations of platinum (single atoms and clusters smaller than billionths of a meter) on the surface of titanium dioxide. They demonstrated how this catalyst significantly enhances the rate of breaking a particular carbon-oxygen bond for the conversion of a plant derivative (furfuryl alcohol) into a potential…
AgilePulse PLUS Transfection System for advanced transfection protocols
BTX, a division of Harvard Bioscience, has released the AgilePulse PLUS Bipolar Transfection System, an advanced electroporation system with voltage and polarity switching capabilities. The AgilePulse PLUS is ideal for automated, high performance delivery of biomolecules to mammalian cells and tissues. Maximum Efficiency. PulseAgile protocols deliver short, high-voltage pulses to porate cell membranes followed by…
Stabilizing freeze-dried cellular machinery unlocks cell-free biotechnology
Researchers at California Polytechnic State University have developed a low-cost approach that improves cell-free biotechnology’s utility for bio-manufacturing and portability for field applications. Cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) is a biotechnology that harnesses active cellular machinery in a test tube without the presence of living cells, allowing researchers to directly access and manipulate biochemical processes. Scientists…
R&D 100 winner plays role in cruise ship evacuation
In 2016, the Containerized Bio-Containment System (CBCS), developed by Kansas City-based MRIGlobal — with support from HHI Corp., GPA Services L.L.C., the U.S. State Department, and The Paul G. Allen Ebola Program — was named one of the R&D 100 winners. The system is a first-of-its-kind, flyable medical transport unit and features full biocontainment. It…
Rice bioengineers 3D-print implants to seed multiple layers of tissue
Who ever said bioengineers can’t get their groove on? The Rice University team led by Antonios Mikos says otherwise with its development of a groovy method to seed sophisticated, 3D-printed tissue-engineering scaffolds with living cells to help heal injuries. The researchers are literally carving grooves into plastic threads used to build the scaffolds. The grooves…
How to invest for a decade of technological change in biopharma
Predicting the future is hard – predicting the future of technology is even harder. In the last 10 years, everything from entertainment to travel has been upended by the likes of Airbnb, Spotify, and Instagram – none of which even existed a decade ago – while Netflix was still delivering DVDs by mail. Now, as…
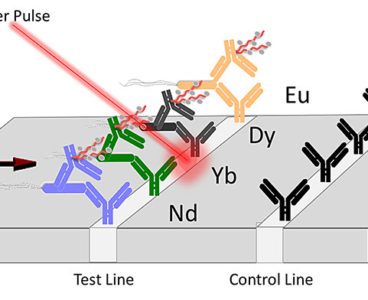
New technology for pathogen detection driven by lasers
Researchers at Purdue University have been working to develop new technologies to help stop the spread of foodborne illnesses, which kill 3,000 people a year, by detecting them more efficiently. They have developed a lanthanide-based assay coupled with a laser that can be used to detect toxins and pathogenic E. coli in food samples, water…
The wild world of microbe-made products—skis now included
This winter, you can carve the fresh powder of the backcountry on a pair of high-performance, eco-friendly skis designed by world-famous athletes and made from a material produced by microscopic algae. Yes, algae. The skis, made by a rather unconventional Bay Area biotech company, are a new addition to the long list of products currently…
Study points to new weapon in fight against lethal fungi
Candida albicans, a commonly found microbe, can turn deadly when it colonizes on devices such as catheters implanted in the human body. While commonly found in healthy people, this microbe can become a serious problem for those who are seriously ill or immune-suppressed. The microbe forms a biofilm when it colonizes using, for example, a catheter…
Horizon Discovery divests animal models business to Envigo
Animal model operations to be transferred to Envigo ownership Divestment in line with Horizon’s corporate strategy to focus on its core markets Envigo, a leading global research model supplier, enters the gene-edited research model field with the addition of Horizon’s business Horizon and Envigo to collaborate on providing CRISPR screening services Horizon Discovery Group plc (LSE:…
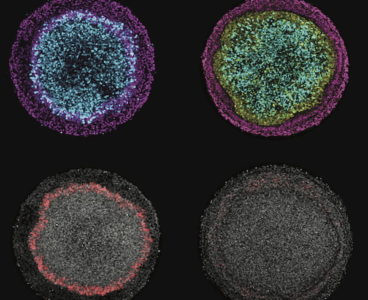
Unique Rice platform helps bioscientists learn how ectoderm cells begin to differentiate
During embryonic development, the entire nervous system, the skin and the sensory organs emerge from a single sheet of cells known as the ectoderm. While there have been extensive studies of how this sheet forms all these derivatives, it hasn’t been possible to study the process in humans – until now. Rice bioscientist Aryeh Warmflash, graduate student…
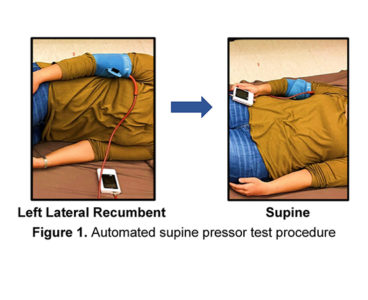
Pregnant women may soon be able to detect their own risk of preeclampsia with a smartphone
Roughly 15% of premature births in the U.S. happen due to a pregnancy complication caused by high blood pressure, called preeclampsia. While sometimes symptoms dissipate after the mother gives birth, preeclampsia can lead to permanent damage to the kidneys or death. Purdue University researchers and colleagues, including Drs. David Reuter from Seattle Children’s Hospital and David Haas…
Research findings may change oxygen use in ICUs across the globe
A trial by researchers at Monash University could change how oxygen is administered to millions of people in intensive care units across the world. The trial found ICU patients are being given unnecessary levels of oxygen that make no difference to their recovery, and in some specific groups less oxygen may actually improve recovery…
Electronic Inhaler Monitoring Reduces Hospitalizations, ER Visits in Patients With COPD
Bayer Invests $150 Million to Build New Cell Culture Technology Center
New Sensors Could Yield Smart Pill Bottle, Other Applications
3D Optical Biopsies Within Reach Thanks to Advance in Light Field Technology
Researchers have shown that existing optical fibre technology could be used to produce microscopic 3D images of tissue inside the body, paving the way towards 3D optical biopsies. Unlike normal biopsies where tissue is harvested and sent off to a lab for analysis, optical biopsies enable clinicians to examine living tissue within the body in…