Oxygen Could Have Been Available to Life as Early as 3.5 Billion Years Ago
Molecular Oxygen in Comet’s Atmosphere Not Created on its Surface
Scientists have found that molecular oxygen around comet 67P is not produced on its surface, as some suggested, but may be from its body. The European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft escorted comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on its journey round the sun from August 2014 – September 2016, dropping a probe and eventually crashing onto its surface. When…
New Type of Photosynthesis Discovered
The discovery changes our understanding of the basic mechanism of photosynthesis and should rewrite the textbooks. It will also tailor the way we hunt for alien life and provide insights into how we could engineer more efficient crops that take advantage of longer wavelengths of light. The discovery, published today in Science, was led by…
Artificial Intelligence Improves Stroke and Dementia Diagnosis in Most Common Brain Scan
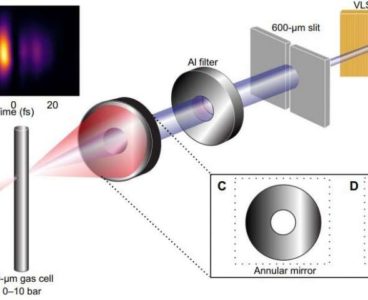
X-rays from Tabletop Lasers Allows Scientists to Peer Through the ‘Water Window’
Studying the fleeting actions of electrons in organic materials will now be much easier, thanks to a new method for generating fast X-rays. The technique means advanced measurements of fast reactions will now be possible in physics labs around the world, without having to wait to use expensive and scarce equipment. It could be used,…
Actual Fossil Fuel Emissions Checked with New Technique
Artificial and Biological Cells Work Together as Mini Chemical Factories
Researchers have fused living and non-living cells for the first time in a way that allows them to work together, paving the way for new applications. The system, created by a team from Imperial College London, encapsulates biological cells within an artificial cell. Using this, researchers can harness the natural ability of biological cells to…
Running on Renewables: How Sure Can we be About the Future?
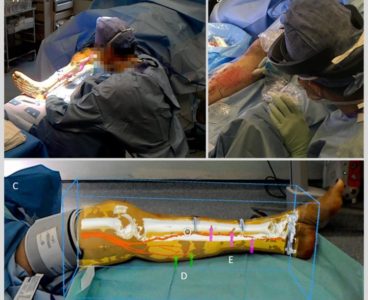
Augmented Reality Helps Surgeons to ‘See Through’ Tissue and Reconnect Blood Vessels
Using augmented reality in the operating theatre could help surgeons to improve the outcome of reconstructive surgery for patients. In a series of procedures carried out by a team at Imperial College London at St Mary’s Hospital, researchers have shown for the first time how surgeons can use Microsoft HoloLens headsets while operating on patients…
3D Printing Creates Super Soft Structures That Replicate Brain And Lungs
A new 3D printing technique allows researchers to replicate biological structures, which could be used for tissue regeneration and replica organs. Imperial College London researchers have developed a new method for creating 3D structures using cryogenics (freezing) and 3D printing techniques. This builds on previous research, but is the first to create structures that are…
Early Disease Diagnosis Could Be Dramatically Improved with New Detection System
The presence of, or changes in the concentration of, certain proteins in biological fluids can be indicators of disease. However, in the early stages of disease these ‘biomarkers’ can be difficult to detect, as they are relatively rare. Detecting important biomarkers in lower concentrations will allow patients to be treated earlier for diseases such as…
Electron Behavior Under Extreme Conditions Described for the First Time
Researchers have modelled the actions of electrons under extreme temperatures and densities, such as those found within planets and stars. The work could provide insights into the behavior of matter in fusion experiments, which may one day lead to a sought-after source of clean energy. Electrons are an elementary component of our world and determine…
New Way to Predict When Electric Cars and Home Batteries Become Cost Effective
Nano-Sized Drug Carriers Could Be Future Treatment Option for Lung Disease Patients
Hands-off Approach to Silicon Chips
The possibility of looking inside silicon chips to see their tiny working parts, without damaging the chips, is a step closer thanks to an international team led by scientists at the LCN. The group at the LCN, led by Dr Neil Curson, have shown that they can generate pictures of tiny three-dimensional components made from phosphorus…
Next-Gen Solar Cells Could Be Improved by Atomic-Scale Redesign
Researchers have uncovered the exact mechanism that causes new solar cells to break down in air, paving the way for a solution. Solar cells harness energy from the Sun and provide an alternative to non-renewable energy sources like fossil fuels. However, they face challenges from costly manufacturing processes and poor efficiency – the amount of…
Drug Used to Treat Weak Bones Associated With Micro-Cracks
MS Treatment That ‘Resets’ Immune System May Halt Disease Progression for Estimated 5 Years
Bacteria ‘Alarm Clock’ May Trigger Repeat Infections
New Sensor Material Could Enable More Sensitive Readings of Biological Signals
Scientists Confirm the Universe Has No Direction
Potential New Test for Bacterial Infections Including Meningitis
Scientists have identified two genes that are switched on only when a child is suffering from a bacterial infection. This could allow doctors to quickly distinguish between a viral or bacterial illness, and identify early cases of potentially deadly infections. The international team of scientists, led by researchers at Imperial College London and funded by the NIHR Imperial…
Scientists Discover Light Could Exist in a Previously Unknown Form
New research suggests that it is possible to create a new form of light by binding light to a single electron, combining the properties of both. According to the scientists behind the study, from Imperial College London, the coupled light and electron would have properties that could lead to circuits that work with packages of light –…