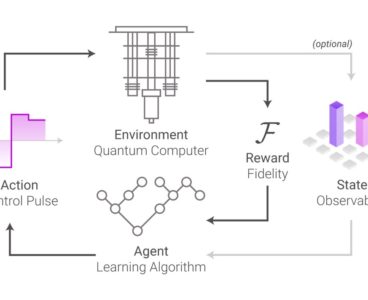
A new AI-based toolset developed by scientists at Q-CTRL enables quantum computers to optimize their own performance autonomously without user intervention. The fundamental building blocks of quantum algorithms are extremely susceptible to errors, posing the most substantial barrier to progress in quantum computing. Q-CTRL’s new tools use custom AI agents to enact algorithms with fewer errors…
CEA is the first research center to acquire a Cryogenic Prober for testing quantum bits
CEA announced today the acquisition of a Cryogenic Wafer Prober manufactured by Bluefors Oy, the Finnish specialist in designing and manufacturing ultralow temperature-dilution refrigerator systems for cutting-edge research in quantum computing and nanotechnology. CEA-Leti, a technology research institute at CEA, is the first microelectronics research institute to install this strategic equipment in its cleanroom. Created…
Quantum computing enables simulations to unravel mysteries of magnetic materials
A multi-institutional team became the first to generate accurate results from materials science simulations on a quantum computer that can be verified with neutron scattering experiments and other practical techniques. Researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory; the University of Tennessee, Knoxville; Purdue University and D-Wave Systems harnessed the power of…
Department of Energy to provide $32 Million for advanced computational research in the sciences
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has announced plans to provide up to $32 million to harness DOE supercomputers for advanced research in a wide range of scientific fields, including materials science, condensed matter physics, chemical sciences, geosciences and energy-related biosciences. The effort is part of a joint program that brings together experts in key…
Bristol researchers publish significant step toward quantum advantage
Researchers from the University of Bristol and quantum start-up, Phasecraft, have advanced quantum computing research, bringing practical hybrid quantum-classical computing one step closer. The team, led by Bristol researcher and Phasecraft co-founder, Dr. Ashley Montanaro, has discovered algorithms and analysis which significantly lessen the quantum hardware capability needed to solve problems which go beyond the…
Cambridge Quantum Computing collaborates with NPL to accelerate quantum computing R&D
Scientists at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) are working with Cambridge Quantum Computing (CQC) to accelerate research and development to support the commercialization and optimization of their quantum technologies, such as IronBridge, and help with the characterization of photonic components. This includes the metrology of emerging ultra-low loss optical connectors, for example, to meet the exacting requirements…
Mammoth “Big Memory” computing cluster to aid in COVID-19 research
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and its partners AMD, Supermicro and Cornelis Networks have installed a new high-performance computing (HPC) cluster with memory and data storage capabilities optimized for data-intensive COVID-19 research and pandemic response. Funded by the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (CARES) Act, the “big memory” cluster, called Mammoth, will be used at LLNL…
Combining electronic and photonic chips enables quantum light detection speed record
Bristol researchers have developed a tiny device that paves the way for higher performance quantum computers and quantum communications, making them significantly faster than the current state-of-the-art. Researchers from the University of Bristol’s Quantum Engineering Technology Labs (QET Labs) and Université Côte d‘Azur have made a new miniaturized light detector to measure quantum features of light in more detail than ever before. The device, made from two silicon chips working together, was used…
CEA-Leti to build quantum-photonics platform to ensure ultra-secure data for essential industries
Eyeing future demand for hack-proof digital communication in a quantum-information world, CEA-Leti today announced plans to build a quantum-photonics platform to develop next-generation technologies for key industries that require ultra-secure data transmission. Quantum technology is expected to provide unconditionally safe data encryption required by the finance, health care, energy, telecommunications, defense and other essential industries…
Sandia to receive Fujitsu ‘green’ processor
By Neal Singer This spring, Sandia National Laboratories anticipates being one of the first Department of Energy laboratories to receive the newest A64FX Fujitsu processor, a Japanese Arm-based processor optimized for high-performance computing. Arm-based processors are used widely in small electronic devices like cell phones. More recently, Arm-based processors were installed in Sandia’s Astra supercomputer,…
MIT joins White House supercomputing effort to speed up search for COVID-19 solutions
Jennifer Chu | MIT News Office The White House has announced the launch of the COVID-19 High Performance Computing Consortium, a collaboration among various industry, government, and academic institutions which will aim to make their supercomputing resources available to the wider research community, in an effort to speed up the search for solutions to the…
Early research on existing drug compounds via supercomputing could combat coronavirus
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have used Summit, the world’s most powerful and smartest supercomputer, to identify 77 small-molecule drug compounds that might warrant further study in the fight against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, which is responsible for the COVID-19 disease outbreak. The two researchers performed simulations on Summit of more…
Creating the heart of a quantum computer: developing qubits
Written by Shannon Brescher Shea A computer is suspended from the ceiling. Delicate lines and loops of silvery wires and tubes connect gold-colored platforms. It seems to belong in a science-fiction movie, perhaps a steam-punk cousin of HAL in 2001: A Space Odyssey. But as the makers of that 1968 movie imagined computers the size…
Cooling unit saves half-million gallons of water at Sandia supercomputing center
A cooling unit installed on the roof of Sandia National Laboratories’ supercomputer center saved 554,000 gallons of water during its first six months of operation last year, says David J. Martinez, engineering project lead for Sandia’s Infrastructure Computing Services. The dramatic decrease in water use, important for a water-starved state, could be the model for…
Universidad Politécnica de Madrid’s latest Magerit-3 supercomputer energizes and enables discovery in nuclear and material physics
By Ken Strandberg The European X-ray Free-electron Laser (European XFEL), recently completed its first experiments that captured images of an antibiotic-disabling enzyme. Scientists use X-rays to bombard molecules and project molecular smatterings on a sensor that reconstructs what the target looks like. With these high-energy X-rays we now have 3D visualizations of actual molecules, like…
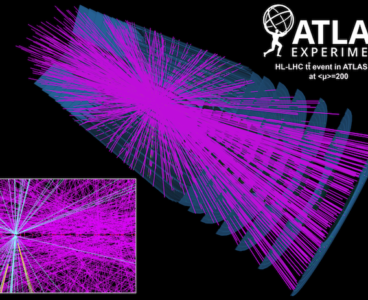
Particle physics turns to quantum computing for solutions to tomorrow’s big-data problems
Giant-scale physics experiments are increasingly reliant on big data and complex algorithms fed into powerful computers, and managing this multiplying mass of data presents its own unique challenges. To better prepare for this data deluge posed by next-generation upgrades and new experiments, physicists are turning to the fledgling field of quantum computing to find faster…
BP looks to ORNL, ADIOS to help rein in data
Researchers across the scientific spectrum crave data, as it is essential to understanding the natural world and, by extension, accelerating scientific progress. Lately, however, the tools of scientific endeavor have become so powerful that the amount of data obtained from experiments and observations is often unwieldy. In other words, it is possible to have too…
Nation’s First Exascale-Capable Supercomputer Advances Clean Fusion Research
Argonne Computational Model to Accelerate Engine Development for Hypersonic Flight
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, working in collaboration with Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and Convergent Science Inc., have created a new numerical modeling tool that allows for a better understanding of a powerful engine that could one day propel the next generation of airplanes and rockets. Rotating detonation…
Supercomputing Dynamic Earthquake Rupture Models
Some of the world’s most powerful earthquakes involve multiple faults, and scientists are using supercomputers to better predict their behavior. Multi-fault earthquakes can span fault systems of tens to hundreds of kilometers, with ruptures propagating from one segment to the other. During the last decade, scientists have observed several cases of this complicated type of…
New German Supercomputer Poised to Significantly Accelerate Research
AI and High-performance Computing Extend Evolution to Superconductors
Owners of thoroughbred stallions carefully breed prizewinning horses over generations to eke out fractions of a second in million-dollar races. Materials scientists have taken a page from that playbook, turning to the power of evolution and artificial selection to develop superconductors that can transmit electric current as efficiently as possible. Perhaps counterintuitively, most applied superconductors…
Quantum Computing Boost From Vapor Stabilizing Technique
Data Science Helps Engineers Discover New Materials for Solar Cells and LEDs
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a high-throughput computational method to design new materials for next generation solar cells and LEDs. Their approach generated 13 new material candidates for solar cells and 23 new candidates for LEDs. Calculations predicted that these materials, called hybrid halide semiconductors, would be stable and exhibit…
Quantum Cloud Computing With Self-check
Many scientists are currently working on investigating how quantum advantage can be exploited on hardware already available today. Three years ago, physicists first simulated the spontaneous formation of a pair of elementary particles with a digital quantum computer at the University of Innsbruck. Due to the error rate, however, more complex simulations would require a…