Experts call for better regulation of a common additive in foods and medicine, as research reveals it can impact the gut microbiota and could lead to inflammatory bowel diseases or colorectal cancer. University of Sydney research provides new evidence that nanoparticles, which are present in many food items, may have a substantial and harmful influence…
World-record Quantum Computing Result for Sydney Teams
A world-record result in reducing errors in semiconductor “spin qubits,” a type of building block for quantum computers, has been achieved using the theoretical work of quantum physicists at the University of Sydney Nano Institute and School of Physics. The experimental result by University of New South Wales engineers demonstrated error rates as low as 0.043…
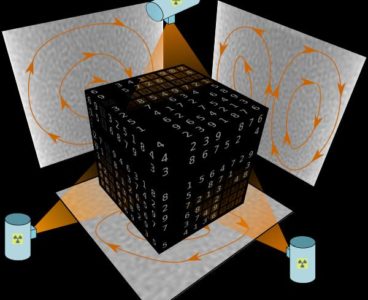
‘Sudoku’ X-ray Uncovers Movements Within Opaque Materials
When strolling along the beach, our footprints tell us that the sand under the surface must have moved but not precisely where or how. Similar movements occur in many other natural and man-made substances, such as snow, construction materials, pharmaceutical powders, and even cereals. To examine these largely unknown granular movements, academics from the Sydney…
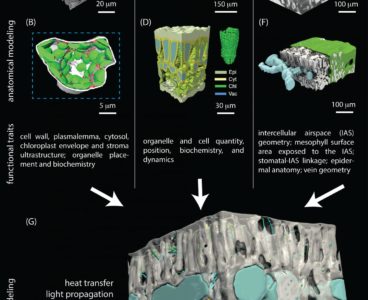
3D Imaging Opens Door to Better Understanding of Fascinating Leaf Complexity
The field of plant science is in the process of being profoundly transformed by new imaging and modelling technologies. These tools are allowing scientists to peer inside the leaf with a clarity and resolution inconceivable a generation ago. In a recent publication, a team of Australian and US scientists demonstrated how three-dimensional (3D) imaging can…
Photonic Chips Harness Sound Waves to Speed Up Local Networks
It used to be known as the information superhighway – the fibre-optic infrastructure on which our gigabytes and petabytes of data whizz around the world at (nearly) the speed of light. And like any highway system, increased traffic has created slowdowns, especially at the junctions where data jumps on or off the system. Local and…
World-first Quantum Computer Simulation of Chemical Bonds Using Trapped Ions
An international group of researchers has achieved the world’s first multi-qubit demonstration of a quantum chemistry calculation performed on a system of trapped ions, one of the leading hardware platforms in the race to develop a universal quantum computer. The research, led by University of Sydney physicist Cornelius Hempel, explores a promising pathway for developing…
A New Chapter in Stem Cell Medicine
Researchers at the University of Sydney have established a method to identify individual nanoparticles released by human cells, opening the way for them to become diagnostic tools in the early-detection of cancers, dementia and kidney disease. The particles, known as extracellular vesicles, or EVs, are routinely released by cells and play a central role in…
Carnivorous Plants Inspire Degradation-Delaying Nano Surfaces
A team of chemistry researchers from the University of Sydney Nano Institute has developed nanostructured surface coatings that have anti-fouling properties without using any toxic components. Biofouling — the build-up of damaging biological material — is a huge economic issue, costing the aquaculture and shipping industries billions of dollars a year in maintenance and extra…
Neutron-Star Merger Creates New Mysteries
The neutron-star merger announced in October has solved one mystery – where gold comes from – but has also raised other questions, an international team reports today in the journal Nature. The merger, dubbed GW170817, took place 130 million light-years away and was detected in August by the gravitational waves it created. Astronomers then followed…
Quantum Trick Blocks Background ‘Chatter’ in Sensing Devices
A University of Sydney team has solved a common problem in quantum sensing devices, which are used in biomedical imaging and have defence applications. Industrial sensors are everywhere in our technology and in order to function successfully they must be able to identify tiny signals from a cluttered background. For most humans this is simple.…
Key Component For Quantum Computing Invented
A team at the University of Sydney and Microsoft, in collaboration with Stanford University in the US, has miniaturised a component that is essential for the scale-up of quantum computing. The work constitutes the first practical application of a new phase of matter, first discovered in 2006, the so-called topological insulators. Beyond the familiar phases of…
Creating the World’s First Quantum Computer
Scientists at the University of Sydney are entering a new phase of development to scale up the next generation of quantum-engineered devices. These devices will form the heart of the first practical topological* quantum computers. A study released today in Nature Communications confirms one of the prerequisites for building these devices. An author of that paper, Dr Maja Cassidy,…
Quantum Detectives in the Hunt for the World’s First Quantum Computer
Scientists at the University of Sydney are entering a new phase of development to scale up the next generation of quantum-engineered devices. These devices will form the heart of the first practical topological* quantum computers. A study released today in Nature Communications confirms one of the prerequisites for building these devices. An author of that paper, Dr Maja Cassidy,…
University of Sydney, Microsoft Forge Global Quantum Computing Partnership
The University of Sydney today announces the signing of a multi-year quantum computing partnership with Microsoft, creating an unrivalled setting and foundation for quantum research in Sydney and Australia. The long-term Microsoft investment will bring state of the art equipment, allow the recruitment of new staff, help build the nation’s scientific and engineering talent, and…
Photonics Breakthrough Paving the Way for Improved Wireless Communication Systems
Researchers from the ARC Centre for Ultrahigh bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems (CUDOS) in the University of Sydney’s Australian Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology have made a breakthrough achieving radio frequency signal control at sub-nanosecond time scales on a chip-scale optical device. Radio frequency (RF) is a particular range of electromagnetic wave frequencies, widely…
Novel Drug Lead Identified in Fight Against TB
Antibacterial compounds found in soil could spell the beginnings of a new treatment for tuberculosis, new research led by the University of Sydney has found. Believed by many to be a relic of past centuries, tuberculosis (TB) causes more deaths than any other infectious disease including HIV/AIDs. In 2015 there were an estimated 10.4 million…