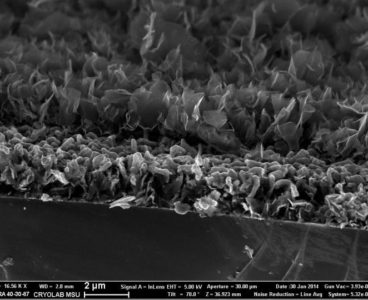
Materials scientists from Lomonosov Moscow State University have explained the laws of dissolution and crystallization of hybrid perovskites, and they have proposed a novel approach for obtaining films for solar cells. They have explained the key mechanisms of interaction of hybrid perovskites with solvents and suggested new approaches to obtain perovskite light-absorbing layers for thin-film…
Antioxidants Developed by MSU Scientists Slow Down Senescence in Plants
Ageing is a complex process involving lots of different mechanisms. One of the main processes on which ageing is based is the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS are molecules formed as a result of a sequential one-electron reduction of oxygen. They are extremely chemically active and oxidize many compounds inside the cells. This…
A New Material Quickly Identifies the Presence of Harmful Ions in Food Products
Controlled Nuclear Transition Will Make Clocks Significantly More Precise Than Atomic Ones
Scientists Dedicated the Birth of a New Black Hole to Stephen Hawking
One of the MASTER Global Robotic Net telescopes (MSU) located on Tenerife (Spain, Canary Islands) helped the scientists observe the gamma-ray burst caused by the collapse of a star and the formation of a black hole in its place. Usual telescopes are unable to point to gamma-ray bursts error-boxes fast enough to monitor the change…
Scientists Developed a Material for the New Type of Liquid Crystal Displays
A team from the Faculty of Physics, MSU together with their foreign colleagues developed a new liquid crystal material with high potential as a basis for brighter, faster, energy saving displays with higher resolution. The results of the work were published in Advanced Functional Materials journal. The LCD devices can be found in almost every…
Scientists Find Out How to Distinguish Beams of Entangled Photons
A team from the Faculty of Physics, MSU developed a method for creating two beams of entangled photons to measure the delay between them. In the future the results of the study may be used in high-precision measurements, material studies, and informational technologies. The article was published in Optics Letters journal. David Nikolaevich Klyshko, professor…
Biomarkers Helped Solving the Mystery of 500-Million-Year-Old Macroorganisms
A postgraduate student of the Faculty of Geology of MSU, working with an international scientific group, participated in chemical analysis of biomarkers — compounds that remained after the decomposition of organic remains of the genus Beltanelliformis. These organisms populated the Earth in the Ediacaran period (about 575-541 mln years ago), and their position on the…
Promising Sensors for Submarines, Mines, and Spacecraft
Researchers from the Physics Department of Moscow State University and their colleagues have discovered a mechanism that allows gas sensors, based on nanocrystalline metal oxides, to work at room temperature. This invention will raise the efficiency of environmental monitoring at nuclear power plants, on submarines and spacecrafts. The discovery was reported in Scientific Reports. Scientists…
Chemists Explain Origin of Green Fluorescence
The members of the Faculty of Chemistry of the Lomonosov Moscow State University in cooperation with Danish molecular physicists have revealed the mechanism, determining the sensitivity of the green fluorescent protein to light exposure. The scientists have proved that an isolated chromophore group is capable of emitting light outside the protein environment, while the protein…
Lithium-ion Batteries Will Get More Efficiency Due to Silicon, Germanium, Carbon Nanowalls
Members of the D. V. Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physic and colleagues from the Faculty of Chemistry of the Lomonosov Moscow State University have developed a new silicon- and germanium-based material that could significantly increase specific characteristics of lithium-ion batteries. The research results have been published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A. Lithium-ion batteries…
Peptide Complex Formed in the Brain is Responsible For Alzheimer’s Disease
Giant Enhancement of Electromagnetic Waves Revealed Within Small Dielectric Particles
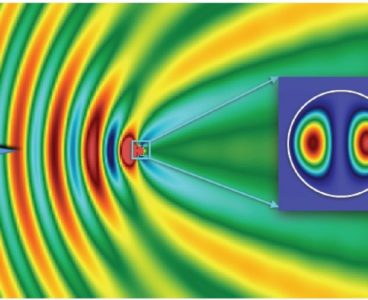
Scientists from the Lomonosov Moscow State University together with their Russian and foreign colleagues have done for the first time direct measurements of giant electromagnetic fields, emerging in dielectric particles with the high refractive index at the scattering of electromagnetic waves. The researchers have presented their project results in the Scientific Reports. The problem of miniaturization…
Giant Enhancement of Electromagnetic Waves Revealed Within Small Dielectric Particles
Scientists from the Lomonosov Moscow State University together with their Russian and foreign colleagues have done for the first time direct measurements of giant electromagnetic fields, emerging in dielectric particles with the high refractive index at the scattering of electromagnetic waves. The researchers have presented their project results in the Scientific Reports. The problem of miniaturization…
Ultrafast Tunable Semiconductor Metamaterial Created
An international team of researchers from Moscow State University (Russia), Sandia National Laboratories (U.S.), and Friedrich-Schiller University (Germany) have devised an ultrafast tunable metamaterial based on gallium arsenide nanoparticles. Their study was published in Nature Communications. The new optical metamaterial paves the way to ultrafast information transfer on the nanoscale. Optical metamaterials are man-made media…
Astrophysicists Discovered a Star Polluted by Calcium
An international team of astrophysicists led by a scientist from the Sternberg Astronomical Institute of the Lomonosov Moscow State University reported the discovery of a binary solar-type star inside the supernova remnant RCW 86. Spectroscopic observation of this star revealed that its atmosphere is polluted by heavy elements ejected during the supernova explosion that produced…
Scientists Develop New Technique for Creating Entangled Photon States
Members of the Faculty of Physics, the Lomonosov Moscow State University have elaborated a new technique for creation of entangled photon states, exhibiting photon pairs, which get correlated (interrelated) with each other. Scientists have described their research in an article, published in the journal Physical Review Letters. Physicists from the Lomonosov Moscow State University have studied…
Measuring Graphene-based Electromagnetic Radiation
A prototype device called a bolometer measures electromagnetic radiation energy flow based on physical parameter variations of thermosensitive elements as a result of heating by absorption of radiation energy. “We studied thermal and optical properties of the carbon structures derived from reduced graphene oxide in a wide range of wavelengths from visible to infrared. In…
How Water Flows Near Superhydrophobic Surface
Water (and other liquids) has an unusual property when it flows closely to some specially designed surfaces: its speed isn’t equal to zero even in the layer that directly touches the wall. This means that liquid doesn’t adhere to the surface, but instead slides along it. Such an effect is called hydrodynamic slip and it…
Bleed Like Hell
Platelets are small anucleated blood cells responsible for stopping bleeding. They detect blood vessel damage and agglutinate, creating aggregates and stopping the blood loss. This process is called hemostasis (from the Greek “haimatos” — blood, “stasis” — stop). Platelets become able to aggregate and plug the wound upon activation. Scientists consider that the platelet is…
Organic Computers are Coming
A team of the Lomonosov MSU researchers in collaboration with their German colleagues from the Institute of Polymer Research in Dresden (Leibniz Institute) managed to find a molecule that, to their opinion, could give the impetus to the development of organic electronics. The results of the work were published in Advanced Materials. Scientists from the Moscow…