Instead of throwing away your broken boots or cracked toys, why not let them fix themselves? Researchers at the University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering have developed 3D-printed rubber materials that can do just that. Assistant Professor Qiming Wang works in the world of 3D printed materials, creating new functions for a variety…
Scientists Find a Way to Enhance the Performance of Quantum Computers
A Biomarker in the Brain’s Circulation System may be Alzheimer’s Earliest Warning
Genetic Mutations Thwart Scientific Efforts to Fully Predict Our Future
Researchers Decode Mood From Human Brain Signals
Could This Material Enable Autonomous Vehicles to Come to Market Sooner?
One of the leading challenges for autonomous vehicles is to ensure that they can detect and sense objects–even through dense fog. Compared to the current visible light-based cameras, infrared cameras can offer much better visibility through the fog, smoke or tiny particles that can scatter the visible light. Within the air, infrared light –within a…
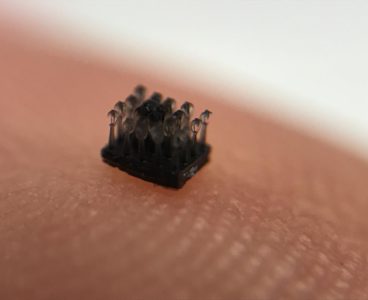
Thin, Flexible Polymers Record ‘Conversations’ Deeper in the Brain With Less Injury-Risk
Can We Imitate Organisms’ Abilities to Decode Water Patterns for New Technologies?
Strings of Electron-Carrying Proteins may Hold the Secret to ‘Electric Bacteria’
Could a unique bacterium be nature’s microscopic power plant? Scientist Moh El-Naggar and his team think it’s possible. They work with the Shewanella oneidensis species of bacteria, one of a group of microbes that essentially “breathe” rocks. As part of their metabolism, the bacteria have developed a way to transfer electrons from the interior of…
What Plants Can Teach Us About Oil Spill Clean-Up, Microfluidics
For years, scientists have been inspired by nature to innovate solutions to tricky problems, even oil spills — manmade disasters with devastating environmental and economic consequences. A new USC study takes a cue from leaf structure to fabricate material that can separate oil and water, which could lead to safer and more efficient oil spill…
AI to Fight the Spread of Infectious Diseases
USC Team Finds Potentially Better Way to Treat Liver Cancer
A Keck School of Medicine of USC research team has identified how cancer stem cells survive. This finding may one day lead to new therapies for liver cancer, one of the few cancers in the United States with an incidence rate that continues to balloon. “Liver cancer is difficult to treat, and most patients who…
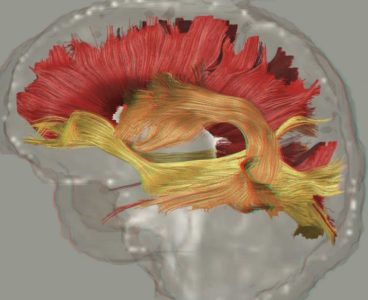
Study: Schizophrenia Disrupts the Brain’s Entire Communication System
Some 40 years since CT scans first revealed abnormalities in the brains of schizophrenia patients, international scientists say the disorder is a systemic disruption to the brain’s entire communication system. The study, published in the Nature journal Molecular Psychiatry on Oct. 17, sets the stage for future research on the debilitating mental illness that, according to the…
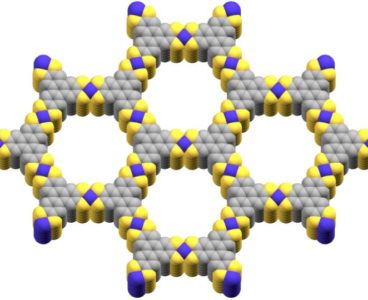
A New Miniature Solution for Storing Renewable Energy
Scientists have long searched for the next generation of materials that can catalyze a revolution in renewable energy harvesting and storage. One candidate appears to be metal-organic frameworks. Scientists have used these very small, flexible, ultra-thin, super-porous crystalline structures to do everything from capturing and converting carbon into fuels to storing hydrogen and other gases.…
Researcher Identifies a New Way To Treat HIV
Researchers Discover What May be Earliest Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease
New Technology Enables 5D Imaging in Live Animals, Humans
A new image analysis technique makes it easier for scientists to quickly find and track important biological molecules including tell-tale signs of disease. Called “Hyper-Spectral Phasor” analysis, or HySP, it could even be useful for diagnosing and monitoring diseases by using cell phone images. It is much faster and far less expensive than current techniques.…
Cooling Breakthrough Could Improve Quantum Computer Performance
Fish Get Arthritis, Too
The very first bony fish on Earth was susceptible to arthritis, according to a USC-led discovery that may fast-track therapeutic research in preventing or easing the nation’s most common cause of disability. The finding contradicts the widely held belief that lubricated joints enabling mobility — called synovial joints — evolved as vertebrates ventured onto land.…