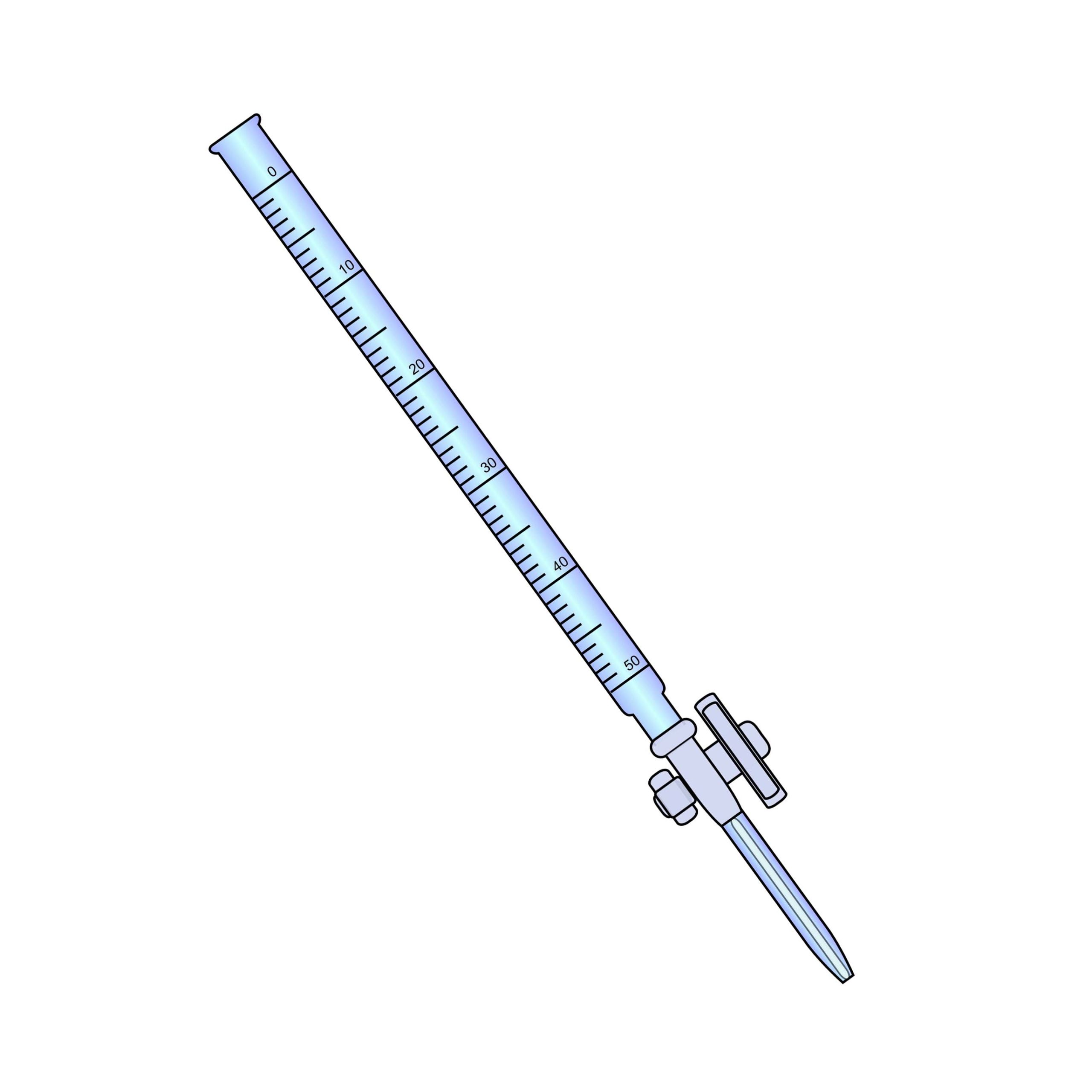
 A burette is used to dispense small volumes of liquid called aliquots, or sometimes gas, with high accuracy. It consists of a long glass tube with a valve at one end to control the flow of liquid. Burettes serve essentially the same purpose as a pipette.
A burette is used to dispense small volumes of liquid called aliquots, or sometimes gas, with high accuracy. It consists of a long glass tube with a valve at one end to control the flow of liquid. Burettes serve essentially the same purpose as a pipette.
Volumetric burettes are manual instruments with graduations inscribed on a glass tube. Gravity causes fluid to flow when the valve is opened. Liquid burettes have the valve at the bottom. In gas burettes, the valve is at the top and a liquid such as water, mercury or oil is used to displace the gas while accurately measuring its volume. Piston burettes can be more precise and use physical actuation of a piston to deliver liquid. They can use either manually read graduations or have a digital readout. They are actuated by either turning a wheel by hand or through a stepper motor.
Burettes may be specified according to their volume, resolution and accuracy. Smaller diameter tubes result in lower volume and increased resolution. Digital burettes may achieve better accuracy and are less dependent on the skill of the operator.
The first burettes were created by chemists in the 19th century. They consisted of simple glass tubes with valves and later added graduations. This basic design is still widely used. It must be carefully observed at eye level, ensuring that the liquid if free of bubbles and the reading is taken at the bottom of the meniscus. The volume delivered is the difference between the starting and finishing reading.
Digital burettes are piston burettes with linear encoders which measure the distance travelled by the piston with very high accuracy. The piston manually actuated using a geared wheel or motorized. Where the piston is motorized the volume of liquid may be specified using the digital display before delivery, or the burette may be controlled through a connected computer for fully automated sequences of operation.





Tell Us What You Think!